* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Remote Access Service
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
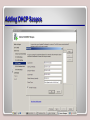
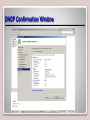
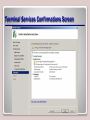
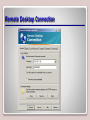
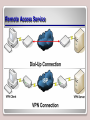
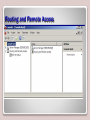
Working with Networking Services Lesson 6 Objectives DHCP • DHCP is short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. • This protocol allows properly configured client computers to obtain IP addresses automatically from a DHCP server. • The IP information obtained might include the following: – IP addresses – Subnet masks – Gateway addresses – DNS server addresses – Other advanced options DORA • DHCP sessions use a four-step process known as DORA. – Discovery: The client computer broadcasts out to the network in order to find a DHCP server. – Offering: The DHCP server sends out a unicast “offering” of an IP address to the client computer. – Request: The client broadcasts to all servers that it has accepted the offer. – Acknowledge: The DHCP server sends a final unicast to the client that includes the IP information the client will use. • DHCP utilizes ports 67 and 68. DHCP Server • Installing a DHCP server consists of the following actions: – Installing the DHCP service – Configuring an IP scope – Activating the scope – Authorizing the server – Configuring advanced IP options (optional) Adding DHCP Scopes DHCP Confirmation Window APIPA • APIPA can get in the way of a client obtaining an IP address properly (e.g., when a client attempts to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server, but the DHCP server is too busy). • Remember that APIPA is used by Windows machines when it cannot connect with a DHCP server to get a dynamic address. Disable APIPA Terminal Services • Terminal Services, also known as Remote Desktop Services, is a type of thin-client terminal server computing. • It allows client computers to access and use applications loaded on the server, as well as to connect to and take control of a server. • Thin-client computers and PCs can connect to servers running Terminal Services. • The service uses port 3389 and is also known as Microsoft WBT Server. WBT stands for WindowsBased Terminal. Terminal Services Confirmations Screen Remote Desktop Connection Remote Access Service • Remote Access Service (RAS) is grouping of different hardware and software platforms to allow remote access to another computer or network device. • Originally used with dial-up services, Microsoft RAS has morphed into RRAS, or Routing and Remote Access Service. Remote Access Service Routing and Remote Access IPSec • Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a protocol within the TCP/IP suite that encrypts and authenticates IP packets. • It is designed to secure any application traffic because it resides on the network layer (or Internet layer, as TCP/IP programmers refer to it). • This protocol is used in conjunction with virtual private networks and is an integral part of IPv6. IPSec • There are three main protocols that IPSec uses to perform its necessary functions: – Security association (SA): This generates the encryption and authentication keys that are used by IPsec. – Authentication header (AH): This provides connectionless integrity and the authentication of data. It also provides protection versus replay attacks. – Encapsulating security payload (ESP): This provides the same services as AH but also provides confidentiality when sending data. DNS • The Domain Name System (DNS) is a worldwide service that resolves host names to IP addresses. • This facilitates proper communication between computers. DNS servers communicate with each other in a hierarchy in an effort to teach each other their name resolutions. • DNS servers use inbound port 53 to accept name resolution requests. Adding the DNS Service WINS • Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) is a service that resolves NetBIOS names to IP addresses. • It is Microsoft’s version of the NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) combined with a name server. Adding the WINS Server Server 2008 Features List Summary • How to install and configure DHCP to hand out IP addresses to client computers. • The four-step DHCP process known as DORA. • How to install and configure Terminal Services so that client computers can connect remotely to a server and take control of it in the GUI. • How to install and configure Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) as a LAN router. • To define IPsec and the various types, including SA, AH, and ESP. • How DNS and WINS function and how to install them in Windows Server 2008, as well as how to create forward lookup zones.