* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CPR and First Aid ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
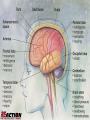
RULE NUMBER 1: DON’T PANIC! RULE NUMBER 2: CALL 911! RULE NUMBER 3: DO NOT TOUCH BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS UNLESS PROTECTED! RULE NUMBER 4: REMEMBER RULE NUMBER 1! Should You Drive or Call Ambulance? Ask these questions: Does the persons condition appear to be life threatening? Could their condition worsen? Could moving the person cause more injury? Questions cont- Does the person need the attention or equipment that first responders provide? Would traffic conditions cause a delay in getting to the hospital? Why people fail to get involved 1. Afraid of law suits 2. Afraid of doing something wrong 3. Afraid of cooties A LAYPERSON HAS NO LEGAL DUTY TO HELP A VICTIM. IF YOU DECIDE TO OFFER HELP, YOU ARE COVERED UNDER THE GOOD SAMARITAN LAW, WHICH WILL GENERALLY PROTECT YOU FROM LIABILITY, AS LONG AS YOU: ACT IN GOOD FAITH. ARE NOT RECKLESS OR NEGLIGENT. ACT AS A PRUDENT PERSON WOULD. DO NOT EXCEED YOUR SCOPE OF TRAINING. LATEX GLOVES. (P.P.E.). BANDAGES / DRESSINGS. FACE SHIELD/POCKET MASK. ICE PACKS. SCISSORS / TWEEZERS. ANTISEPTIC. TAPE. BLEEDING CONTROL. SEIZURES. DIABETES. FALLS / FRACTURES. SYNCOPE / FAINTING. ALLERGIC REACTIONS. BURNS. CPR / AED Blood Borne Pathogens Diabetes Breathing difficulties Fainting Seizures Heart Attacks Strokes Allergic Reactions Shock *Sprains / Strains *Lacerations *Fractures *Amputations *Shock *Burns 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) RECOGNIZE AN ILL OR INJURED PERSON. ASSESS THE SCENE FOR SAFETY. DON’T PANIC! ASSESS THE VICTIM. ALERT EMS! 6)ATTEND TO THE VICTIM: CHECK ABC’S. EXAMINE THE PATIENT. CHECK FOR BLEEDING. TREAT THE VICTIM. ASK BYSTANDERS. 7) REMAIN WITH THE VICTIM. ARE YOU TAKING ANY MEDS? DO YOU HAVE ANY ALLERGIES? DO YOU HAVE ANY MEDICAL PROBLEMS? WHAT HURTS? MEDIC ALERTS! 29 CFR 1910.1030 Originally issued December 6, 1991. Places responsibility for protection of personnel on to the employer: Mandatory in-service training. Work practice controls/engineering controls. Incident reporting/treatment protocols. Hepatitis B vaccinations. Disease Producing Organisms Virus Generally only live inside the cells of another organism Bacteria Capable of living outside the cells of another organism Parasite Live within a host and feed upon it Fungus Generally live on the outside of a host Infectious disease Caused by micro-organisms Not transmissible from person to person Communicable disease Caused by micro-organisms May be transmitted from person to person Direct Transmission Contact with the blood or body fluids directly from another person Indirect Transmission Contact with blood or body fluids or micro-organisms on an object Modes Of Transmission Food borne Ingested by eating or drinking Air borne Droplets inhaled Blood borne Piercing of the skin barrier Contamination of mucous membranes Mucous Membranes Eyes Nose Mouth Vagina Anus AIDS – The Process HIV enters body and attaches to the T-cells. HIV reprograms T-cells to produce more HIV. T-cells produce HIV until they burst and spread more HIV. New HIV seeks out more T-cells. AIDS Stages HIV Primary Infection (Asymptomatic) From infection to symptoms – up to 10 years HIV (Symptomatic) From symptoms to specific T-cell count (200 cells per micro-liter) AIDS