* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
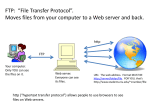
Level 2 Diploma Unit 10 Setting up an IT Network OSI Layers 1 to 4 OSI Physical layer 1 Network media – the cables/wireless and adapters OSI Data link layer 2 Method of transferring data between network adapters Organises data streams into frames Uses MAC addresses OSI Network layer 3 Routes packets between networks Uses IP addresses OSI (Open Systems Interconnect) model 7 layers Each layer provides a service for the layer above and uses the services of the layer below Each layer (except the physical) attaches a header Headers provide control information Frames Address used is the 48 bit unique MAC (Media Access Control) address hard coded into the adapter Network Layer 3 Data messages are split into smaller packets Better chance of successful delivery Easier to resend if lost or damaged Routers Choose the path that packets take around the network Packets are given a time to live (TTL) to prevent them travelling for ever Internet Protocol (IP) and IP addressing Provides network identification and addressing An IP address is a 32 bit binary value expressed as dotted decimal 00001010.00000001.1010000.00001100 is easier as 10.1.80.12 Restricted addresses Type Range Comment Private 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 Class A 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255 172.16.0.0 – 169.254.255.255 Class B 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 Class C Loopback 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 Multicast 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255 Reserved 0.0.0.0 - 0.255.255.255 Tests host function Broadcast to many hosts Not permitted 128.0.0.0 – 128.0.255.255 Not permitted 191.255.0.0 – 191.255.255.255 Not permitted 192.0.0.0 – 192.0.0.255 Not permitted 223.255.255.0 – 223.255.255.255 Not permitted I. P Addresses •11000000101010000000000100000101 •What is a ’bit’? •192.168.1.5 •www. Network Address Translation Private networks connect to the Internet via a router Host’s private address is translated to a valid public address by the router using NAT Easier IP configuration Hosts protected from direct internet access Can map 1:1 or use port addresses to map n:1 ARP and ICMP ARP (Address resolution protocol) Network layer Converts IP addresses to MAC addresses Converts MAC addresses to IP addresses ICMP (Internet control message protocol) Used for diagnostic and troubleshooting tools PING TRACERT TCP and UDP Layer 4 TCP Transmission Control Protocol Reliable Connection oriented packet transfer TCP/IP applications use a unique identification number called a port An IP address and a port make a socket Socket to socket connections make a path http:215.58.254.252:80 where 80 is the port number Common port numbers Port Number Process Name Description 20 FTPDATA File transfer protocol – Data 21 FTP File transfer protocol – Control 22 SSH Secure shell 23 TELNET Telnet 25 SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol 53 DNS Domain Name Service 69 TFTP Trivial FTP 80 HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol 110 POP3 Post Office Protocol 3 119 NNTP Network News Transfer Protocol 123 NTP Network Time Protocol 139 NetBIOS Session port 143 IMAP4 Internet Mail Access Protocol 389 LDAP Directory Access Protocol 443 HTTPS HTTP Secure HTTP and HTML Hypertext transfer protocol Web browsers request resources from web servers by ○ connecting to port 80 ○ Using a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) Common web servers are ○ Apache (open source) ○ Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) HTTP is used to serve HTML (Hypertext MarkUp language) pages which describe how the text should be displayed SSL/TLS HTTP is not encrypted and does not authenticate SSL (Secure sockets layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) Provide cryptographic security Used with HTTPS ○ Uses port 443 ○ Puts https:// in the URI ○ Adds a padlock icon in the browser E-mail Plain text File attachments encoded in MIME (multipurpose internet mail extensions) Send mail out using SMTP Simple mail transfer protocol Receive mail using POP3 or IMAP4 Can be secured using PGP (Pretty Good Privacy or Secure MIME FTP File transfer protocol More efficient then e-mail Plain text transfer Most browsers include an FTP client ○ ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/ Instant Messaging Exchange of text messages with contacts Domain names Every host on the internet has a unique, 32 bit IP address For convenience each host also has a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Domain Name Servers cross reference between domain names and IP addresses An FQDN is hierarchical www.google.com local domain Top level domain Subdomain www as a local domain indicates the resource is a web server A Subdomain has to be registered and identifies a company, organisation or individual Top level domain names Domain Name Description edu Educational and research institutes gov Government agencies mil Military institutions net Network companies (ISPs) com Commercial organisations org Other organisations uk United Kingdom au Australia jp Japan Uniform Resource Identifier A URI (sometimes known as a URL): Has all the information to identify a resource http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/8013709. stm ○ http:// is the protocol being used ○ News.bbc.co.uk is the FQDN ○ /1/hi/sci/tech/8013709.stm is the file path on the server email address An email address consists of: The user name A separator symbol (@) A domain name ○ [email protected] Task (criteria P5) You have been asked by a friend to explain how network communications work in a company. Describe how hardware, software and addressing combine to use a web browser to send an e-mail to another system. Include a diagram making sure you show how the components are connected together Make sure you explain: ○ NIC, cable, switches, routers, modems, servers ○ NOS, E-mail client, web browser ○ IP and MAC addresses