* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DHCP for Wireless Ad
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Real-Time Messaging Protocol wikipedia , lookup
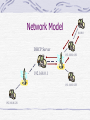
DHCP for Multi-hop Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Presented by William List Problem Statement DHCP is designed to work on the wired internet with bridges, switches and routers DHCP messages sent from a client are broadcast, not unicast Nodes in an ad hoc network need to know what address to use! DHCP Basics (RFC 2131) When a client boots, it attempts to obtain a usable IP address A DHCPDISCOVER message is broadcast to locate available DHCP servers Server responds with a DHCPOFFER message containing the new address DHCPREQUEST and DHCPACK confirm the assignment DHCP Relays A DHCP relay will forward DHCP messages back and forth between a client and server The relay knows the address of the DHCP server DHCP packets allow for only one relay (gateway) DHCP Packet Format 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | op (1) | htype (1) | hlen (1) | hops (1) | +---------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+ | xid (4) | +-------------------------------+-------------------------------+ | secs (2) | flags (2) | +-------------------------------+-------------------------------+ | ciaddr (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | yiaddr (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | siaddr (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | giaddr (4) | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | | | chaddr (16) | | | | | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ DHCP Packet Fields ciaddr yiaddr giaddr chaddr : The client’s previous IP address : The address offered by the server : Relay address : Client’s hardware address DHCP Message Exchange DHCPDISCOVER Hello!? I’d like an IP address please! DHCPOFFER How about 192.168.0.1? DHCPREQUEST Sounds good. DHCPACK Glad to hear it. Have fun! Client Server Discover Offer Request ACK Using a Relay Client Relay Server 0.0.0.0 giaddr: 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.1 The relay can be another host or a router Solution Make every node in the network run the DHCP relay once configured Include the DHCP server IP address in AP beacons Unicast messages towards DHCP server rather than broadcasting Assumptions Every node in the network can reach the Access Point Either directly or through multiple hops DCHP server(s) assigns IP addresses Allows for network monitoring and accounting Should be able to run over any ad-hoc routing protocol Network Model 0.0.0.0 DHCP Server 192.168.0.130 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.129 192.168.0.128 Client Node Waits for a beacon from an AP Once the IP address of the DHCP server is obtained: Add an entry in routing table specifying same next-hop as for the associated AP Generate a DHCPREQUEST message Unicast towards DHCP server Neighboring Nodes Next hop towards DHCP server receives the DHCP request from source The giaddr field is filled in with the node’s IP address Packet is forwarded to DHCP server Intermediate Nodes Nodes between the designated relay node and the DHCP server Are unaware of the DHCP messages and simply forwards packets back and forth DHCP Server Access Point must know the IP address of the DHCP server (for beacons) DHCP server uses giaddr as the destination for responses Source address must remain 0.0.0.0 IP masquerading and NAT complicated Best if ad-hoc nodes are on the same subnet as the DHCP server Alternate Model Client broadcasts DHCP messages Do not need to wait for a beacon Multiple neighbors serve as relays Client might receive multiple responses from the same server Client will select best offer Relays unicast to the DHCP server Other Alternatives The Access Point knows the location of the DHCP server Client could unicast DHCP messages to AP Issues DHCP server probes for used addresses ICMP ping packets will be forwarded by nodes in the ad hoc network What if the packet is dropped somewhere? Broadcasting DHCP messages introduces added network traffic Address assignment is only done once, unless the node is highly mobile Conclusion DHCP fundamentally works as-is in a multi-hop environment Future Work Run more scenarios AP could broadcast ping packets several times for the DHCP server, rather than just once Integration with a Internet gateway