From specific T-cell count (200 cells per micro-liter) till death AIDS Transmission NOT transmitted by: Sitting next to an infected person Shaking hands with an infected person Eating in public areas Using public restrooms mosquitoes IS transmitted by: Sexual contact Sharing of needles and syringes with infected person Blood transfusion Exposure to blood or body fluid of infected person AIDS – Cure? No known cure at this time Treatments • Anti-viral drugs • Immune system booster drugs • Surgery • Radiation • Other drug treatment Early diagnosis and treatment are the keys to survival Hepatiti s Inflammation of the liver Chronic Acute Leads to cell damage resulting in cirrhosis or cancer Hepatitis Strains HAV Fecal/oral Acute HBV Blood, semen, vaginal fluids Chronic Interferon effective in 35-45% of cases Hepatitis Strains HCV Blood Chronic Interferon is effective in 10-20% of cases Hepatitis – Strains HDV Blood, semen,vaginal fluids Chronic Only infects persons with HBV HEV Fecal/oral Acute Hepatitis Vaccines Hepatitis A Only recommended for persons in the risk groups who are leaving the United States Hepatitis B Offered free to all department personnel Series of three shots Extremely effective, even postexposure Hepatitis – Signs and Symptoms Light stools Dark urine fatigue Fever Jaundice Meningit is There is a viral strain Highly contagious Signs/Symptoms Fever Severe headache Stiff neck Sore throat Children with undiagnosed fever may be meningitis Hazards in the Workplace Cleanliness in station Patient care equipment in station living area Co-workers Body fluids on scenes Sharp objects on scenes Exposure Control Plan Identifies which personnel are at risk Provides procedures for investigation of exposures Provides engineering and work practice controls Mandates Hepatitis B vaccinations and record keeping Outlines post-exposure procedures and record keeping Exposure Control Plan Contains Personal Protective Equipment Gloves Eye protection Respiratory protection Sharps containers Sharps shuttles Sharps boxes Pocket masks Exposure Control Plan Scene Operations Scene control Wash hands No eating, drinking, smoking, etc No recapping of needles CPR Respiratory protection Medical information Exposure Control Plan Post Response Location for cleaning of equipment Disinfection with bleach No eating, drinking, smoking, etc Durable equipment Delicate equipment Exposure Control Plan Post Exposure Report Any Needle sticks Break in skin Splash into mucous membranes Mouth-to-mouth Other exposure To your Immediate Supervisor REMEBER Washing hands and utilizing proper Personal Protective equipment is the best method. If it is not your body fluid, then do not touch it. If exposed wash as soon as possible and use hand cleaner. Skin is largest organ and natural protector keep in tack. DIABETES IS CAUSED BY THE BODY’S INABILITY TO PROPERLY PROCESS SUGAR. THIS IS CAUSED BY A DEFICIENCY IN INSULIN PRODUCTION. SOME DIABETICS TAKE INSULIN SHOTS. THIS ALLOWS THE BODY TO PROCESS SUGAR INTO THE CELLS. ANOTHER TYPE OF DIABETES IS CONTROLLED BY DIET AND / OR ORAL MEDICATIONS. SOMETIMES A DIABETIC MAY NOT EAT ENOUGH AFTER TAKING THEIR INSULIN. THIS CAUSES THE SUGAR LEVEL TO DROP. (HYPOGLYCEMIA) Most Common SINCE THE BRAIN RUNS ON SUGAR, A LOW SUGAR LEVEL WILL CAUSE CONFUSION, OR UNCONSCIOUSNESS. SIGNS & SYMPTOMS INCLUDE: CONFUSION,DIZZINESS, DROWSINESS. FEELING OR LOOKING ILL. ABNORMAL PROFUSE