* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download rheumatology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
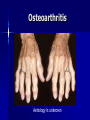
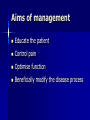
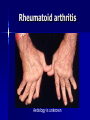
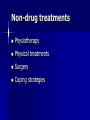
Management of Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis & Gout Dr. Eoin Casey MD FRCPI, FRCP Background Reading Davidson’s Principles & Practice of Medicine, 50th Anniversary Ed, 2002 Musculoskeletal disorders, Ch 20: pg 957-1047 Clinical Assessment of the Musculoskeletal System (handbook) Arthritis and Rheumatism Council UK http://www.arc.org.uk/about_arth/opubs/6321/6321.pdf General Assessment History Clinical examination Functional anatomy Physiology Investigations Major manifestations of musculoskeletal disease Symptoms & Signs Joint pain Stiffness Swelling Inflammation Skin changes Muscle changes Deformity Non-specific systemic symptoms (weight↓; appetite↓; energy ↓; concentration ↓; mood ↓) Osteoarthritis Aetiology is unknown Aims of management Educate the patient Control pain Optimise function Beneficially modify the disease process “It is much more important to know what sort of a patient has a disease than what sort of a disease a patient has.” William Osler 1849-1919 Management of OA Patient’s personality Attitude Holistic factors - activities of daily living - co-morbid disease Availability, cost & logistics of evidence-based intervention Patient education Randomized controlled trials have shown that education results in substantial improvement and prolonged benefit Management of OA Exercise - aerobic fitness - local strengthening exercises Weight reduction Simple analgesia - eg Paracetamol 1g 4-6 hrly Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - (NSAIDS) NSAIDS >40 NSAIDS available in Ireland Top most prescribed drugs in the world In favour of their use are - effectiveness - lack of toxicity - affordability Variable individual tolerance and response Non-responders to one agent may improve with another NSAIDS Mechanism of Action - ↓ prostaglandin levels - inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) Cyclo-oxygenase isoforms COX I - housekeeping enzyme - expressed in gastric mucosa, platelets & kidney COX II - inflammatory enzyme - expressed in various tissues largely at sites of inflammation The COX II controversy Selective COX II inhibitors Gastric side effects of NSAIDS GIT toxicity - up to 30% Aetiological factor in 30% gastric ulcers 10% of RA/OA patients hospitalised annually for NSAID associated bleeding Endoscopic evidence of ulceration in 20% of NSAID users even in absence of symptoms 2000 deaths per annum in UK Risk factors for NSAID gastritis Age > 60 years Past history of PUD Past history of adverse effects with NSAIDS Steroid use High doses Multiple NSAIDS Specific NSAIDS eg Indomethacin, Azapropazone ↓risk - Proton pump inhibitors; Ranitidine Cyto-protection with Mesoprostil NSAIDS side effects Older people are at greatest risk for - renal - cardiovascular - GIT toxicity Other treatment modalities Nutri-pharmaceuticals - Glucosamine - Chondroitin Sulphate Topical agents Physiotherapy Occupational therapy Rheumatoid arthritis Aetiology is unknown Approach to management Holistic approach to assessment Education is as important as medications NSAIDS Corticosteroids Disease modifying agents (slow acting) Steroids in Rheumatoid Arthritis Glucocorticoids in low doses <7.5mg daily are very effective to bridge the gap of the latent period before disease modifying drugs work Local intra-articular steroid injections Disease modifying agents Hydroxychloroquine Salazopyrine Penicillamine Gold Methotrexate Azathioprine Luflunomide Cyclophosphamide, Cyclosporine Anti TNF agents eg Adalimumab (Humira), Etanercept (Embrel), Infliximab Non-drug treatments Physiotherapy Physical treatments Surgery Coping strategies Gout Gout Crystal deposition Negatively bi-refringent sodium monouric crystals in joints, bursa, tendons and kidney Not always associated with hyperuricaemia Stages of Gout 1. Acute Gout 2. Inter critical periods 3. Chronic tophaceous Gout Treatment of acute attack One of the most painful conditions known NSAIDS Colchicine (main s/e diarrhoea) Steroids Long term management Uricosuric agents - Allopurinol 100mg od increasing to 300mg od MOA: Xanthine oxidase inhibitor 2-3 weeks after acute attack initiation may precipitate an acute attack Gout in Older People Association with thiazide diuretics Increased toxicity to Allopurinol