* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Moeller software tools - X-Spider
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
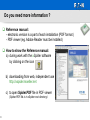
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
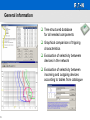
xSpider 1 1 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information The xSpider is a graphically oriented design software for dimensioning low-voltage networks fitted with protective devices of Eaton brands. 2 2 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information The xSpider is intended primarily for designers, computational and checking engineers Design of networks TN/TT/IT of various voltage systems up to 1000 V Design of radial or meshed networks Design of networks supplied from one or more different power sources All calcualtions are based on IEC standards (voltage drops, load distribution, short-circuits, impedances) 3 3 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information User-friendly interface allowing easy and fast design User operation similar to standard CAD systems (eg. AutoCAD) Independent software requiring only the operating system of Windows95/98/NT/2000/XP or Vista Available free of charge after registration via internet 4 4 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information xSpider software provides needed calculations: voltage drops (DU) load distribution (nominal load In / overload) short-circuit currents (Ik“, Ikm , ….) carries out check of suitability of cables (In, I, …) carries out check of suitability of protection devices calculation of impedances (Zv, …) etc. 5 5 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information Tree structured database for all needed components Graphical comparison of tripping characteristics Evaluation of selectivity betweem devices in the network Evaluation of selectivity between incoming and outgoing devices according to tables from catalogue 6 6 Observe protective note ISO 16016 General information Export of graphics (drawings) - to DXF format (suitable for CAD systems, like AutoCAD) Print of graphics on different papier size - A5, A4, A2, A1, A0 Print of tables with results - direct print on a papier (A4) - export to Excel data format 7 7 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Do you need more information ? Reference manual: - electronic version is a part of each installation (PDF format ) - PDF viewer (eg. Adobe Reader must be installed) How to show the Reference manual: a) during work with the xSpider software by clicking on the icon b) downloading from web, independent use http://xspider.moeller.net c) to open Spider.PDF file in PDF viewer (Spider.PDF file is in xSpider root directory) 8 8 Observe protective note ISO 16016 How to obtain the xSpider ? xSpider is available on: www.moeller.net Direct home page adress: http://xspider.moeller.net xSpider is provided for free via internet after registration A licence number is provided via e-mail – acc. to the registration form Language versions: EN, D, RU, CZ, PL, HU Technical support: [email protected] 9 9 Observe protective note ISO 16016 xSpider 1 10 10 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2 3 4 5 System of work with the xSpider 11 11 Observe protective note ISO 16016 System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations 5: Tripping characteristics 6: Results 12 12 Observe protective note ISO 16016 System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations 5: Tripping characteristics 6: Results 13 13 Observe protective note ISO 16016 1. Definition of project Start with New project 14 14 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Open already existing project Open DEMO 1. Definition of project Network and voltage system 1 2 Change of network and voltage (if it is necessary) Default setting: TN network, 230/400 V 3 15 15 Observe protective note ISO 16016 System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations 5: Tripping characteristics 6: Results 16 16 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram First of all it is necessary to have an idea about required network wiring diagram (acc. to the existing project) The wiring diagram is taken as a pattern for creation of the final wiring diagram with use of xSpider Any existing network wiring diagram, which was created by the xSpider, can be quickly modified acc to new needs 17 17 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram Sources Component groups: quick creation of wiring diagram (typical combinations) Lines Breakers Outlets Cap. Individual components: creation of wiring diagram step by step (universal use, modifications) 1 Eg. Transformer Selection of type 3 2 Database 18 18 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4 2. Network wiring diagram Network nodes are created automatically Use of: Supply network, Generator, Transformer Possibility to use more sources in any possitions Radial network Meshed network Circle network 19 19 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Line with supply from one side 2. Network wiring diagram Standard functions used for graphics editing: Copy, Move, Erase, Stretch Standard functions for display control: Zoom, Pan Possibility to add free graphics: Line, Circle, Rectangle, Text Option to transfer an object among projects by means of the clipboard Possibility to switch between more open projects (Windows) 20 20 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram Example of solution: the wiring diagram can be prepared with a) individual compoments or b) with use of pre-defined groups of components (this si reccomended way) A) Power supply group B) Outlet groups 21 21 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram Example of solution: A) selection of power supply group 1 Inserting power supply group 3 22 22 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2 Power supply groups 2. Network wiring diagram Example of solution: B) Enlarge view Zoom window 3 2 23 23 Observe protective note ISO 16016 1 2. Network wiring diagram Example of solution: C) selection of outlet group 1 2 3 Inserting 24 24 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Outlet groups 2. Network wiring diagram: How to use the DEMO ? In a case the user wants to start with calculation in a short time, it is reccomended to use some of DEMO pre-defined wiring diagrams. How to do it: 1. Open some of DEMO by click on icon 2. Modify properties of components by double click onto the relevant component With use of modified drawing (Erase of componets or change of operational status of devices On/Off) and after modification of parametras according to needs (Database) it is possible to start with calculation within 10 - 20 minutes !! 