PULSE (RAPID/WEAK). SWEATING. LOOK FOR A MEDIC ALERT TAG! IF THE PERSON IS CONSCIOUS , GIVE THEM FLUIDS CONTAINING SUGAR. WATCH THE PERSON CAREFULLY, THEY MAY LOSE CONSCIOUSNESS OR COME COMBATIVE. IF THE PERSON IS UNCONSCIOUS: CALL 911, AND ENSURE THAT THE PATIENT HAS AN OPEN AIRWAY. MONITOR THE PATIENT. CAUSED BY A TEMPORARY REDUCTION OF BLOOD FLOW TO THE BRAIN. MANY PATIENTS FALL, CAUSING INJURY. SOME CAUSES OF SYNCOPE: STRESSFUL EVENT (SIGHT OF BLOOD). PAIN. HEART DISEASE. SUDDEN SOME STANDING. CAUSES MAY BE SERIOUS! SIGNS/SYMPTOMS PALE INCLUDE: SKIN. NAUSEA. DIZZINESS. SWEATING. VISION DISTURBANCE. TREATMENT: NORMALLY SELF-CORRECTING IN A SHORT PERIOD OF TIME. IF THE PATIENT FALLS, KEEP PATIENT STILL TO INSURE NO FURTHER INJURY. RAISE FEET APPROX. 12” OFF FLOOR SYNCOPE CAN BE A SIGN OF A MORE SERIOUS MEDICAL CONDITION. ANYONE THAT FAINTS SHOULD CONTACT THEIR PHYSICIAN OR BE EVALUATED AT A HOSPITAL. MANY CAUSES, SOME VERY SERIOUS OR LIFE THREATENING. SYMPTOMS INCLUDE: HIVES, SWELLING, SHORTNESS OF BREATH, DECREASED B/P, REDNESS, HOARSENESS. COMMON INSTIGATORS: BEES SHELLFISH MEDICINES PLANTS CALL 911! KEEP PATIENT CALM. BENADRYL EPI-PEN. MAY BE GIVEN. A DISRUPTION OF THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE BRAIN. THIS DISRUPTION CAN CAUSE LOSS OF BODY CONTROL, KNOWN AS A SEIZURE. EPILEPSY: CHRONIC CONDITION THAT CAUSES SEIZURES, CONTROLLED BY MEDICATION. FEVER: CAUSED BY FEVERS >102 DEGREES, USUALLY OCCUR IN CHILDREN < 5 YEARS OLD. PREGNANCY: THESE CAN BE VERY SERIOUS, EVEN LIFE THREATENING! HEAD INJURY: FROM FALLS, MVA’S, ETC. MAY NOT OCCUR UNTIL DAYS AFTER THE EVENT. MENINGITIS: INFECTION. BRAIN TUMORS. “JERKING MOTIONS”; MAY INVOLVE ENTIRE BODY OR JUST A PART OF THE BODY. CONFUSION AFTER THE EVENT. DROWSINESS. INCONTINENCE. EYES ROLLING BACK. REMAIN CALL CALM! 911. CLEAR AREA FROM AROUND THE PATIENT, TO PREVENT INJURY. PROTECT FLOOR. PATIENTS’ HEAD FROM THE DO NOT PLACE ANYTHING IN THE PATIENT’S MOUTH! THE PATIENT MAY BE VIOLENT! THIS CANNOT BE HELPED, BE CAREFUL! WHEN THE SEIZURE STOPS, POSITION THE PATIENT ON THEIR SIDE. REMEMBER! MANY INDIVIDUALS THAT HAVE SEIZURES FALL AND INJURE THEMSELVES. TRY NOT TO MOVE THE PERSON ANYMORE THAN NECESSARY. • Causes Asthma Emphysema COPD Bronchitis Hyperventilation Most individuals that have chronic breathing problems carry an inhaler or other prescribed medications. Most are metered doses and only work after 1 or 2 sprays. Place Do not agitate / argue. Give If patient in position of comfort. oxygen if allowed and possible. unconscious check ABC, Start CPR Also known as MI’s, (Myocardial Infarctions) MEN: chest pain sweating shortness of breath pain in arms, jaw, neck, back WOMEN: indigestion unusual fatigue weakness possibly chest / back pain shortness of breath CARE CALL 911, DO NOT HESITATE! PLACE PT. IN POSITION OF COMFORT. OBTAIN HISTORY (ASPIRIN)? GIVE OXYGEN IF AVAILAE AND QUALIFIED. BE PREPARED FOR CPR / AED. Stroke: Any vascular injury to the brain Also known as “cerebrovascular accident” (CVA) 80% are ischemic (blockage) 20% are hemorrhagic (bleeding) (ruptured aneurysm, trauma 750,000 strokes per year in the United States 4,000,000 stroke survivors in the US #1 cause of disability #3 cause of death (#2 World) Major Risk Factors Risk Factor Prevalence HTN 35% Heart Disease 10 – 20 % Previous CVA 2% Carotid Bruit 4% Diabetes Smoking 4-6% 25% Bleeding into the subarachnoid space Commonly results from aneurysmal rupture Rapid onset of symptoms Results in severe sudden headache due to marked increase in pressure around the brain Weakness Unable to walk Unable to talk Dizzy Numbness Found down Confused ANY OF THESE COMPLAINTS COULD BE A STROKE! PLACE PT. IN POSITON OF COMFORT. CALL 911 BE PREPARED DO CONDUCT CPR CONDUCT STROKE ASSESMENT PTS. MAY BE CONFUSED, A-B-C SAMPLE HISTORY VITALS DURATION OF SYMPTOMS MONITOR AIRWAY O2 IF INDICATED IMMOBILIZE ? 