* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 5 * Triangles and Congruence
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
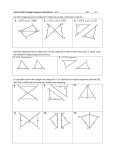
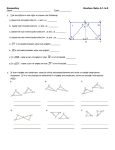
Ch 5 – Triangles and Congruence 5.1 – Classifying Triangles Triangle: Parts of a triangle: Classifying Triangles by Angles: Classifying Triangles by Sides: Parts of an Isosceles Triangle: Example: Classify each triangle by its angles and by its sides. Example: Find the measure of XY and YZ of isosceles triangle XYZ if X is the vertex angle. 5.2 – Angles of a Triangle Theorem 5.1 – Angle Sum Theorem: Example: Find mP in MNP if mM 80 and mN 45 . Example: Find the value of each variable in ABC . Theorem 5.2: Example: Find mJ and mK in right triangle JKL. Equiangular Triangle: Theorem 5.3: 5.3 – Geometry in Motion Translation: Reflection: Rotation: Example: Identify each motion as translation, reflection, or rotation. Preimage/Image Example: In the figure, RST XYZ by translation. Name the image of T . Name the side that corresponds to XY . Example: In the figure, LMN QRS by a rotation. Name the image of M . Name the angle that corresponds to S . Name the image of LM . Name the side that corresponds to LN . Isometries: Example: Identify the types of transformations that were used to complete the work. 5.4 – Congruent Triangles Congruent Triangles: Corresponding Parts: Definition of Congruent Triangles: CPCTC: Example: If ABC EFD , name the congruent angles and sides. Then draw the triangles, using arcs and slash marks to show congruent angles and sides. Example: The corresponding parts of two congruent triangles are marked in the figure. Write a congruence statement for the two triangles. Example: UVW is congruent to GHI . If mV 90 and mh 3x 15 , find the value of x. 5.5 – SSS and SAS Postulate 5.1: Example: In two triangles, DF UV , FE VW , and DE UW . Write a congruence statement for the two triangles. Example: In two triangles, ZY FE , XY DE , and XZ DF . Write the congruence statement for the two triangles. Included Angle: Postulate 5.2: Example: Determine whether the triangles are congruent. If so, write a congruence statement and explain why the triangles are congruent. If not, explain why not. 5.6 – ASA and AAS Included Side: Postulate 5.3: Example: In DEF and ABC, D C , E A, and DE CA . Write a congruence statement for the two triangles. Theorem 5.4: Example: XYZ and QRS each have one pair of sides and one pair of angles marked to show congruence. What other pair of angles needs to be marked so the two triangles are congruent by AAS? Example: Determine whether each pair of triangles is congruent by SSS, SAS, ASA, or AAS. If it is not possible to prove that they are congruent, write not possible.