* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Local Area Network Concepts and Architecture
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
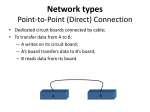
Chapter 5 Local Area Network Concepts and Architecture • • • • Network Fundamentals Local Area Network (LAN) Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) LAN Architectures Network Fundamentals • • • • • Definitions Classifications Network topology Network types Local Area Network Definition • Network • Backbond network Classification • • • • Topology Ownership Geography Transmission Network Topology • • • • • • Star Hierarchical Mesh Bus Ring Hybrid Star Network • Usage – Centralized processing or communication • Pros – Expansion – Implementation – No limit to no. and length of arms • Cons – Single point of failure – Overload of mater during peak traffic Hierarchical Network • Usage – Distributed processing • Tree structure with a root • pro – No single point of failure Mesh Network • Web structure • Usage – Public telephone system • Pro – Alternative communication route • Con – Line cost Bus Network • Usage – Date entry or office environment • Pros – Independent between nodes – High reliability • Cons – Limited number of attached device – Hard to locate the problems Ring Network • Usage – Manufacturing • Pros – Less attenuation – Error control – Network management • Cons – Failing of a node Hybrid Networks • Usage – Connecting different networks • Pro – Communication between networks • Con – Conversion device and costs – Compatibility Network Ownership • Private networks • Public networks • Valued added networks Private networks • Full control • Special needs • Expense Public networks • Controlled by carriers • Regulated by government • Inexpensive Valued Added Networks • Functions – Code translation – Speed conversion – Store message and delivery • Examples – – – – Telex SWIFT SITA (airline) IVAN (insurance) Networks by Geography • Wide area network (WAN) • Metropolitan area network (MAN): 30 miles • Local area network (LAN): 5 miles LAN Characteristics • • • • • • • Limited distance within a few miles High data rate - 2 to 1000Mbps Low error rate Good response time Private owned No regulation Share hardware, software, and data files Business Needs • • • • • • Corporate asset for competitive edge Data accessibility (information distribution) Less expenses Better service - response time and reliability Higher productivity Control or secure LAN Analysis & Design • Meet business objectives (strategic planning) • Prevent technological obsolescence LAN Hardware & Software • Hardware – PC: servers and clients – Network interface card (NIC): physical address – Media or Cables • • • • Unshielded twisted pair (inexpensive) Coaxial cable (faster, expensive) Optical fiber (fastest, expensive) Air for wireless – Hub (compatible) • connect wires and cables, repeater, error detection • Software: network operating system Open System Interconnection Model • International Standards Organization • Interconnection of dissimilar network • Seven Layers – – – – – – – Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Application Layer • Utilities support end-user application program • Determine data to be send at originating end • Process data at receiving end Presentation Layer • Change data format • Compression/expansion • Encryption/decryption Session Layer • Communication rules of machines or application programs • Accounting functions Transport Layer • Identify receiving address • Flow control: rate of transmission • Recovery: calculate and check checksum of entire message Network Layer • Route message • Dissemble and assemble data (packets) • Accounting functions Data Link Layer • • • • • • By IEEE 802 Establish link between two ends Detect and correct transmission error Add header and trailer Divide data unit for transmission (frames) Sublayers – Media access control (MAC): token ring or Ethernet – Logical link control (LLC): assembling and disassembling frames, error control, flow control Physical Layer • Electrical, mechanical, procedural specifications for data transmission • Hardware specification by RS-232-C Other Concepts • Protocol • Encapsulation/ de-encapsulation Standards • • • • • IEEE 802.2: LLC protocol IEEE 802.3: CSMA/CD baseband bus IEEE 802.4: token passing bus IEEE 802.5 token passing ring Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Standard LAN Architecture Model • Network architecture includes – Access methodology – Logical topology – Physical topology • Network configuration includes – Network architecture – Media choice Access Methods • Contention: carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) – Inexpensive NIC – For: office application – Not for: manufacturing due to inconsistent response time • Token passing: 24 bits of token (free or busy) – More efficient at higher network utilization rate – More expensive NIC – Supported by IBM Topology • Logical – Sequential – Broadcast • Physical – Bus: line broken – Ring: PC or NIC broken – Star (hub, concentrator, MAU (multistation access unit, repeater, switching hub): single