* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT_CH07
Survey
Document related concepts
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Games for Windows – Live wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Security Essentials wikipedia , lookup
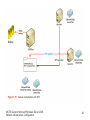
Transcript
MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration Chapter 7 Configuring File Services in Windows Server 2008 Objectives • Discuss File Services in Windows Server 2008 • Install the Distributed File System in Windows Server 2008 • Discuss and create shared file resources in Windows Server 2008 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 2 Introduction to File Services • Functions of the Windows Server 2008 File Services role – – – – – File Server Distributed File System File Server Resource Manager Services for Network File System Windows Server 2003 File Services MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 3 Installing the File Server Role • File Server role – Install by activating File Services if necessary – Role services, and other features can be installed through the graphical user interface (GUI) MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 4 Installing the File Server Role (continued) • Activity 7-1: Installing the File Server Role • Time Required: 5 minutes • Objective: Install the File Server role to implement Windows 2008 Server File Services MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 5 File and Folder Sharing • Sharing creates – A network access point for clients to access data across the network • Clients use – Server Message Block (SMB) connections to access shared resources MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 6 Public and Standard Sharing • Public folder sharing – Allows users to share files with all the users logged on locally or on the network, if that feature is enabled – Public folders are located in the • %systemdrive%\Users\Public directory MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 7 Public and Standard Sharing (continued) • Activity 7-2: Using Public Folder Sharing • Time Required: 10 minutes. • Objective: Learn how to use public folder sharing MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 8 Public and Standard Sharing (continued) • Standard file sharing – Makes files and folders accessible from a network location – NTFS • The preferred format in Windows Server 2008 • Shares on FAT32 volumes can only use share permissions MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 9 Access Control • Share-level permissions – Defined at the shared resource level – Allow clients access to a network share – Apply only when a file or folder is being accessed via the network – Do not apply to a user logged into the machine locally MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 10 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 11 Access Control (continued) • Default and administrative shares – Administrative shares can be identified by name because they always end with a dollar sign ($) – Default shares include: • • • • Drive Letter Shares Admin$ IPC$ NETLOGON MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 12 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 13 Access Control (continued) • Activity 7-3: Creating and Verifying Administrative Shares • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Create and verify administrative shares MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 14 Access Control (continued) • User-level permissions – Defined at the folder or file level – NTFS • The preferred file system used in Windows networks • Permissions apply anytime a file or folder resource is accessed • Permissions are divided into two types: file permissions and folder permissions MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 15 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 16 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 17 Access Control (continued) • Activity 7-4: Modifying NTFS Permissions Using Windows Explorer • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Modify NTFS permissions MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 18 Access Control (continued) • Activity 7-5: Modifying NTFS Permissions Using the CACLS Command • Time Required: 5 minutes • Objective: Modify NTFS permissions with CACLS MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 19 Access Control (continued) • Access control lists – Used by NTFS to define permissions to resources • Authentication – Token: object attached to a user’s account that validates the user’s identity and privileges – Security identifiers (SIDs): used to make every user, computer, and resource on a network unique MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 20 Deploying Shares • File and folder sharing can be implemented through: – – – – Shared Folders console Windows Explorer Net share command Share and Storage Management console MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 21 Deploying Shares (continued) • Deploying shares with the Shared Folders console – Shared Folders console is available through the Computer Management consol • Deploying shares with Windows Explorer – Network file and folder sharing, or sharing, is performed when using the File Sharing Wizard • Deploying shares with Net share – Net share allows you to create and manage shared folder resources MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 22 Deploying Shares (continued) • Activity 7-6: Managing Shared Folders through the Shared Folders Console • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Explore the Shared Folders console and close open sessions MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 23 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 24 Deploying Shares (continued) • Activity 7-7: Creating a Shared Folder through Windows Explorer • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Create a shared folder in Windows Explorer MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 25 Deploying Shares (continued) • Activity 7-8: Modifying the Advanced Sharing Properties on a Share through Windows Explorer • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Modify a share using Advanced Sharing properties MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 26 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 27 Deploying Shares (continued) • Activity 7-9: Creating a Shared Folder Using the CLI • Time Required: 15 minutes. • Objective: Use the CLI to create shared folders MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 28 Deploying Shares (continued) • Offline files – Allow shared file resources to be available to clients when they are not connected to the network – Caching: defined by administrators at the shared resource level MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 29 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 30 Deploying Shares (continued) • Activity 7-10: Creating a Document