* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Etiology of Caries 2004
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
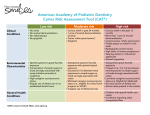
CAMBRAtm a New System CAMBRA, LLC. (CONFIDENTIAL) V. Kim Kutsch, DMD. Doug A. Young, DDS. MS. The Problem Dental caries is a bacterial infection that is expressed by symptoms (cavities), for which there is no system for the screening, risk assessment, diagnosis and treatment of. Goal To create a plug and play system to accurately screen, assess, diagnose and treat the bacterial infections that causes dental caries. Etiology of Caries 2004 • Caries: an infectious microbiological disease of the teeth that results in localized dissolution and destruction of calcified tissues. It is a bacterial infection of Mutans streptococci and Lactobacilli. Mutans streptococci A pandemic infection in humans most strongly associated with the onset of enamel caries. CM Sturdevant 1995 Classifies caries into pit and fissure, smooth surface and root surface lesions with different rates of progression and morphology. Pit and fissure caries have a small site of origin but a wide base at the DEJ. Initial cavitation of the fissure walls cannot be seen on the occlusal surface making these lesions more difficult to detect. John Featherstone 2003 The Caries Balance “It is very useful and constructive clinically to consider caries in its progression or reversal as an ongoing and often changing balance between pathologic factors and protective factors.” Dr. Steven M Adair “Dentistry must begin reorienting its approach to caries from a primarily surgical approach to a medical-management approach. Dental caries is a steady-state disease with a variable expression over time. A surgical approach to a steady-state disease is inefficient, creating a constant state of playing “catch-up”.” Caries Risk Assessment 2004 Risk is defined as the probability that some harmful event will occur. Caries risk assessment is the calculation of of whether new carious lesions will occur or incipient lesion will develop. GV Black, 1924 “The idea that dental practice is purely mechanical and not dependent upon knowledge of the pathology of dental caries, should be abandoned forever. It is an anomaly of science that should not continue. It has the tendency plainly apparent to make dentists mechanics only.” JDB Featherstone, 2003 “With so much disease, it is easy to get caught up in an endless treatment cycle to “fix” the problem using traditional surgical restorative approaches.” Paradigm Shift Dental caries as an infectious disease model involves focusing on treatment of the entire disease process not just surgically treating cavities. “The primary goal of operative dentistry is to maintain primary oral health, defined as the absence of disease of the teeth, periodontium and mucosa.” Lutz F, Krejci I. Resin composites in the post-amalgam age. Compendium December 1999. 20(12):1138-1148. Dental Caries is an Infection! “Dental caries can be considered an infection, caused by the colonization by Mutans Streptococci.” Martens L, Surmont P, D’Hauwers R. A decision tree for the treatment of caries in posterior teeth. Quintessence Intl March 1990. 21(3):239-246. “Dental caries is an infectious and transmissible disease. Detailed knowledge regarding the acquisition and transmission of infectious agents facilitates a more comprehensive approach to prevention.” Berkowitz RJ. Acquisition and transmission of mutans streptococci. JCDA February 2003. 31(2):135-138. “The appearance of mutans streptococci in the pits and fissures is usually followed by caries 6-24 months later”. Sturdevant CM. The Art and Science of Operative Dentistry Third Ed. 1995, Mosby. “Caries risk assessment should be one of the most important goals of the child’s initial dental examination.” Fadvai S. Management of early childhood caries. General Dentistry Jan-Feb 2003. 51(1):38-40. Caries Risk Assessment • • • • • • Medical history Dental history and exam Homecare habits Dietary habits Saliva rate / buffering capacity CRT score Medical History • Medications reducing salivary flow • Medications with sugar base • Mental or physical handicaps Dental History & Exam • • • • • DMF score Recare visits / last prophy Fluoride use Existing active lesions Plaque index Homecare Habits • Brushing/flossing habits • Fluoride rinses Dietary Habits • • • • • Timing of sugar intake Frequency of sugar units Type of sugar units Chewing gum Pepsi generation “Cola soda consumption increased from 22.2 gal/yr. in 1970 to 56 gal/yr. In 1999. The average 12-19 year old drinks 28 oz/day.”