point of failure Ethernet • Functionality – Access method: CSMA/CD – Logical topology: broadcast – Physical topology: bus or star • Ethernet II – – – – Header (preamble) for synchronizing Destination & source address (MAC layer address) Type field for network protocol Data field – Frame check sequence (FCS): CRC-32 • IEEE 802.3 replace type field with length field Media-related Ethernet • • • • 10BaseT 10Base2 (Thinet with RG-58 coax) 10Base5 (thick coaxial cable RG-11) 100BaseT Fast Ethernet with 100-Mbps – 100BaseTX (2 pair of Category 5 UTP or 1 pair of Type 1 STP) – 100BaseT4 (4 pair of Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP) – 100BaseFX (fiber optic cable) – Trade off between speed and maximum network diameter • Gigabit Ethernet (1000Base-X) Token Ring • Functionality – Access method: token passing – Logical topology: sequence – Physical topology: ring or star • IEEE 802.5 – Starting delimiter alert NIC about token approaching – Access control field (1 for busy, 0 for free) – Frame control field indicate regular data or network management frame – Destination & source address (MAC layer address) – Routing information field for multiple token ring LANs – Data field – Frame check sequence (FCS): CRC-32 – Ending delimiter (ending or intermediate frame) – Frame status field for successful delivery Fiber Distributed Data Interface • Fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) by American National standard Institute (ANSI) • Functionality – Access method: Modified token passing – Logical topology: sequential – Physical topology: dual counter-rotating rings • Build-in reliability and longer distance • Single-attachment stations (SAS) or dualattachment stations (DAS) Fiber Distributed Data Interface • High speed backbone between LANs • Primary ring and secondary ring - 100Mbps token ring • Fault tolerance • High-priority station having longer access time • Maximum 500 stations • Maximum length of 200 kilometers (rings) • Maximum 2 kilometers between stations • Constant data rate for video and voice Fiber Distributed Data Interface • Applications – Campus backbone – High-bandwidth workgroups (multimedia application) – High-bandwidth subworkgroup connection (servers) • Hardware: FDDI concentrator or hub, FDDI/Ethernet bridge • Media: fiber optic cable or copper distributed data interface (CDDI) for limited distance (100m) 100VG-AnyLAN • Ethernet and token ring packets • Demand priority access (DPA) or demand priority protocol: round robin polling scheme • Priority is assigned by application program and ports • Max 4 hubs between two nodes 100VG-AnyLAN • Hardware: 100VG-AnyLAN hubs arranged in a hierarchical form • Media: 4 pair of Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP; 1 pair of Type 1 STP; or single mode and multimode fiber optic cable Isochronous Ethernet • Iso-Ethernet in IEEE802.9a (Isochronous Ethernet Integrated Services) • Synchronize all circuits with a single common clocking reference • Guaranteed delivery time for voice and video • Use ISDN WAN link Isochronous Ethernet • 16.144-Mpbs bandwidth – P channel for Ethernet traffic – C channel ( B channel and D channel) • Service Modes – 10BaseT – Mutiservice: multimedia – All-isochronous: real time video or voice distribution Isochronous Ethernet • Hardware: – hubs: Iso-Ethernet attachment units (AU) – Workstation with Iso-Ethernet NIC: integrated service terminal equipment (ISTE) Wireless • • • • Transmitter and receiver 100 - 300 feet Infrared technology (line-of-sight) Spread spectrum technology (no ling-ofsight) • Special application Performance Factors • • • • • • Protocol (CSMA/CD, token ring) Speed of transmission (line) Amount of traffic Error rate Software Hardware Selection Process • Long range thinking, planning and forecasting • Selection team • Checklist of criteria • Cost & benefit analysis • Technical alternatives • Management and Maintenance Selection Criteria - I • • • • • • • Number of user Geographic spread Applications Performance Cost Security Wiring Selection Criteria - II • • • • • • • Installation Maintenance Vendor support and training Future expansion Workstations Compatibility to existing LANs Interface to other networks Costs • • • • • • • • • Workstations Servers Printers Cabling Bridges, routers, brouters, gateways Training People (consultant, administrator etc.) Maintenance Space & Environment Installation • Choices – Suppliers or dealers – In house • Tasks (project management) – – – – – – Install hardware and software Test access and capability Trouble shoot Document Train user Help center Management & Maintenance • • • • • • • • • Organization: LAN administrator Management: policies and procedures Documentation Hardware and software control Change control Back up (hardware and software) Security (logical and physical) Application (compatibility, integrity, & efficiency) Performance monitoring Security • • • • • • • • • • Password Sign off Encryption Backup Downloading Viruses protection Dial-up access Legal software Internal and external auditing Written policy and procedure Assignment • Review chapter 5 • Read chapter 6