* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20088-2 CCNA3 3.1-01 Questions Scaling IP Addresses
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
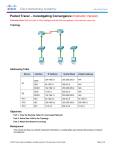
Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless The subnet 192.168.32.16/28 has been selected to be further subnetted to support point-to-point serial links. What is the maximum number of serial links that this plan can support? 1. 2 2. 3 3. 3 if ip subnet-zero is enabled 4. 4 5. 6 6. 8 5/25/2017 Page 1 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless The subnet 192.168.32.16/28 has been selected to be further subnetted to support point-to-point serial links. What is the maximum number of serial links that this plan can support? 1. 2 2. 3 3. 3 if ip subnet-zero is enabled 4. 4 5. 6 6. 8 5/25/2017 Page 2 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following statements are true regarding RIP v1 and v2? (Choose three.) 1. Both RIP versions use hop count. 2. Both RIP versions can provide authentication of update sources. 3. Both RIP versions use 16 hops as a metric for infinite distance. 4. RIP v1 uses split horizon to prevent routing loops while RIP v2 does not. 5. RIP v1 uses hold-down times to prevent routing loops while RIP v2 does not. 6. RIP v1 broadcasts routing table updates, while RIP v2 multicasts its updates 5/25/2017 Page 3 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following statements are true regarding RIP v1 and v2? (Choose three.) 1. Both RIP versions use hop count. 2. Both RIP versions can provide authentication of update sources. 3. Both RIP versions use 15 hops as a metric for infinite distance. 4. RIP v1 uses split horizon to prevent routing loops while RIP v2 does not. 5. RIP v1 uses hold-down times to prevent routing loops while RIP v2 does not. 6. RIP v1 broadcasts routing table updates, while RIP v2 multicasts its updates 5/25/2017 Page 4 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless A new network is to be configured on a router. Which of the following tasks must be completed to configure this interface and implement dynamic IP routing for the new network? (Choose three.) 1. Select the routing protocol to be configured. 2. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface. 3. Update the ip host configuration information with the device name and new interface IP address. 4. Configure the routing protocol with the new network IP address. 5. Configure the routing protocol with the new interface IP address and subnet mask. 6. Configure the routing protocol in use on all other enterprise routers with the new network information. 5/25/2017 Page 5 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless A new network is to be configured on a router. Which of the following tasks must be completed to configure this interface and implement dynamic IP routing for the new network? (Choose three.) 1. Select the routing protocol to be configured. 2. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface. 3. Update the ip host configuration information with the device name and new interface IP address. 4. Configure the routing protocol with the new network IP address. 5. Configure the routing protocol with the new interface IP address and subnet mask. 6. Configure the routing protocol in use on all other enterprise routers with the new network information. 5/25/2017 Page 6 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Router1 and Router2 shown in the topology have been configured with the no ip subnet-zero command. Which of the following valid VLSM network numbers could be used for the serial link between Router1 and Router2? (Choose two.) 1. 192.168.1.0/30 2. 192.168.1.4/30 3. 192.168.1.8/30 4. 192.168.1.96/30 5. 192.168.1.138/30 6. 192.168.1.190/30 5/25/2017 Page 7 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Router1 and Router2 shown in the topology have been configured with the no ip subnet-zero command. Which of the following valid VLSM network numbers could be used for the serial link between Router1 and Router2? (Choose two.) 1. 192.168.1.0/30 2. 192.168.1.4/30 3. 192.168.1.8/30 4. 192.168.1.96/30 5. 192.168.1.138/30 6. 