* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stair Principles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
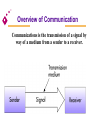
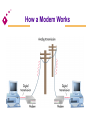
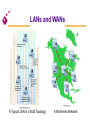
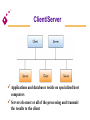
Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Overview of Communication Communications is the transmission of a signal by way of a medium from a sender to a receiver. Telecommunications Electronic transmission of signals for communications Telephone Radio Television Lessens barriers of time and distance Telecommunications Data communications Specialized subset of telecommunications Includes the electronic collection, processing, and distribution of data Telecommunications media Anything that carries an electronic signal and interfaces between a sending device and a receiving device Elements of a Telecommunications System [Figure 6.3] Analog and Digital Signals Analog Continuous fluctuations over time between high and low voltage Digital A discrete voltage state Analog and Digital Signals Analog signal Fig. 6.4 Digital signal Analog Waves Frequency The number of times per second a continuous wave completes one cycle Amplitude The difference of the extremes from the midpoint in a cycle Basic Modulation Techniques Amplitude modulation (AM) Converts digital data to analog signals using a single frequency carrier signal High-amplitude wave denotes a binary 1 Low-amplitude wave denotes a binary 0 Basic Modulation Techniques Frequency modulation (FM) Uses a constant amplitude carrier signal and two frequencies to distinguish between 1 and 0 Phase modulation Uses a phase shift at transition points in the carrier frequency to represent 1 or 0 Communications Speed Bits per second (bps) Number of bits that can be transferred in one second Bandwidth Range of signal frequencies that can be sent over a medium at the same time Broadband Bandwidth of 256,000 to 1 million bps Types of Communications Media Twisted wire cable Coaxial cable Fiber-optic cable Microwave transmission Cellular transmission Infrared transmission Twisted Wire Cable A cable consisting of pairs of twisted wires The twist helps the signal from “bleeding” into the next pair Coaxial Cable Inner conductor wire surrounded by insulation, called the dielectric Dielectric is surrounded by a conductive shield, which is in turn covered by a layer of nonconductive insulation, called the jacket Fiber-Optic Cable Consists of many extremely thin strands of glass or plastic bound together in a sheathing Transmits signals with light beams Wireless Transmission Microwave: Terrestrial Microwave: Satellite Cellular PCS Telecommunications Devices Modems Fax modems Special-purpose modems Multiplexers Communications processors How a Modem Works Multiplexers Allow several telecommunication signals to be transmitted over a single communications medium concurrently Time division multiplexer (TDM) Multiple incoming signals are sliced into small time intervals Frequency division multiplexer(FDM) Incoming signals are placed on different frequency ranges Time Division and Frequency Division Multiplexers [Figure 6.14] Communications Processors Called front-end processors because they are in front of and before the main system CPU Incoming and outgoing jobs [Figure 6.15] Main system Front-end processor Telecommunications Carriers and Services Common carriers Long-distance telephone companies Value-added carriers Companies that have developed private telecommunications systems and offer their services for a fee Telecommunications Carriers and Services Switched line Standard telephone line that uses switching equipment to allow one transmission device to be connected to others Dedicated line Provides a constant connection between two points Also called a leased line Telecommunications Carriers and Services Private branch exchange (PBX) Manages both voice and data transfer within a building and to outside lines Wide area telephone services (WATS) A billing method for heavy users of voiceband media Phone and dialing services Additional services from the common carriers (i.e. ANI) Telecommunications Carriers and Services Integrated services digital network (ISDN) Technology that uses existing common-carrier lines to simultaneously transmit voice, video, and image data in digital form Digital subscriber line (DSL) Businesses/homes that have a DSL over existing phone wires can use a special modem that transmits up to 768 Kbps Telecommunications Act of 1996 Completely rewrites the 62-year-old Communications Act Goal: To promote competition and eliminate monopolies for a wide range of communication services May cause profound changes in U.S. communications that can lead to a complete renovation in the way information is delivered to consumers Global Telecommunications One of the largest and fastest growing sectors of the global economies Criticality of implementing and managing global networks Increase of international acquisitions and mergers Need to compete on a global basis Computer Network Includes communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more computer systems and/or devices Benefits of a Network Can turn a company into an agile, powerful and creative organization, giving it long-term competitive advantage Can be used to share hardware, programs, and databases across the organization Basic Data Processing Strategies Centralized processing All processing occurs in a single location Decentralized processing Processing devices are placed at various remote locations Distributed processing Computers at remote locations are connected to each other via telecommunications devices Network Concepts and Considerations Network topology Logical models that describe how