.” Chase WD. Dentistry takes a hard look at soft drinks. Dentistry Today September 2001. 20(9):32. “This increase in soft drink consumption has been paralleled by increasing rates of obesity in children and reports of rampant tooth decay.” Shenkin JD, Heller KH, Warren JJ, Marshall TA. Soft drink consumption and caries risk in children and adolescents. General Dentistry JanFeb 2003. 51(1):30-36. “Daily between meal consumption of soft drinks three or more times a day increases the risk of dental caries by 179%.” Ismail AI, Burt BA, Eklund SA. The cario-genicity of soft drinks in the United States. JADA 1984. 109:241-245. Saliva • Buffering capacity – pH 5 - 7 is normal – pH < 5 is low • Rate of flow: – < 0.7 ml/minute is high risk – 0.7 - 1.0 ml/min is moderate risk – > 1.0 ml/min is low risk/normal CRTbacteria • MS, Lactobacilli CFU/ml saliva – < 105 CFU/ml is low risk/normal – 105 CFU/ml is moderate risk – > 105 CFU/ml is high risk Salivary and tongue levels of Mutans Streptococcus correlate well with plaque levels. Tanzer JM. Salivary and plaque microbiology tests and the management of dental caries. J Dent Ed. 61:866-874. Vivadent CRTbacteria Vivadent Cultura Oven CRT Materials CRT Analysis Low Risk Patient Not taking medications that affect saliva, regular check-ups, no cavitations, good homecare, limited sugar intake, saliva flow >1 ml/min, pH 7, CRT < 105 CFU/ml. Moderate Risk Patient Not taking medications that affect saliva, fairly regular check-ups, no cavitations, average homecare, some sugar intake, saliva flow 0.7-1.0 ml/min, pH 5-7, CRT 105 CFU/ml. High Risk Patient May be taking medications that affect saliva, infrequent check-ups, at least 1 cavitation, poor homecare, frequent sugar intake, saliva flow <0.7 ml/min, pH <5, CRT > 105 CFU/ml. Extreme Risk Patient May be taking medications that affect saliva, no check-ups, several mandibular anterior cavitations, poor homecare, frequent sugar intake, saliva flow <0.5 ml/min, pH <5, CRT >> 105 CFU/ml. Treatment Protocols Classify the patient as low, moderate, high or extreme risk for dental caries. Base treatment on caries risk assessment. “Antibacterial therapy must be used to combat high bacterial challenge. Preventive factors must outweigh the pathological factors.” Featherstone JD. The science and prevention of caries. JADA 2000 July. 131(7):887-99. “At age 5, the DMF in the xylitol group was 70% lower than the fluoride or chlorhexidine group.” Isokangas P, Soderling E, Pienihakkinen K, Alanen P.Occurrence of dental decay in children after maternal consumption of xylitol gum. J Dent Res 2000 Nov. 79(11):1885-9. “In this study glass ionomer with fluoride showed superior antibacterial action compared to pit and fissure sealant resins.” Kozai K, Suzuki J, Okada M, Nagasaka N. In vitro study of antibacterial activities of sealants and glass ionomers. ASDC J Dent Child 2000. Mar/Apr 67(2):117-22, 82-3. “Iodine is among the most potent of bactericidal agents. Its effect is not time dependent; once bacterial contact is made, its action is immediately lethal.” DenBesten P, Berkowitz R. Early childhood caries: an overview with reference to our experience in California. JCDA February 2003. 31(2):139-143. Recaldent: CPP-ACP • CPP: Casein Phosphopeptides – Milk protein – Protects the ACP component – Delivery vehicle, very sticky ACP Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Functions: Remineralization/Desensitization Fugi Triage – new class of glass ionomer • Light initiated chemical cured – – – – Absolutely no resin Highest Fl release Limit bacterial growth Ca and Fl from saliva diffuse through – Fl and Sr available from Triage material – Allows enamel maturation while protecting “Long term caries pathogen suppression is feasible with current products, can result in significant caries inhibition.” Hildebrandt GH, Sparks BS. Maintaining MS suppression with xylitol chewing gum. JADA 2000 July. 131(7):909-16. Low Risk Patient • Maintain primary oral health • Counsel patient about risk factors • Monitor risk factor changes Moderate Risk Patient • Direct counseling to specific risk factors as appropriate • Treat bacterial infection • Monitor infection control until CRT is < 105 MS CFU/ml saliva • Fluoride therapy to remineralize any decalcification areas High Risk Patient • Direct counseling at