* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lec9 Networking
Survey
Document related concepts
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
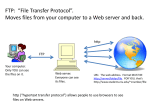
Lecture 9 Unix Networking (see chapter 7) Unix Networking & Internetworking History Overview DNS Typical Communication Utilities Network History Internet research started in the 1960’s ARPA – Advanced Research Planning Agency Began work on packet switching. ARPANET – late 1970’s TCP/IP Prototype Internet was developed. Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol 1st used by academic institutions, research organizations, & the U.S. military. Internet Growth 1983 – Internet sites = 562 1986 – Internet sites = 2,308 Doubled every year for the next 10 years. 1996 – 9.5 million Web Browser Key to easy network utilization. 1st browser – Mosaic – Developed by NCSA National Center for Supercomputer Applications. Launched in 1991 Web browsing surpassed FTP File Transfer Protocol Size Now Between 50 – 100 million computers 1 million computer networks Unix has a special role in that most of the network protocols were initially implemented on Unix platforms. Most servers run on Unix based machines. Networks & Internetworks Two or > hardware resources connected. Can be computers, printers, plotters, scanners, etc. A hardware resource is a host. A typical network configuration Network Types LAN – Local Area Network MAN – Metropolitan Area Network WAN – Wide Area Network These distinctions are based on the maximum distance between hosts. LAN Local Area Network Hosts are in a room, building, or close buildings Distance from a few meters to about 1km MAN Metropolitan Area Networks Hosts between a city or between small cities Distance between hosts is about 1 to 20 km WAN Wide Area Network Hosts distance range from tens of kilometers to a few thousand kilometers. Internetwork Internetwork is a network of networks. Can connect networks within a campus or networks thousands of kilometers apart. Connected with routers or gateways. Internet is an internetwork of tens of thousands of networks Routers & Gateways Routers – Connect similar networks Gateways – Connect dissimilar networts. Convert messages to suitable form for each network. Reasons for Networks Sharing resources – Printers, plotters, scanners, software, etc. Communication between people Costs savings Reliability > 1 computer TCP/IP Kernel handles the communications. The communications hardware (NIC) Network Interface Card The Unix kernel handles the details. DNS Name Server Domain name service (DNS) is central to the Internet When URLs are entered in a Web browser, a DNS server converts the name to an IP address, allowing the client to send a packet to the Web server as requested The information in DNS can be thought of as an inverted hierarchical tree, where the top of the tree is called root and is represented by a period Users typically don’t refer to roots, but to the last part of domain names called top-level domains DNS Name Server DNS Name Server Setting Up a DNS Name Server Resolving a domain to an IP address using DNS, also called querying the DNS server, stores, or caches, the conversion information resulting in speedier DNS queries Each domain has a master DNS server which contains database files that provide IP addresses to every host in that domain Each domain should have a slave DNS server which acts as a backup to the master Setting Up a Basic Name Server The program that implements a DNS server is called named, the name daemon, which is controlled by a system script in /etc/rc.d/init.d named is found in the BIND package on most Linux systems; selecting the Red Hat Linux name server component provides bind-conf, bind-utils, and caching-nameserver Caching name servers have no preconfigured domain information, but simply query other DNS servers and cache the results Name Server Resolver functions like: gethostbyname To invoke DNS service Maps a host name to its IP address gethostbyaddr Maps an IP address to its hostname View Information ifconfig command View the IP address & other info about your hosts interface to the network. Usually in the /sbin directory (Type /sbin/ifconfig) View Information nslookup Display the IP address of a host nslookup ibm.com Returns the address. Modern forms: host or dig Popular Internet Services Electronic Mail – SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) File Transfer – FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Remote Login – Telnet (and ssh) Time – Time Web Browsing – HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) Client-Server Model Internet services are implemented by service partitioned in two parts. Part on the computer (host) where the user is logged onto is the client software. The part that starts running when a server boots is the server software. Client-Server The server runs forever – Waiting for a client request A request is handled & then waits for another request. Client starts running when a user runs the program for a service the client offers. Web Site URL – Universal Resource Locator URL is given to the client process to view a page. http://machine Displays the home page of machine List of users List of users using hosts on a network. rwho – Remote who Displays users using machines on your network. rwho –a Users currently idle Testing a network Connection ping – If host is alive it echoes a datagram. whereis – Finds the location finger – Display information about a user Problem Areas Size of networks continues to grow. Big problem – Too many