networks are structured or configured Star network A network that has a central hub or computer system Four Basic Types of Network Topology (a) ring (b) bus (c) hierarchical (d) star [Figure 6.17] Types of Networks Local area networks (LAN) Connect computer systems and devices within the same geographical area Regional networks Tie regional areas together via telecommunications systems Types of Networks Wide area networks (WAN) Tie large geographic regions together using microwave and satellite transmission or telephone lines Private WANs Computer equipment owned by users and data communications equipment provided by a common carrier Value-added networks (VAN) Offer services in addition to those offered by a traditional network (e.g., CompuServe) International networks Link system together between countries Terminal-to-Host “Dumb” terminal Fig 6.20 Applications and databases reside on the same host computer User interacts with the application using a “dumb” terminal LANs and WANs [Figure 6.18] A Typical LAN in a BUS Topology [Figure 6.19] A Wide Area Network File Server Fig 6.21 Applications and databases reside on the same host computer File server transfers data and programs to PCs on the network, which do the processing Client/Server Fig 6.22 Applications and databases reside on specialized host computers Servers do most or all of the processing and transmit the results to the client The Client/Server Approach Advantages Cost potential Improved performance Increased security Disadvantages Increased cost potential Loss of control Complex multivendor environment Functions of Communications Software Error checking Message formatting Communications logs Data security and privacy Translation capabilities for networks Communications Software Network operating systems Systems software that controls the computer systems and devices on a network and allows them to communicate with each other Network management software Software tools and utilities available for managing networks Communications Protocols Open systems interconnection (OSI) A protocol (or standard) endorsed by the International Standards Committee TCP/IP Developed by the U.S. government to link its defense research agencies SNA IBM’s communications protocol Ethernet A popular protocol often used with local area networks Other protocols Bridges, Routers, and Gateways Bridge Connects two or more networks Router Features more sophisticated addressing software than bridges Gateway Links LANs or networks that employ different higher-level protocols Bridges, Routers, and Gateways [Figure 6.24] Coordinating Communications and Networks Polling A procedure in which the main computer checks each device one at a time to see if there are any messages waiting to be communicated to other network devices Token passing A technique in which an electronic “token” is passed from one device to another Contention A procedure in which a device checks to see if a message is currently being transmitted Data Transfer Modes Packet switching Communications process that divides electronic messages into small segments (data packets) Frame relay Uses wideband communications media and high speed switching devices Voice-over frame relay Moves voice traffic onto frame relay to bypass the public telephone network Data Transfer Modes Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) A high-speed network technology that provides transport for voice, video, text, and other multimedia data Fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) Designed specifically to serve the needs of highperformance, mission-critical LAN applications Telecommunications Applications Links between PCs and mainframes Facilitates the upload or download of data Voice storage and forwarding Sometimes called voice mail Allows users to leave, receive, and store verbal messages for and from people around the world Telecommunications Applications Electronic mail Users connected to a network can send messages to others by computer Electronic document distribution Involves transporting documents over communications lines and networks Telecommunications Applications Electronic software distribution Involves installing software on a file server for users to share by signing onto the network and downloading the software onto their computers over the network Telecommuting Working at home on a PC and communicating with the central office or other workers via networks Telecommunications Applications Teleconferencing Allows groups to have conferences in one connected voice phone call Videoconferencing An extension of teleconferencing that combines voice, video, and audio transmission Telecommunications Applications Electronic data interchange (EDI) Uses network systems and follows standards and procedures that allow output from one system to be processed directly as input to other systems, without human intervention [Figure 6.27] Telecommunications Applications Public network services Give PC users access to vast databases and other services, usually for an initial fee plus usage fees [Figure 6.28] Telecommunications Applications Specialized information systems Include legal, patent, and technical information Regional information systems Include local electronic bulletin boards and electronic mail facilities that offer information regarding local club, school, and government activities Distance learning Extends the classroom by using telecommunications Network Design Considerations Reliability Security Response time Privacy issues Vendor services and support Company support Communications Audits Purpose: To make sure the communications system is operating as intended Types of communications audits: Walk-thorough Software check Network check Policy and procedures Program and database check