appropriate risk factors • Restore cavitated lesions, treat bacterial infection • Treat until CRT is < 105 MS CFU/ml, check monthly • Monitor CRT annually Extreme Risk Patient • Direct counseling at appropriate risk factors • Treat bacterial infection first • Treat until CRT is < 105 MS CFU/ml, check monthly • Then restore cavitated lesions with GIC • Monitor CRT annually Insurance Re-imbursement • CDT III Codes – D0415 Bacteriology studies – D0425 Caries susceptibility test • CDT IV Codes – D0415 Bacteriology studies – D0425 Caries susceptibility test • Medical Codes CPT Cariogram Malmo University Previser Caries/perio Risk Assessment: www.previser.com Internet Cariology Sites http://www.cdafoundation.org http://www.wcmicrodentistry.com http://www.db.od.mah.se/car/carhome.html http://www.dentistry.uic.edu/courses http:/www.dent.ucla.edu.com National Institute Health Library Google>Pubmed or Medline>NIHL “He needed immediate caries control to maintain his dentition. However this would not have left him with sufficient tooth structure to build on so full coverage IPS Empress crowns were the only possible restorative option.” Myles W. Aesthetic dentistry: it’s more than meets the eye. Aurum Ceramics News. Feb 2002. 6(1):8. “The overall objective of this document is to provide the basis for a cross-disciplinary approach among medicine, dentistry, nursing, and other agencies that affect dental health to reduce or eradicate dental caries in children in every county, community and culture in California by the year 2010.” Featherstone JDB, et al. Caries Management by risk assessment: consensus statement, April 2002. JCDA March 2003. 31(3):257-269. The Solution CAMBRAtm, a New System By CAMBRA, LLC System Components • • • • Screening Test Risk Assessment Form Bacterial Culture Antimicrobial Treatment – Therapeutic Rinse – Daily Maintenance Rinse Component A: Screening Test • ATP Bioluminescence • Non-specific bacterial and somatic ATP levels RLU’s from mouth at rest, selecting swab for two teeth surfaces • Somatic ATP presence • MS ATP levels? • Correlation between non-specific ATP levels and CRT bacterial cultures • Real time (15 second ) inexpensive test for identifying high risk from low risk individuals Hygenia ATP Bioluminescence • • • • $800 retail? handheld light meter $1.75 ?retail per swab disposable 15 second real time test results Identify with high sensitivity and specificity for high vs. low risk caries patients • Needs university based clinical trial validation UOP with Dr. Doug Young Market Potential • Dentistry is 80 B annual industry • 300,000,000 dental check-ups per year • Argument could be made as standard of care for screening test and caries risk assessment to be performed at each check-up appointment • Total market size could be 300M tests/year • Need to establish as standard of care Strategic Plan First Year • Beta test with 10-20 clinical trial sites at Rendezvous complete June 2005 • 300-500 procedures in Beta test • Introduce to 300 dentists at WCMID • 3,000-5,000 procedures in Q3 and Q4. • Introduce at 5 California Dental Schools • Introduce to all 50 dental schools December • Introduce to early adopters (6-10,000 dentists) Component B: Risk Assessment Form Clinical Validated CAMBRA Form Adopted by VKK from Featherstone CAMBRA Form • Updated form weighing high, moderate and low risk factors • Clinical validation • Indicates Bacterial culture for high risk patients Component C: Bacterial Culture Rapid culture for MS CAMBRAcult • • • • • Rapid culture specific for MS 3-24 hours Color change indicator? Validates diagnosis of clinical caries Identifies individuals for therapeutic rinse regimen followed by maintenance rinse Component D: Therapeutic Oral Rinse Active antimicrobial treatment to eliminate MS infection CAMBRA Therapeutic Rinse • Two component rinse for short term antimicrobial treatment of MS infection • Sodium Hypochlorite active ingredient • Additional components include: fluoride 0.5%, polyphenols, xylitol CAMBRA Maintenance Rinse • Daily use to prevent MS numbers from returning to >105 CFU’s • Single component oral rinses • Active ingredients: polyphenols, fluoride, xylitol, anthocyanidins CAMBRA Decision Tree Component A Screening test: positive negative Component B Component C CAMBRAcult Positive CAMBRA Risk Assessment Form Positive Negative Negative Component D Therapeutic Rinse Maintenance Rinse Component C CAMBRAcult Positive Negative Recare Appointment USA