* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
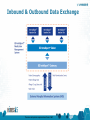
Smart Device Integration Improved Documentation Accuracy in Anesthesia DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily represent official policy or position of HIMSS. The views and opinions expressed are those of BD Documentation Causes 16% of Injectable Medication Errors 1 IMSP high alert medication list, IMS data 2 Weigner et al, 1994 The views and opinions expressed are those of BD Case Study #1: Unintentional Misdocumentation Example: Rocuronium Administration Data Inaccuracies Situation: Challenge: Desired Solution: • Hospital was meticulous in assessing muscle relaxant use. • Received daily report of all cases with the use of drugs like Rocuronium, as well as monitoring used. • Hospital was certain a drug like Rocuronium was given, but nothing was logged in Epic. • Believed if this was happening with one drug, it was happening with many more. • Ability to see an injected drug was logged in Epic and billed. The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 3 Case Study #2: Unintentional Misdocumentation Example: Retrospective Charting During Emergencies Situation: Challenge: Desired Solution: • Despite implementing an AIMS, difficult to defend anesthesiologists’ actions during adverse events. • Caused by incomplete retrospective charting that occurs during emergencies. • Inappropriate for clinicians to divert their attention from the patient to charting while emergency is occurring. • Effective solution to assure the reliable and accurate documentation of intravenous medications for use during emergency situations. The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 4 Case Study #3: Patient Safety Risk Identification Example: Prophylactic Perioperative Antibiotic Dosing • Higher than expected surgical site infections (SSIs) despite anesthesia records suggesting strong compliance with intraoperative intravenous antibiotics. • The Infection Control Committee felt this was due to failures to give perioperative antibiotics at the appropriate time. • In some cases, the Committee felt a different antibiotic would have decreased the likelihood of the SSI. • A more reliable and accurate method of capturing intravenous antibiotic dosing. • Decision support that recommends the most appropriate antibiotic regimen at the time of pre-incision administration. Situation: Challenge: Desired Solution: The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 5 Overarching Documentation Challenges Medication administration data entry is largely a manual and tedious process within the Anesthesia workflow • Data inconsistencies between medications administered and documented • Retrospective documentation during emergencies • Limited narcotic auditing and decision support solutions • Complex legacy HIT systems with limited integration capabilities The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 6 The Solution • A new class of device is being brought to market for automating the electronic capture of IV injectable drug data. • These devices are similar to infusion pumps: – They provide integration with hospital IT systems, – Offer improved clinical workflows and – Real-time patient safety checks for IV drug delivery. • At the same time, they are sufficiently different from infusion pumps to warrant an independent device classification. 7 The views and opinions expressed are those of BD The BD Intelliport™ System A medication management solution for IV bolus injections that may help manage the risk of medication errors and improve documentation accuracy. 8 The views and opinions expressed are those of BD Aligned with APSF Recommendations APSF Recommendations: “Every anesthetizing location should have a mechanism to: 1. Identify medications before drawing up or administering them (bar code reader) and a mechanism to 2. Provide feedback, decision support, and 3. Documentation (automated information system).” BD Intelliport™ System Features: Identifies source container drug name and concentration via barcode scanning Automatically identifies drug name and concentration Audibly announces drug and concentration Performs real-time, patient-specific allergy checking with audible alerts Captures real-time drug identification and dose measurement data Captures time given Wirelessly sends medication administration data directly into the patient’s EMR The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 9 Designed for Standards-Based Interoperability • BD Intelliport™ Gateway was architected from the bottom-up to support Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise’s (IHE) PCD-01 Profile • Utilizes common HL7 messaging structures for inbound and outbound interfaces • Integration has been, or is in the process of being, developed with the following IT partners: The views and opinions expressed are those of BD Inbound & Outbound Data Exchange 11 The views and opinions expressed are those of BD Improved Documentation Accuracy via Smart Device Integration Documentation Challenges: BD Intelliport™ System: Documentation data inaccuracies Retrospective documentation during emergencies Limited decision support solutions Automatic documentation that • reduces manual documentation efforts, • improves documentation accuracy and • eases charge capture by wirelessly sending information on drug, dose, time, and route of administration directly into the patient’s EMR. Automated med administration data collection that • can help support assessment of some National Quality Hospital Measures, such as Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP). Controlled substance reporting that • aids anesthetists and pharmacists with med reconciliation. The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 12 Thank you The views and opinions expressed are those of BD 13