* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networks and Networking - INASP
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
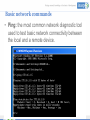
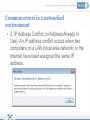
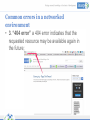
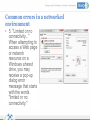
Networks and Networking Management of networks and networking in the library Aims and Objectives • During the workshop, the following contents will be covered: – What is a Network and how is it applied – Basic components of a network – Common networking errors – Troubleshooting common networking errors Outcomes • Define a network, and identify different types • Name the basic features and its functionality • Explain advantages and disadvantages of a network • Identify constraints under which errors in a network can be identified and provide solutions. • Be able to manage and troubleshoot network problems and errors Workshop Format • Informal—questions please! • Presentations • Group discussion What is a Network? • A computer network is a collection of two or more computers connected together. • When computers are joined together they form a network How is it applied in a library environment? • Computers, networks and electronic information systems are essential resources for accomplishing library’s mission of information access, research, and service outreach. A networked library environment enables: • Information Access Support Tools • Enhancing Usability of resources • Collaboration by Library Users and Librarians What types of networks are available? • LANs are networks usually confined to a geographic area, such as a single building or a college campus. • Wide area networking combines multiple LANs that are geographically separate. This is accomplished by connecting the different LANs using services such as dedicated leased phone lines, dial-up phone lines (both synchronous and asynchronous), satellite links, and data packet carrier services. Typical network setup in a library environment? • The term Client/server refers to the concept of sharing, it involves processing data between the client computer and the most powerful server computer. • The client/server network is the most efficient topology for a library setup in that it provides: Databases and management of applications such as Spreadsheets, Accounting, Communications and Document management. Network management. Centralized file storage. Advantages of Computer Networking • 1. Easy Communication and Speed • 2. Ability to Share Files, Data and Information • 3. Sharing Hardware • 4. Sharing Software • 5. Security • 6. Speed Disadvantages of Networking • 1. Breakdowns and Possible Loss of Resources • 2. Expensive to Build • 3. Security Threats • 4. Bandwidth Issues What makes up a network • At least two computers Server and or Client workstation. • NIC (Network Interface Card): Every device on the network has to have a network interface of some design. • Media (Cabling): A connection medium • Switch: it is a hardware part of a network; it is used to connect multiple devices on the same network within a building or campus. • Router: A valuable component of a Network they are used to tie multiple networks together • Firewalls: Firewalls are the most important aspect of a network with respect to security. A firewalled system does not need every interaction or data transfer monitored by a human 25/05/2017 13 Managing and controlling a network Basic network commands Common errors in a networked environment Troubleshooting a network Basic network commands • Ping: the most common network diagnostic tool used to test basic network connectivity between the local and a remote device. • IPconfig: It shows the IP address of the computer and also it shows the DNS, DHCP, Gateway addresses of the network and subnet mask. Common errors in a networked environment • 1. "A Network Cable is unplugged": This message appears as a Windows desktop balloon Common errors in a networked environment • 2. IP Address Conflict (or Address Already in Use): An IP address conflict occurs when two computers on a LAN (local area network) or the Internet have been assigned the same IP address. Common errors in a networked environment • 3. “404 error” a 404 error indicates that the requested resource may be available again in the future; Common errors in a networked environment • 4. “Server not found": Server not found" or similar errors, in which a connection to the destination server could not be made at all Common errors in a networked environment • 5. "Limited or no connectivity..." When attempting to access a Web page or network resource on a Windows shared drive, you may receive a pop-up dialog error message that starts with the words "limited or no connectivity." Troubleshooting a network • 1. Physical layer: The Media (Cable, fiber or wireless) Possible causes: – Damaged or dirty cabling or terminations – Insufficient cable bandwidth – Excessive signal attenuation – Wireless interference Troubleshooting a network • 2. Network Layer: Ethernet and IP Possible causes: – Damaged networking devices – Incorrect or sub-optimal device configurations – Authentication and association issues – Insufficient network bandwidth Troubleshooting a network • 3. Switches and VLANs Possible causes: – Excessive utilization – Too many errors – Incorrectly assigned VLAN membership – Traffic priority issues Best practices for successful LAN troubleshooting include these steps: • 1. Identify the exact issue or problem: Have the person who reported the problem explain how normal operation appears, and then demonstrate the perceived problem. 2. Recreate the problem if possible: Ask yourself if you understand the symptoms, and verify the reported problem yourself if possible. 3. Localize and isolate the cause: Attempt to isolate the problem to a single device, connection, or software application. Best practices for successful LAN troubleshooting • 4. Formulate a plan for solving the problem: Research and/or consider the possible solutions to the problem. Consider the possibility that some solutions to the problem at hand may introduce other problems. 5. Implement the plan: Your actual solution to the problem may be replacing hardware, implementing a software patch, reinstalling the application or component or cleaning a virus infected file. If the problem is the user account, the user’s security settings or logon scripts may need to be adjusted. 6. Test to verify that the problem has been resolved: After you have implemented the solution, ensure that the entire problem has been resolved by having the user test for the problem again. Best practices for successful LAN troubleshooting • 7. Document the problem and solution: Documentation can be used for future reference to help you troubleshoot the same or similar problem. You can also use the documentation to prepare reports on common network problems for management and/or users, or to train new network users or members of the network support team. 8. Provide feedback to the user: This encourages users to report similar situations in the future, which will improve the performance of your network. If the user could have done something to correct or avoid the issue, providing feedback may reduce the number of future network problems. Some Common Problems and their solutions • Can’t connect to other computers or share files and printers on the network – • Can't connect to the network (Cabled or wireless connection) • There's a duplicate IP address on the network • Can't share the root of a drive Thank you Questions This work is licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. 25/05/2017 29