servers. Usually one server per application – 1 for data base, 1 for accounting, etc. Virtualization Virtualize the many servers employed. One server with the capability of replacing many specialized servers. Goldman Sachs (brokerage firm) – Had 250 network people & 30 million lines of specialized code. Large number of servers, regional, intl., etc. Virtualization The number of specialist can be greatly reduced. The network complexity can also be reduced. The one major problem is having one machine for critical functions. Typical Communication Utilities in UNIX The talk Command A Complete talk Session A Complete talk Session A Complete talk Session The write Command E-Mail Programs Some Programs available in Unix/Linux Mail – most basic, low level mail command ELM PINE (PINE Is Not Elm), more user friendly text mail Outlook, GUI driven Eudora Netscape Mailer Email Address The mail command The mail command You can use the mail command in several ways: mail -- by itself, it opens your messages and lets you read them mail person@address -- lets you compose a message to someone at a certain address. mail -s (subject) person@address -- lets you send a message to someone at an address, with a certain subject. mail -s (subject) person@address < text_file -- lets you send a message to someone with text_file as the body of the email. Using mail When you are writing the mail message body, use ^D or <enter> . <enter> to end editing and send the message. If cc: shows up, this is a list of other addresses you can enter if you wish to send a message to other people. ^C will kill a mail message you are typing. The mail Command (Sending Mail) Header Editing While editing a message you may use… ~h -- lets you edit the header (to, subject, cc, bcc) These may also work: ~s ~t ~c ~b -- edit the subject. -- edit the to list. -- edit the cc (carbon copy) list. -- edit the bcc (blind carbon copy) list. Message Editing Commands Use these while writing the actual message ~r <file> -- Add a file into the message. ~f <num> -- add another email into the message (forwarding). ~w <file> -- write the message to a file. ~q -- quit without saving ~p -- print the contents of the message. Mail Command Example The mail Command (Read Mail) Mail reading commands These commands are used in mail at the & prompt q -- quit and save x -- quit without making any changes. R or r -- reply to a message (r = senders and recipients, R = senders only.) f <numbers> -- view the message headers. p or t <numbers> -- show those messages More mail commands d <numbers> -- delete messages. u <numbers> -- undelete messages. s <numbers> <file> -- append the messages to <file> with headers. w <numbers> <file> -- append messages to <file> -- message only. PINE A menu-driven client Uses pico as an editor Allows MIME attachments Main Menu C - Compose to write a message I or L - View messages Q - Quit Figure 7-10 Local login Figure 7-11 Remote Login Remote Login rlogin host rlogin paris rlogin –l username host exit to leave telnet from UNIX telnet open host close quit Shortcut: telnet host Secure Shell SSH or Open SSH Encrypted connections ssh –l loginID remote.machine.name Encryption Corporate earnings are up 45% this quarter Corporate earnings are up 45% this quarter 1 3 ssh installed ssh installed Decrypt Client Server 2 Encrypt fdh37djf246gs’b[da,\ssk File Transfer Protocol: ftp ftp open host Shortcut: ftp host login password ftp help: ? ftp command help: ? Command ? binary quit Getting a file with ftp Use binary or bin if needed to go to binary mode (default is ASCII) Use cd to go to the remote directory with your file Use lcd to go a directory on your local machine (where you want the file to go after you ftp) Use get filename to copy a file from the remote directory to the local directory Getting many files with ftp Use binary or bin if needed to go to binary mode (default is ASCII) Use cd to go to the remote directory with your file Use lcd to go a directory on your local machine (where you want the file to go after you ftp) Use mget to copy multiple files at once from the remote directory to the local directory mget filename1 filename2 filename3 mget with wildcard: mget * Toggle the prompt: prompt Sending a file with ftp Use binary or bin if needed to go to binary mode (default is ASCII) Use cd to go to the remote directory (where you want to put your file) Use lcd to go a directory on your local machine (where the file is located) Send the file using put filename Sending many files with ftp Use binary or bin if needed to go to binary mode (default is ASCII) Use cd to go to the remote directory with your file Use lcd to go a directory on your local machine (where you want the file to go after you ftp) Use mput to copy multiple files at once from the local directory to the remote directory Use wildcards File Archival Creating an archive file with tar To archive everything in a directory, tar –cf archivename originaldirectory Use ls to confirm that a .tar file was created. Verify contents by viewing the table of contents for the .tar file: tar –tf archivename.tar Restoring tar files tar –x filename.tar destinationdirectory Use ls to confirm that the extracted files are in the directory you specified. File Compression Common compression programs: compress, uncompress, PKZIP, PKUNZIP, pack, unpack Using compress compress filename compress archivename.tar Confirm that compressed file (.z) created with ls filename.z archivename.tar.z Uncompress uncompress filename.z Use ls to confirm that the uncompressed file is there (the .z file should be gone)