* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Strengthening Health Systems for Chronic Care and NCDs
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Preventive healthcare wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
HIV and pregnancy wikipedia , lookup
Patient safety wikipedia , lookup
Long-term care wikipedia , lookup
Diseases of poverty wikipedia , lookup
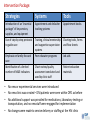
Strengthening Health Systems for Chronic Care and NCDs: Leveraging HIV Programs to Support Diabetes Services in Ethiopia Zenebe Melaku, ICAP Ethiopia Ahmed Reja, Ethiopian Diabetes Association Miriam Rabkin, ICAP Columbia University Making the HIV-NCD connection • In many resource-limited countries, HIV scale-up has created the first national chronic disease program. • In these same countries, the burden of other chronic diseases, including NCDs such as diabetes, is high and growing rapidly. • We conducted a rapid proof-of-concept study to explore the feasibility of adapting HIV-specific resources for use in a DM program at Adama Hospital in Ethiopia. • Following a baseline assessment, we adapted key strategies, systems, and tools originally developed for the Adama HIV clinic, and introduced them into the OPD for use with adult DM patients. A follow-up assessment was conducted after six months. Intervention Package: Strategies Systems Tools Introduction of an “essential package” of key services, supplies, and equipment Appointment and defaulter tracking systems Appointment books Use of step-by-step protocols to guide care Training, clinical mentorship and supportive supervision systems Charting tools, forms and flow sheets Emphasis on family-focused care Peer educator programs Job aids Identification of a limited number of M&E indicators Chart review/quality assessment conducted and used by clinic staff Patient education materials • No new or experimental services were introduced • No new clinic was created – DM patients were seen within OPD as before • No additional support was provided for medications, laboratory testing or transportation, and no new staff were engaged for implementation • No changes were made to service delivery or staffing at the HIV clinic % of charts with service documented Services offered and documented at least once in the past 3 visits (n = 260 patients) 100% 90% 82% 80% 82% 81% 80% 81% 77% 74% 70% 60% 45% 50% 56% 50% 49% 40% 30% 17% 20% 10% 2% 1% 3% 3% 6% 4% 5% 2% 0% Weight Blood pressure Fundoscopic Foot exam Neurologic Oral/dental Assessment DM Next Medication exam exam exam of visual education appointment adherence acuity provided documented assessed Baseline Follow up Six-month outcomes included: • Marked increase in documented service delivery with no added staff; • Expansion of services to include peer education and point-of-service DM screening for patient family members; • Rapid improvement in standards of care.