* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Joint Injections in Primary Care
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
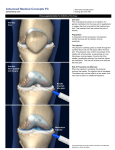
Joint Injections in Primary Care Marc A. Aiken, MD Watauga Orthopaedics Objectives • Understand when it is appropriate to inject /aspirate a joint • Review common injection medications • review pertinent anatomy for safe injection technique • Review technique for injections in most common joints • When to refer The Most Common Joints Injected • Knee • Shoulder (glenohumeral jt.) • Shoulder (subacromial bursa) Indications Diagnostic • Evaluate fluid aspirate for: • Infection • Inflammatory arthropathy • Trauma • Relief of pain immediately following injection indicates an intraarticular source Indications Therapeutic • Relief of pain/inflammation caused by: • Effusion • OA, RA, Gout • Bursitis • Selected tendonopathies Absolute Contraindications • Local cellulitis • Prosthetic joint • Septicemia • Acute fracture • Patella and achilles tendonopathy • Allergy to injection medications Relative Contraindications • Anticoagulated/coagulopathic patient • Diabetes • Immunocompromised patient • Minimal or no relief with 2 prior injections • Local osteoporosis • Inaccessible joints Medications • Corticosteroid • Local anesthetic • Hyaluronic acid Steroid • Betamethasone (Celestone Soluspan) • Agent of choice in my practice • Long acting • 6-12mg for large joint (knee, shoulder) • 1.5-6mg for small/intermediate joints Other Steroids • Triamcinolone (Aristospan) • Dexamethasone (Decadron) • Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol) Local • 1% Lidocaine (Xylocaine) without epi • useful for intraarticular injection and subcutaneous injection when aspirating • onset within minutes • can be diagnostic tool Local • Bupivicaine (Marcaine) • Potential cause of chondrocyte death • Avoid intraarticular use Hyaluronic Acid • “Lube job” for the knee • Replaces HA deficient arthritic knee fluid with thick viscous HA. • Expect 6 months of relief • Given in 3 injections 1 week apart • Relief may not be obtained for up to 8wks following last injection. Reactions/Complicati ons • 2-5% - Post injection (steroid) flare • 0.8% - Steroid arthropathy (AVN, Chondrolysis, etc.) • Iatrogenic infection • Flushing • Skin atrophy and depigmentation Reactions/Complicati ons • Loss of glucose control in DM • Increased appetite • Insomnia • Irritability General Considerations • Evaluate the patient • Patient education • Consent • Patient Comfort • Sterile preparation and technique • Documentation Evaluate the Patient!! • Avoid the “Knee hurt....me inject” mentality. • Get a complete history • Examine the patient including other joints • Obtain x-rays • MRI only if appropriate Patient Education • What medications are being used • What is the injection expected to do for them • What it is not expected to do • When they will notice effects of injection • What if the expected results are not achieved Consent • Written Vs. Verbal • Your choice Patient Comfort • Lying down for knees (superolateral approach) • Sitting up for shoulders • Take your time • Use ethyl chloride (cold spray) immediately before injection • Explain the steps of the procedure as you do them • Patient Comfort • In patients with severe anxiety regarding needles, provide alternatives or allow them to schedule the injection on a different date. This may allow them time to mentally prepare for the injection. • Injections are usually far less painful than patient anticipate Sterile Prep/Technique • Make sure injection site is fully exposed • Should not be visibly soiled • Use iodine or chlorhexidine prep over site to be injected • Alway use aseptic technique • Consider use of sterile gloves • Sterile drapes generally unnecessary Documentation • Document the history and physical exam findings that support the decision to perform aspiration/injection • Site (which joint and which side) • Anatomic placement (med, lat, ant etc) • medications and doses injected • Expiration dates and lot numbers Document • Amount of fluid aspirated • color, clarity and viscosity of fluid • purulent? • Blood? (trauma) • Lipid?(trauma/occult fx) Send Fluid for Analysis • Labs ordered from fluid: • Cell Counts (stat if infection suspected) • Cultures • Gram stain (stat) • Polarized light microscopy Post Injection Care • Remove visible prep solution • Bandaid • Pressure dressing on free bleeders • Rest and Ice for 24 hours • Warn about limitation of local anesthetic • Warn about steroid flare Injection Technique • Intraarticular knee • Intraarticular Shoulder • Subacromial bursa Supplies Knee Aspiration/Injection • Superolateral approach most reliable • 93% accuracy vs. 71-75% with bent knee anteromedial/anterolateral approach Superolateral Approach • • Patient Supine with knee extended Palpate bony landmarks • • Patella Lateral Femur Palpate Patella X Marks the Spot • • Palpate lateral border of patella and Lateral femur at the PF joint The space between these bony structures is your injection site The Injection • • • Reassure patient Relaxed quads = more space at PF jt Needle Trajectory • • 15-20 degrees Toward trochlea of femur Needle Trajectory Anterior Approach (bent knee) Anterior Approach • Less reliable/accurate than superolateral approach • Can be easier in the obese knee • Patient sitting with knee bent to 90 degrees Anterior Approach • Palpate landmarks • Inferior pole of patella • Patella tendon • Tibial Plateau Landmarks - Patella Landmarks - Plateau Landmarks Injection Site • • • • May inject medial or lateral to patella tendon 1cm above tibial plateau or Half the distance from plateau to inferior pole of patella Trajectory of needle should be toward intercondylar notch Trajectory Shoulder (GH joint) • Anterior approach • Position patient sitting facing provider • Palpate bony landmarks • Clavicle • Coracoid Landmarks Palpate - Clavicle Clavicle Coracoid Needle Placement • • • Inject just lateral to coracoid process 20 degree angle Reposition if you encounter resistance Shoulder (SA Bursa) • Given lateral or posterior • Just beneath the angle of the acromion Acromion Subacromial Injection • Direct needle under acromion Questions?