* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 4 - cda college
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Parallel port wikipedia , lookup
Hypertext Transfer Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
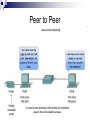
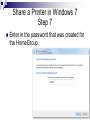
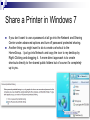
Protocols COM211 Communications and Networks CDA College Olga Pelekanou Email: [email protected] www.cdacollege.ac.cy/site/info-com-technology-ll/ Communication Protocols A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications. Protocols may include signaling, authentication and error detection and correction capabilities. A protocol defines the syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication. A protocol can therefore be implemented as hardware or software or both. Layering Layering : decomposes the problem of building a network into more manageable components. Rather than implementing a monolithic piece of software that does everything you will ever want, you can implement several layers, each of which solves one part of the problem. it provides a more modular design. If you decide that you want to add some new service, you may only need to modify the functionality at one layer, reusing the functions provided at all the other layers. Encapsulation Wrapping data in a particular protocol header. OSI and TCP/IP Client/Server Model In the client/server model, the device requesting the information is called a client and the device responding to the request is called a server. Client and server processes are considered to be in the Application layer. The client begins the exchange by requesting data from the server, which responds by sending one or more streams of data to the client. Application layer protocols describe the format of the requests and responses between clients and servers. Peer to Peer Application Layer Protocols HTTP POP SMTP SSH DNS FTP HTTP HyperText Transport Protocol. An application-level protocol based on a request/reply paradigm and used in the World Wide Web. HTTP uses TCP connections to transfer data. Use TCP port 80. POP Post Office Protocol (POP) is an application-layer Internet standard protocol used by local e-mail clients to retrieve email from a remote server over a TCP/IP connection and port 110. SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. The electronic mail protocol of the Internet. SMTP was first defined by RFC 821. SMTP is specified for outgoing mail transport and uses TCP port 25. SSH The Secure Shell (SSH) provides a remote, encrypted login service and is intended to replace the less secure Telnet and rlogin programs used in the early days of the Internet. Use TCP port 22. DNS Domain name system. The distributed naming system of the Internet, used to resolve host names (ex. cdacollage.ac.cy) into IP addresses (ex. 67.15.203.26). DNS is implemented by a hierarchy of name servers. Use UDP port 53. FTP File Transfer Protocol. The standard protocol of the Internet architecture for transferring files between hosts. Built on top of TCP. Use TCP port 21 for control commands and TCP port 20 for data transfer. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 1 Go to Control Panel and click on “Choose homegroup and sharing options” or just type “homegroup” without quotes into the start menu search bar. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 2 Next click on the Create a homegroup button. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 3 In the Create a Home Group screen select what you want to share with the other machines. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 4 After the group is created you will get a password to access it from the other computers. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 5 After you get the Password you’re brought back to the Home Group screen where you can make additional changes if you want. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 6 On the other Windows 7 computer(s) go into the HomeGroup feature and click to join the group you just created. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 7 Enter in the password that was created for the HomeGroup. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 8 When the password is accepted the connection will take place and your finished. Share a Printer in Windows 7 Step 9 To share a printer make sure to select Printers when creating the group and when you go into Devices and Printers on the Start menu you should see it and can set it as the default if you wish. Share a Printer in Windows 7 If you don’t want to use a password at all go into the Network and Sharing Center under advanced options and turn off password protected sharing. Another thing you might want to do is create a shortcut to the HomeGroup. I just go into Network and copy the icon to my desktop by Right-Clicking and dragging it. A more direct approach is to create shortcuts directly to the shared public folders but of course it’s completely up to you.