25 25 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram: How to use the DEMO ? Using a suitable DEMO (pre-defined wiring diagrams) - quick way for instant work with the xSpider A) After each opening xSpider B) B) To click onto the icon DEMO A) 26 26 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram: How to use the DEMO ? Selection of a suitable DEMO List of all Demos - see Reference manual (Part III, Chap. 25.3) 27 27 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2. Network wiring diagram: How to use the DEMO ? Modification of component properties by double click Example: selection of another type of transformer 1 Double click onto the symbol of transformer 1 3 2 Click on Database button 3 Select new group from database tree Select new item from data table 2 4 Click on Insert button 4 5 28 28 Observe protective note ISO 16016 5 Click on OK button System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations 5. Tripping characteristics 6: Results 29 29 Observe protective note ISO 16016 3: Parametras of network components Database of components - a) direct access 1 2 Selection of Database Selection of Type 4 3 4 5 The tree structured database is built as open-ended. Each user can create own database – User defined. 30 30 Observe protective note ISO 16016 3: Parametras of network components Database of components - a) use of individual icons Supply network Generator Transformer 1 Switchboard busbar 3 Database Selection of type in the tree structured database 2 Cable Busbar trunking system Circuit breaker Fuse, Fuse disconnector Switch disconnector Motor Load Compensation unit 31 31 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4 System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations 5. Tripping characteristics 6: Results 32 32 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations A. Basic calculation modes: - calculations which are needed in all projects Voltage drops and load distribution (ΔUnode, ΔUwl, Inode, Iwl) 3-phase symetrical short-circuit current (Ik3p“, Ikm) 1-phase asymetrical short current and tripping time (Ik1p“, Ttr) B. Additional calculation modes: - advanced possibilities for more detailed information 2-phase symetrical short-circuit current (Ik2p“, Ikm) calculation of impedances (Zsv, Z1, Z0) the complex expression of results (real and imaginar compoments of currents and impedances) 33 33 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Selection of a calculation mode 1 2 Network calculation modes - selection 3 34 34 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Check the network connection logic control of possible user‘s mistakes - before start of any calculation 1 2 Check Network connection logic 4 a) OK It is possible to continue. b) not OK 3 35 35 Observe protective note ISO 16016 It is necessary to correct the displayed mistake(s) and repeat the check once again !! 4. Calculations Voltage drops and load distribution mode: possibilities: Check, if voltage drop does not exceed the user-defined maximum value Simultaneous factor is considered in radial networks Load distribution in the network branches Check of correct dimensioning the circuit protection equipment and conductors according to IEC 60364-5-523 Check of line protection for overload and short circuit according to IEC 60364-4-43 Power factor calculation – optimalisation of compensation 36 36 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Voltage drops and load distribution mode: setting conditions: The xSpider respects all actual conditions of IEC 60364-5-523 Define cable installation and needed parametras is possible by double click on the cable 37 37 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Voltage drops and load distribution: calculations 1 2 red colour of text = problem 38 38 Observe protective note ISO 16016 3 Correction of displayed problematical parametras 4 Next calcualtion (steps 1– 4) up to situation with correct result 4. Calculations Voltage drops and load distribution: display of results eg. as the 3-phase outlets Component with error: current Iwl in the line is higher than In of the cable Voltage drop in the line (dUwl) Load in the line (Iwl) Voltage drop in the node (dUnode) Load in the node (Inode) 39 39 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Load optimalisation by use of the Operating state On/ Off 1 2 DOUBLE CLICK onto the device Ics Icu 3 40 40 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Load optimalisation by use of the utilization factor Ku Can be defined for loads (motor, general load) Example for motor application: 7.5kW motor fitted in the project, with maximum 80% load during ordinary operation – utilization factor Ku=0.8 1 DOUBLE CLICK onto the device 2 3 41 41 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Load optimalisation by use of the simultaneous factor Ks Can be defined for nodes (Switchboard trunk component) Defines the simultaneousness of consumptions from the node (ratio between the number of devices in operation and the total number of devices) Taken into account only with radial networks. 