on a Remote Server and Setting Up Offline Availability • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Set caching requirements for offline files MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 31 Distributed File System • Distributed File System (DFS) – Set of client and server services that allows companies to deploy their shared file resources as a single file structure – Comprised of two technologies • DFS namespace • DFS replication MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 32 Introduction to DFS • DFS namespace – Allows you to create an entry point for shared file resources using a naming convention of your choice – Two types of implementations • Domain-based • Stand-alone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 33 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 34 Introduction to DFS (continued) • Activity 7-11: Adding DFS Role Services • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Install the DFS Role services MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 35 Introduction to DFS (continued) • DFS replication – Responsible for synchronizing the data within a DFS structure • Load balancing – By replicating your file resources across multiple servers, you can spread the usage load to multiple sources • Fault tolerance – By replicating data across multiple servers, a copy is maintained on a separate system should you experience a failure MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 36 Introduction to DFS (continued) • Backup centralization – DFS can facilitate centralized backups – Once deployed, DFS has a hierarchical namespace structure that allows users to locate information using a UNC path location MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 37 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 38 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 39 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 40 Configuring DFS • Steps for deploying DFS – Install the File Services role and the Distributed File System role services – Create a namespace – Add folders to the namespace – Configure the DFS referral order – Create a DFS replication group MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 41 Configuring DFS (continued) • File Services and Distributed File System roles – You need to install the File Services role along with the DFS services of your choosing • Namespaces – Create a DFS namespace to act as the central point for clients to access network shared data • Namespace folders – After you create your namespace, you can populate the folder MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 42 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 43 Configuring DFS (continued) • Activity 7-12: Creating a Namespace for the Applications Folder • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Create a new DFS namespace MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 44 Configuring DFS (continued) • Activity 7-13: Adding Folders to the DFS Namespace • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Add folders to DFS MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 45 Configuring DFS (continued) • Adding servers to DFS namespace – Once added to the DFS namespace • The new server creates the file system hierarchy for the namespace in its DFS root located at c:\DFSRoot • Configuring the DFS referral order – DFS namespaces use a referral order to determine the DFS server that will provide shared resources to client requests MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 46 Configuring DFS (continued) • Activity 7-14: Adding Servers to a DFS Namespace • Time Required: 5 minutes • Objective: Add servers to the DFS namespace MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 47 Configuring DFS (continued) • Activity 7-15: Creating a DFS Replication Group • Time Required: 20 minutes • Objective: Configure DFS replication between DFS namespace servers MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 48 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM • FSRM allows administrators to perform various tasks in managing files and disk volumes through the FSRM console, including: – Managing file and disk quotas – Screening files using built-in and custom templates – Creating reports on storage resources MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 49 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM (continued) • Activity 7-16: Installing FSRM • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Install the FSRM role service MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 50 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM (continued) • Managing File and Disk Quotas – FSRM quotas use actual file size instead of the logical file size • Screening Files Using Built-In and Custom Templates – Filter screening: allows administrators to block specific types of files from being stored in Windows Server 2008 file directories • Creating Reports on Storage Resources – FSRM can help you forecast space needs and plan for deploying additional storage MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 51 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM (continued) • Activity 7-17: Creating Quotas • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Create a custom file quota MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 52 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM (continued) • Activity 7-18: Creating a File Screen • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Create a file screen to block files MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 53 Managing Windows Server 2008 with FSRM (continued) • Activity 7-19: Running a Storage Report • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Create a storage report MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 54 Summary • DFS – Provides a framework for creating a centralized point of entry for accessing network data • File and folder sharing – Creates a network access point, or share, for clients to access data across the network • Share permissions can be read, change, or full control • User permissions – Based on NTFS settings and are defined at the file level MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 55 Summary (continued) • NTFS – Uses ACLs to define permissions to resources • You can implement file and folder sharing using: – – – – Shared Folders console Windows Explorer The net share command Share and Storage Management console • DFS technologies – Include the DFS namespace and replication MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 56 Summary (continued) • In Windows Server 2008, DFS allows you to: – Create an entry point for shared file resources using your preferred naming convention • DFS replication – Responsible for synchronizing all of the data within a DFS structure • DFS – Can be used to provide load balancing for shared file services MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 57