192.168.1.190/30 5/25/2017 Page 8 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless How does a router know of paths to destination networks? (Choose two.) 1. inspection of the destination IP address in data packets 2. ARP requests from connected routers 3. manual configuration of routes 4. updates from other routers 5. DHCP information broadcasts 6. updates from the SMTP management information base 5/25/2017 Page 9 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless How does a router know of paths to destination networks? (Choose two.) 1. inspection of the destination IP address in data packets 2. ARP requests from connected routers 3. manual configuration of routes 4. updates from other routers 5. DHCP information broadcasts 6. updates from the SMTP management information base 5/25/2017 Page 10 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Refer to the network shown. How will Router1 summarize and advertise the four networks attached to its Ethernet ports? 1. 172.16.16.0/20 2. 172.16.19.0/20 3. 172.16.16.0/20 and 172.16.19.0/20 4. 172.16.16.0/22 5. 172.16.18.0/24 6. 172.16.0.0/24 5/25/2017 Page 11 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Refer to the network shown. How will Router1 summarize and advertise the four networks attached to its Ethernet ports? 1. 172.16.16.0/20 2. 172.16.19.0/20 3. 172.16.16.0/20 and 172.16.19.0/20 4. 172.16.16.0/22 5. 172.16.18.0/24 6. 172.16.0.0/24 5/25/2017 Page 12 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless In the network shown in the graphic, three bits were borrowed from the host portion of a Class C address. How many valid host addresses will be unused on the three pointto-point links combined if VLSM is not used? 1. 3 2. 4 3. 12 4. 36 5. 84 6. 180 5/25/2017 Page 13 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless In the network shown in the graphic, three bits were borrowed from the host portion of a Class C address. How many valid host addresses will be unused on the three pointto-point links combined if VLSM is not used? 1. 3 2. 4 3. 12 4. 36 5. 84 6. 180 5/25/2017 Page 14 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless A Class C address has been assigned for use in the network shown in the graphic. Using VLSM, which bit mask should be used to provide for the number of host addresses required on Router A, while wasting the fewest addresses? 1. /31 2. /30 3. /29 4. /28 5. /27 6. /26 5/25/2017 Page 15 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless A Class C address has been assigned for use in the network shown in the graphic. Using VLSM, which bit mask should be used to provide for the number of host addresses required on Router A, while wasting the fewest addresses? 1. /31 2. /30 3. /29 4. /28 5. /27 6. /26 5/25/2017 Page 16 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following are contained in the routing updates of classless routing protocols? (Choose two.) 1. 32-bit address 2. next hop router interface 3. subnet mask 4. unicast host address 5. Layer 2 address 5/25/2017 Page 17 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following are contained in the routing updates of classless routing protocols? (Choose two.) 1. 32-bit address 2. next hop router interface 3. subnet mask 4. unicast host address 5. Layer 2 address 5/25/2017 Page 18 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following is a summarization address for the networks 172.21.136.0/24 and 172.21.143.0/24? 1. 172.21.136.0/21 2. 172.21.136.0/20 3. 172.21.136.0/22 4. 172.21.136.0/2 5/25/2017 Page 19 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless Which of the following is a summarization address for the networks 172.21.136.0/24 and 172.21.143.0/24? 1. 172.21.136.0/21 2. 172.21.136.0/20 3. 172.21.136.0/22 4. 172.21.136.0/2 5/25/2017 Page 20 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless An additional subnet is required for a new Ethernet link between Router1 and Router2 as shown in the diagram. Which of the following subnet addresses can be configured in this network to provide a maximum of 14 useable addresses for this link while wasting the fewest addresses? 1. 192.1.1.16/26 2. 192.1.1.96/28 3. 192.1.1.160/28 4. 192.1.1.196/27 5. 192.1.1.224/28 6. 192.1.1.240/28 5/25/2017 Page 21 Module 1 Cisco 3 - Classless An additional subnet is required for a new Ethernet link between Router1 and Router2 as shown in the diagram. Which of the following subnet addresses can be configured in this network to provide a maximum of 14 useable addresses for this link while wasting the fewest addresses? 1. 192.1.1.16/26 2. 192.1.1.96/28 3. 192.1.1.160/28 4. 192.1.1.196/27 5. 192.1.1.224/28 6. 192.1.1.240/28 5/25/2017 Page 22



























![[RIP] - School of Computing](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008734696_1-cf06dba4c0ce902042221af117bfaa99-150x150.png)


