* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An Introduction to Computer Networking
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
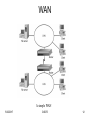
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
An Introduction to Computer Networking Objectives • Identify elements of a network • Describe several specific uses of a network • Distinguish between client/server and peer-to-peer networks 5/25/2017 CIS275 2 Networks and Standalone Computers • Network – Group of computers and other devices connected by some type of transmission media – Networks enable users to share devices and data, collectively called a network’s resources • Standalone computer – Uses programs and data only from its local disks and is not connected to a network 5/25/2017 CIS275 3 Local and Remote Computers • Local computer – Computer on which user is working • Remote computer – Computer that user controls or works on via network connection 5/25/2017 CIS275 4 Peer-to-Peer Network • Computers communicate on single segment of cable and share each other’s data and devices • Simple example of a local area network (LAN) 5/25/2017 Simple peer-to-peer network CIS275 5 Local Area Network (LAN) • Network of computers and other devices confined to relatively small space • LANs involving many computers are usually server-based – On a server-based network, special computers (known as servers) process data for and facilitate communication between other computers on the network (known as clients) 5/25/2017 CIS275 6 Networking Basics • Workstation – Computer that typically runs a desktop operating system and connects to a network • Client/server architecture – Networking model in which clients use central server to share applications, devices, and data 5/25/2017 CIS275 7 Networking Basics • Client/server network – Network based on client/server architecture • Network operating system – Special software designed to manage data and other resources on a server for a number of clients 5/25/2017 CIS275 8 Networking Basics LAN with a file server 5/25/2017 CIS275 9 Advantages of Server-Based over Peer-to-Peer Networks • User login accounts and passwords can be assigned in one place • Access to multiple shared resources can be centrally granted • Servers are optimized to handle heavy processing loads and dedicated to handling requests from clients • Servers can connect more than a handful of computers 5/25/2017 CIS275 10 MANs and WANs • Metropolitan area network (MAN) – Network connecting clients and servers in multiple buildings within limited geographic area • Wide area network (WAN) – Network that spans large distance and connects two or more LANs – The Internet is an example of a very intricate and extensive WAN that spans the 5/25/2017 globe CIS275 11 WAN A simple WAN 5/25/2017 CIS275 12 Elements Common to All Server-Based Networks • Client – In addition to referring to a computer on the network, may also refers to human user of client workstation • Server • Workstation • Network interface card (NIC) – Enables workstation to connect to the network and communicate with other computers 5/25/2017 CIS275 13 Elements Common to All Server-Based Networks • Network operating system (NOS) • Host – Server that manages shared resources • Node – Client, server, or other device that can communicate over a network and that is identified by a unique identifying number, known as its network address 5/25/2017 CIS275 14 Elements Common to All Server-Based Networks • Topology: It is the physical layout of computer network •Commonly used network topologies are: 5/25/2017 CIS275 15 Elements Common to All Server-Based Networks • Protocol – Rules network uses to transfer data • Data Packets – The distinct units of data transmitted from one computer to another on a network • Addressing – Scheme for assigning unique identifying number to every workstation on network – The number that uniquely identifies each workstation and device on a network is its address 5/25/2017 CIS275 16 Elements Common to All Server-Based Networks • Transmission media – Means through which data are transmitted and received 5/25/2017 CIS275 17 How Networks Are Used • Services – Features provided by a network • • • • • 5/25/2017 File and print services Communications services Mail services Internet services Management services CIS275 18 Network Services • File services – Refers to capability of a server to share data files, applications, and disk storage space – Server that provides file services is called a file server • Print services – Allows printers to be shared by several users on a network 5/25/2017 CIS275 19 Network Services • Communications services – Allow remote users to connect to a network • Remote user – Person working on a computer in a different geographical location from the LAN’s server – Communications server • Server that runs communications services • Also referred to as access servers and remote access servers 5/25/2017 CIS275 20 Network Services • Mail services – Coordinate storage and transfer of e-mail between users on a network • Gateway – Combination of software and hardware enabling two different kinds of networks to exchange data • Internet services – Enable networks to communicate with the Internet 5/25/2017 CIS275 21 Network Services • Management services – Centrally administer and simplify complicated management tasks on the network – Numerous services fall under category of network management 5/25/2017 CIS275 22 Important Management Services • Traffic monitoring and control – Traffic • Data transmission and processing activity taking place on a computer network at any given time – Segment • Part of LAN that is logically separated from other parts of LAN and that shares fixed amount of traffic capacity 5/25/2017 CIS275 23 Important Management Services • Load balancing – Distributing process activity evenly across a network so that no single device is overwhelmed • Hardware diagnosis and failure alert – Determining when a network component fails and automatically notifying network administrators through e-mail or pager 5/25/2017 CIS275 24 Important Management Services • Asset management – Collecting and storing data on number and types of software and hardware assets in an organization’s network • License tracking – Determining how many copies of a single application are currently in use on a network 5/25/2017 CIS275 25 Important Management Services • Security auditing – Evaluating what security measures are currently in force and notifying network administrator if a security breach occurs • Software distribution – Automatically transferring data file or program from the server to a client on the network 5/25/2017 CIS275 26 Important Management Services • Address management – Centrally administering a finite number of network addresses for an entire LAN • Backup and restoration of data – Backing up • Copying critical files to a secure storage area – Restoring • Retrieving data if original files are lost or deleted 5/25/2017 CIS275 27