* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ellye
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
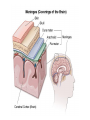
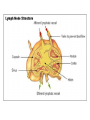
Acute Pyogenic Meningitis Mrs. S.N: • 67 years old • Caucasian • 103 lbs 5’4’’ • Smoker (1/2 pack per day for 45 years) • vaccinated for influenza six months ago Medical History several severe episodes of chronic bronchitis and one episode of pneumonia in the past two years She has never suffered from episodes of angina or symptoms of heart failure denies any past history of head trauma, sinus infection, immunodeficiency disorders, and medications that cause immunosuppression. Her emphysema is being managed with ipratropium bromide Acute Pyogenic Meningitis • Acute: Severe or Intense • Pyogenic: involving or relating to the production of pus • Meningitis: inflammation of the layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord (meninges) and of the fluid-filled space between the meninges (subarachnoid space) Patient Case Question 1. What is the significance of the patient’s productive cough with rust-colored sputum? -Possible bacterial pneumonia being coughed up from the lower airways. Patient Case Question 2. List three clinical manifestations that strongly suggest that the patient has developed meningitis. -Stiff neck (painful w flexion) -Sluggishly reactive to light -Neck shows mild anterior cervical lymphadenopathy Patient Case Question 3. Explain the abnormalities in the vital signs. -Temp: 101.5 ° F -High Blood Pressure Patient Case Question 4. Is the patient technically considered underweight, overweight, obese, or does the patient have a healthy weight based on height? -BMI= 17.5 (Underweight) Patient Case Question 5 Why is it appropriate for the physician to examine the patient for a head injury? -Nares flared, purulent discharge visible Patient Case Question 6 List two clinical signs that are consistent with and specific for an upper respiratory tract infection. -Nares slightly flared, purulent discharge visible Pharynx red with purulent post-nasal drainage Patient Case Question 7. Define papilledema and explain the significance of a lack of papilledema in this patient. Optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. No detection of papilledema suggests that the meningitis has been detected early. Patient Case Question 8. Explain the pathophysiology behind this patient’s lymphadenopathy. Lymph Nodes are highly organized centers of immune cells that filter antigen from the extracellular fluid. There is disease involving the reticuloendothelial system, secondary to an increase in normal lymphocytes and macrophages in response to an antigen. Patient Case Question 9. What is the cause of the patient’s “significant use of accessory muscles”? -Emphysema -Clear Left Lung -Breath sounds in RML and RLL have decreased Patient Case Question 10 What is the significance of lack of a skin rash? -Early detection