1 DOUBLE CLICK onto the device 2 4 Run Voltage drop and load flow calculation 3 42 42 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Short currents in the low voltage network Conditions in the TN system during of 1-phase short current to the earth (asymmetric short current, Ik1p“) 43 43 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations 3-phase short-circuit current mode: possibilities Prospective maximal short-circuit current during 3-phase symmetrical fault Ik3p“ Calculation according to IEC 60909 Check of faults: a) in all nodes - global overview about situation in the network b) in the selected node - optimalisation of network, focuse to the selected problematical details Check of correct dimensioning: - breaking capacity of circuit breakers (Icu, Ics) - withstand current of conductors (Icw) 44 44 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations 3-phase short-current circuit mode: parametras Ik“ - Initial impulse short-circuit current: the r.m.s. value of symmetrical short-circuit current without the direct-current component at the time of the short-circuit formation. Ikm (ip) - Peak short-circuit current: the first amplitude (peak value) of the asymmetric short-circuit current with the DC component (iss). Ike - Thermal equivalent short-circuit current: the r.m.s. value equivalent or imaginary symmetric (balanced) short-circuit current value Ik - Steady-state short-circuit current: the effective (symmetric) short-circuit current value after all the transient components disappear. In a case of electrically remote short-circuits (the majority of cases in practice), it equals to the initial impulse short-circuit current Ik“ 45 45 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations 3-phase short-circuit current: a) check the entire network in all nodes 1 2 Selection of the calculation mode 3 1 6 4 5 7 46 46 Observe protective note ISO 16016 2 3 8 9 4. Calculations 3-phase short-circuit current: a) display of results in all nodes Zoom 47 47 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations 3-phase short-circuit current: b) check in the selected node 1 2 Selection of the calculation mode 3 4 9 5 1 6 2 3 7 48 48 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4 8 4. Calculations Cascading – a solution where the first c.b. (1) is able to reduce a short current value to level which can be switched-off by the second c.b. (2) Checking the breaking capacities of the outgoing protective devices with respect to the breaking capacity of incomming protective components Example: Icu1 = 50 kA Icu2 = 15 kA Ik“ = 25 kA 49 49 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Itr = 30 kA i Prospective short current (effective value) Limited current (max. value) Let-through energy I2t t 4. Calculations Check of cascading: optional check during short-circuit current calculation mode 1 2 3 4 Selection of cascading in the node 5 50 50 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Selectivity function to evaluate the selectivity of circuit-breakers based on selectivity tables specified in the catalogue A) comparison of both circuit-breakers selected from the database 1 2 3 4 5 51 51 Observe protective note ISO 16016 4. Calculations Selectivity function to evaluate the selectivity of circuit-breakers based on selectivity tables specified in the catalogue B) comparison of circuit-breakers in the project (cascade must be defined for every network node) 1 52 52 Observe protective note ISO 16016 3 2 4. Calculations 1-phase short-circuit current: display of results Check of faults: a) in all nodes – RM-1.1, Z1, ... global overview about network b) in the selected node – eg. Z1 optimalisation of problem details Ttr disconnection time of protective devices (check of compliance with the requirements of IEC 60364) Ik1p“ 1-phase asymetrical short-circuit current (minimal short-circuit current) 53 53 Observe protective note ISO 16016 Node with value of short-circuit current System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations and optimalisations 5: Tripping characteristics 6: Results 54 54 Observe protective note ISO 16016 5. Tripping characteristics Comparison of tripping characteristics Eg. optimalisation of selectivity between fuse and circuit breaker by change of release settings. A 55 55 Observe protective note ISO 16016 B 5. Tripping characteristics Release setting Adjustable parametras - acc. to the type of protective device 56 56 Observe protective note ISO 16016 5. Tripping characteristics Tripping units of MCCBs (NZM type) - A type - AE type - M type - ME type - VE type - ME Ir Ir Ir Ir Ir Ii Ii tr Isd tr Isd tsd Ii (I2t - on/off) -VE I2t - off I2t - on Load characteristic of engine 57 57 Observe protective note ISO 16016 System of work Main steps: 1: Definition of project 2: Network wiring diagram 3: Parametras of network 4: Calculations and optimalisations 5: Tripping characteristics 6: Results 58 58 Observe protective note ISO 16016 6. Results The list of unsuitable components is displayed immediately after performing the calculation and it can be printed out. The calculated values for the individual components are displayed in the network wiring diagram. It can be printed on any output device for which a driver is available in the Windows (printer, plotter). The list of components with the calculation results - possibility to print tables. The list of components with their parameters - possibility to print tables including the list of cables. 59 59 Observe protective note ISO 16016 6. Results Print of the last calculation: eg. 3-phase short-circuit current 1 3 Print Preview 2 4 60 60 Observe protective note ISO 16016 6. Results Save of project: a) after definition of project (see Step 1) b) anytime during work c) after finishing project 1 2 3 61 61 Observe protective note ISO 16016 xSpider Thank you for your attention. xSpider team 62 62 Observe protective note ISO 16016