Dental Demographics • • • • • 170,000 dentists in USA (primary market) 150,000,000 patients in USA 14 year adoption curve in dentistry Early adopters account for 6-10,000 dentists Typical J-curve adoption sequence with chasm between early adopters and early majority Market Potential • Dentistry is 80 B annual industry • 300,000,000 dental check-ups per year • Screening test could be performed at each re-care appointment • Bacterial culture could be recommended in 25% of visits, or 75 M procedures • Need to establish as standard of care CAMBRAcult Market Potential by Dollars • Dentistry is 80 B annual industry • 75 M procedures for CAMBRAcult per year at 6-10 per procedure • At $6 per procedure = $4.5 M • At $10 per procedure = $7.5 M CAMBRAcult Market Potential by Dentist • • • • 170,000 Dentists in US 30 check-ups per week times 50 weeks per year 255,000,000 dental check-ups per year Screening test could be performed at each recare appointment • Bacterial culture could be recommended in 25%, or 65 M procedures • Procedure will be performed twice on the high risk patients or 130 M procedures CAMBRAcult Market Potential by Patient • 150,000,000 patients in US (50% of population) two check-ups per year • 300,000,000 dental check-ups per year • Screening test could be performed at each recare appointment • Bacterial culture could be recommended in 25% of visits, or 75 M procedures • Procedure will be performed twice on high risk patients for 150 M procedures Strategic Plan • Beta test with 10-20 clinical trial sites at Rendezvous • Validate clinical trials at UOP/Young • Introduce to 300 dentists at WCMID • Introduce to CAMBRA Coalition, significant thought leaders, influencers (Featherstone, Christensen, CRA) • Introduce at 5 California Dental Schools • Introduce to all 50 dental schools • Introduce to early adopters (6-8,000 dentists) Additional Strategy Issues • Patent protection for system, trademarks for CAMBRA • Short term market strategies around early adopters • Establish as standard of care in 5 California schools, then broaden to all US schools. • Establish as standard of care in California • Year two attack foreign markets, AU, NZ, EEU, dental schools and early adopters Strategic Plan First Year • Beta test with 10-20 clinical trial sites at Rendezvous complete June 2005 • 300-500 procedures in Beta test • Introduce to 300 dentists at WCMID • 3,000-5,000 procedures in Q3 and Q4. • Introduce at 5 California Dental Schools • Introduce to all 50 dental schools December • Introduce to early adopters (6-8,000 dentists) Q1 2006 through DentalTown Strategic Plan Second Year • Introduce to early adopters in California 2,000 dentists • 100 CAMBRAcult procedures per dentist per year • 500 Screening swabs per dentist per year • 200,000 cultures, 1,000,000 screening swab procedures in Year Two • At $15 per procedure = $3.0 M retail Marketing Focus: California • Legal standard of care since July 2004 • 22,000 dentists in California; 2,000 early adopters • Education DVD to market system to dentists in California • Support education with programs at major meeting CDA Anaheim and San Francisco • Advertise in CDA journal Dental Schools • By creating a standard of care issue in the dental schools: dental students we may be able to short circuit the 14 year adoption rate • Need to make standard of care in the mind of 4500 annual dental school graduates • Still a mission/education sell to the market at large, needs to be a simplified system that is plug and play Initial Kit Components $1,500 Target Retail • Screening Test: Light meter/200 swabs • Risk Assessment: Kutsch/CAMBRA form at low or no charge, electronic format • Bacterial Culture: Culture oven/12 culture tubes • Therapeutic Rinse: 6 patient kits of Therapeutic Rinse (12 - 8 oz. bottles) • Maintenance Rinse (12 – 8 oz bottles) Component Competitors • Screening Test: none • Risk Assessment: Featherstone/CAMBRA Coalition/CDA Foundation at no charge • Bacterial Culture: Vivadent CRT <1% after 15 years in market • Therapeutic Rinse: There are no specific rinses for the treatment and maintenance of dental caries from a purely antimicrobial standpoint. • Chlorhexidine, ACT fluoride rinses. • No complete system Risks • Hygenia issues for private label components, patent issues • Bacterial culture issues • Clinical trials on oral rinses • Inability to convince dental market to adopt medical approach to treating caries, vs. the traditional surgical approach