911! ARTERIAL BLEED (SPURTS) CAPILLARY BLEED VENOUS BLEED (DRIPS) (OOZES) PPE! DIRECT PRESSURE. ELEVATION. PRESSURE BANDAGE. PRESSURE POINTS. TOURNIQUET. USING A 4X4 DRESSING, PINCH BOTH NOSTRILS AND LEAN PATIENT FORWARD. SOME NOSEBLEEDS CAN BE SEVERE, AND SHOULD BE EVALUATED BY A PHYSICIAN. VARIOUS CAUSES. THE PATIENT WILL BE VERY DISORIENTED, CONFUSED, AND TIRED. THIS IS NORMAL, AND USUALLY GOES AWAY IN A SHORT TIME. SOME BLEEDING MAY BE SEEN FROM THE MOUTH. Approximately 8000 people die each year from choking. Someone choking needs immediate attention or they will go unconscious and need CPR. Ask can you speak? If so encourage to cough and prepare to give abdominal thrust (Heimlich Maneuver). Stand behind patient, place hands just above belly button and give 5 quick thrusts inward and upward. After 5 thrusts an object has not expelled continue until object is freed or pt. goes Unconscious. When pt goes unconscious Lower to the floor an start cycles Of CPR. Looking in the Airway after compressions Make sure 911 has been called CLASSIFIED 1ST AS: DEGREE / SUPERFICIAL. (SUNBURN) 2ND DEGREE / PARTIAL THICKNESS (BLISTERS, VERY PAINFUL.) 3RD DEGREE / FULL THICKNESS (SKIN DESTROYED, MAY BE PAINLESS!) ENSURE SCENE SAFETY! REMOVE DO PATIENT FROM SOURCE! NOT BECOME A VICTIM YOURSELF! CALL 911! CHEMICAL BURNS: FLUSH THOROUGHLY WITH WATER, AWAY FROM THE PATIENT. IF EYES INVOLVED, FLUSH WITH COPIOUS AMOUNTS OF WATER. FOR THERMAL BURNS, COOL AREA WITH WATER AND WET CLOTHS. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: DEFORMITY. SWELLING / DISCOLORATION. PAIN. INABILITY BONE TO MOVE INJURED AREA. EXPOSED. TREATMENT: IMMOBILIZE AREA TO STOP MOVEMENT. ELEVATE THE ICE EXTREMITY. PACKS. WATCH FOR SHOCK. 2005 American Heart Association Guidelines: A cycle of CPR is Infant…………0-1yr. 2 minutes or 5 Child………….1-8 yrs cycles of 30:2 Adult………….8yrs > Compression Rates / Ratios: Compressions 100 per minute at a ratio of 30:2 infants, children, and adults. Compression depths; 1/3 to 1/2 the chest thickness for infant, 1” to 1 ½ for a child, and 1 ½ to 2” for an adult depending on size of patient. Determine unresponsiveness, if infant and child perform 2 minutes of CPR prior to calling 911 if alone. Adult; determine level of responsiveness, call 911, then start the cycles of CPR if needed or place in recovery position, and wait for emergency crews. Get AED if available. If AED available and patient was witnessed going into cardiac arrest place AED on patient immediately, if unwitnessed arrest, conduct 2 minutes or 5 cycles of CPR prior to placement of AED. Do not place pads on a conscious patient only having chest pains. If in cardiac arrest; open unit, place pads in designated location, turn on unit, and follow prompts, if no shock continue CPR for appropriate time, AED will count down, reanalyze and indicate shock or no shock, continue CPR. If AED indicates shock, clear patient and press shock button. ??QUESTIONS??