* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
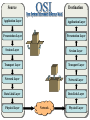
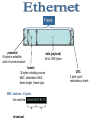
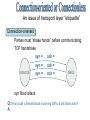
OSI Model Routing Connection-oriented/Connectionless Network Services Destination Source Application Layer Application Layer Presentation Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Transport Layer Network Layer Network Layer Data Link Layer Data Link Layer Physical Layer Network Physical Layer IDS 7 - Application Layer Supports transmission from services Unit: message Uses: ftp, NFS, telnet 6 - Presentation Layer Provides data translation Unit: message Uses: encryption, compression 5 - Session Layer Maintains connectivity until task completion Unit: message Uses: RPC, netBIOS firewall 4 - Transport Layer router 3- Network Layer bridge switch repeater Partitions/reconstructs message Unit: segment Uses/standards: TCP, UDP Delivers from logical device to logical device Unit: packet Uses/standards: IP, IPX, Appletalk 2 - Data Link Layer Delivers from physical device to device Unit: frame Uses/standards: Ethernet, FDDI, T1 1- Physical Layer Transmits raw data through net equipment Unit: bit Uses/standards: RS-232, 802.11 Source: • receive frame from data link • transmit as raw bits Wires & connections Signal levels Repeaters and hubs (amplifiers/splitters) Frame stupid Logical link control Source: • wraps packet within a frame • forward frame to physical layer Destination: • checks frames for integrity • reconstruct packet from frame(s) Media Access Control (MAC) addresses Bridges and switches (connect by MAC) Frame preamble 8 bytes to establish start of communication data (payload) 46 to 1500 bytes header 14 bytes including source MAC, destination MAC, frame length, frame type MAC address - 6 bytes this machine: 00:0d:93:87:80:10 broadcast: CRC 4 byte cyclic redundancy check Packets find their way through the network Source: • wraps segment into a packet • packet must contain network (IP) address Destination: • packets received only if the logical device address matches the packet • strip away frame header & CRC Routers select network path based on logical address of destination • An IPv4 address consists of 4 octets. • The range of an octet is 0 through 255. Class 1st Octet Subnet Mask Available Addresses A 1 - 127 B 128 - 191 C 192 - 223 D 224 - 255 reserved for broadcast Bridges vs. Routers QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 10.2.2.1 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 10.2.2.2 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 10.2.2.1 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 10.2.3.1 Handles message partitioning/reconstructing Source: • accepts message from session layer • partitions message into sequence of segments (will fit into frame) Destination: • gathers together segments identified by their sequence numbers Examples: TCP - Transport Control Protocol UDP - User Datagram Protocol SPX - for IPX ATP - for AppleTalk Maintains the complete “conversation” Source: • attaches proper port address Destination: • listens & directs from port to service • maintains service integrity (e.g. directing to proper window of web browser) performs encryption/decryption if needed. note: headers are added later so not encrypted typical services: SNMP, FTP, telnet, SMTP A router connects logical networks. Its purpose is to route packets between subnets. Routing is performed according to routing tables. Four types of routers static distance vector link state label switching Static Routing The routing table is manually configured. • simple • efficient routing • good security (if properly configured) • requires the most maintenance Distance Vector Routing The table is built from Routing Information Protocol. • oldest, most popular, routing • tables rely upon “advertised” hop information • distance vector used to determine “best” routes • vulnerable to spoofing Link State Routing The table is built from Link State Protocol. • LSP sends actual hop data. • LSP frames can be requested from other routers • uses some authentication (password & MD) Label Switching Routing The table is built from Multiprotocol Label Switching • MPLS faster by permitting by using MAC • packets include label(s) of routing info • route efficiency (not just hop count) is used • standards? An issue of transport layer “etiquette” Connection-oriented Parties must “shake hands” before communicating. TCP handshake syn = , ack = syn = , ack = source syn = , ack = dest. syn flood attack Q: How could a firewall block incoming traffic & still allow acks? A: Port/protocol Service Purpose 20 / tcp ftp data transfers file content 21 / tcp ftp transfers ftp commands 22 / tcp ssh secure shell (remote access) 23 / tcp telnet remote computer login 25 / tcp smtp email delivery 43 / tcp whois Internet domain lookup 80 / tcp http web browser 110 / tcp pop pop email service 119 / tcp nntp network news 143 / tcp imap imap email service 161 / udp snmp remote system management 443 / tcp ssl secure socket layer (tunnel) 445 / tcp smb MS network file system 593 /tcp MSRPC MS remote procedure call 1433 / tcp MS-SQL MS SQL server • Ports 0-1023 statically assigned • Ports 1024-65535 - upper ports can be dynamically assigned • Vulnerability: dynamic port assignment • A defense: 7 - Application Layer 6 - Presentation Layer 5 - Session Layer 4 - Transport Layer 3- Network Layer 2 - Data Link Layer 1- Physical Layer OSI Model HTTP FTP Telnet UDP TCP IP radio pointEthernet packet to-point TCP/IP Protocols