* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Labeling theory wikipedia , lookup
Social exchange theory wikipedia , lookup
Social Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Social constructionism wikipedia , lookup
Development theory wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Parasocial interaction wikipedia , lookup
Social network wikipedia , lookup
Structuration theory wikipedia , lookup
Structural functionalism wikipedia , lookup
Social network analysis wikipedia , lookup
Social rule system theory wikipedia , lookup
Postdevelopment theory wikipedia , lookup
Social norm wikipedia , lookup
Social group wikipedia , lookup
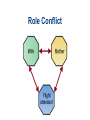
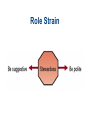
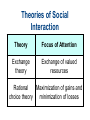
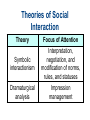
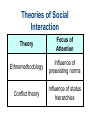
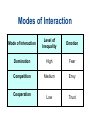
Chapter 4 Social Interaction Chapter Outline • • • • What is Social Interaction? The Sociology of Emotions Modes of Social Interaction Micro, Meso, Macro and Global Structures Elements of Social Interaction • Status means recognized positions occupied by interacting people. • Social interaction requires roles or sets of expected behaviors. • Social interaction requires norms or generally accepted ways of doing things. Role Set and Status Set Polling Question • Most of the time you can be sure that other people want the best for you. A. Strongly agree B. Agree somewhat C. Unsure D. Disagree somewhat E. Strongly disagree Role Conflict Role Strain Emotions and Social Interaction • Emotions are less spontaneous and uncontrollable than we commonly believe. • Your status in an interaction and in larger society affects how much you laugh and what you laugh at. • People manage their emotions in personal life and at work according to “feeling rules” that reflect cultural standards and the demands of organizations. Laughter and Humor • When people of different statuses interact, people with higher status get more laughs. • People with lower status laugh more. • Laughter in everyday life is often a signal of dominance or subservience. How We Get Emotional Emotion Management • We have expectations about: – What we should feel. – How much we should feel. – How long we should feel it. – With whom we should share our feelings. Grief in Historical Perspective • In Europe as late as 1600, life expectancy was only 35 years. • Many infants died at birth. • People invested less emotionally in their children than we do. • As health conditions and the infant mortality rate improved, emotional investment in children increased. Modes of Social Interaction • Exchange theory - involves trade in attention and other resources. • Rational choice theory - try to maximize benefits and minimize costs. • Dramaturgical analysis- social interaction is role-playing. Polling Question • People who are better off should help friends who are less well off. A. Strongly agree B. Agree somewhat C. Unsure D. Disagree somewhat E. Strongly disagree Ethnomethodology • The study of how people make sense of what others do and say by adhering to preexisting norms. • Everyday interactions could not take place without pre-existing shared norms and understandings. Nonverbal Communication • • • • Facial expressions Gestures Body language Status cues Power and Social Interaction: 4 points 1. Competitive exchange of valued resources: – People communicate to get something out of the interaction. – If they prevent others from getting much out of the interaction, communication will break down. – This is exchange and rational choice theory. Power and Social Interaction: 4 points 2. We mold values, norms, roles, and statuses to suit us as we interact with others. – We engage in impression management so others see us in the best possible light. – This is a major argument of dramaturgical analysis. Power and Social Interaction: 4 points 3. Norms exist before interaction takes place. – Sustained interaction would be impossible without shared understandings. – This is the core argument of ethnomethodology. Power and Social Interaction: 4 points 4. Nonverbal communication greatly facilitates social interaction. – These include: facial expressions, hand gestures, body language, and status cues. Theories of Social Interaction Theory Focus of Attention Exchange theory Exchange of valued resources Rational Maximization of gains and choice theory minimization of losses Theories of Social Interaction Theory Symbolic interactionism Dramaturgical analysis Focus of Attention Interpretation, negotiation, and modification of norms, rules, and statuses Impression management Theories of Social Interaction Theory Focus of Attention Ethnomethodology Influence of preexisting norms Conflict theory Influence of status hierarchies Big Structures, Small Processes Modes of Interaction Mode of Interaction Level of Inequality Emotion Domination High Fear Competition Medium Envy Low Trust Cooperation Quick Quiz 1. Role strain occurs when: a. people communicate face-to-face, acting and reacting in relation to other people b. a cluster of roles are attached to a single status c. a single individual occupies an entire ensemble of statuses d. incompatible role demands are placed on a person in a single status e. none of these choices Answer: d • Role strain occurs when incompatible role demands are placed on a person in a single status. 2. According to sociologists, the reason women laugh more than men do in everyday conversation is: a. when dealing with men, women have more to laugh at b. people with lower status laugh more c. speakers laugh more than listeners d. all of these choices e. none of these choices Answer: b • According to sociologists, the reason women laugh more than men do in everyday conversation is people with lower status laugh more. 3. Rational choice theory focuses on: a. the resources that are exchanged in the course of social interaction b. the way interacting parties weigh the costs and benefits of interaction c. impression management d. the way pre-existing norms shape social interaction e. the influence of status hierarchies on social interaction Answer: b • Rational choice theory focuses on the way interacting parties weigh the costs and benefits of interaction. 4. Dramaturgical analysis focuses on: a. the resources that are exchanged in the course of social interaction b. the way interacting parties weigh the costs and benefits of interaction c. impression management d. the way pre-existing norms shape social interaction e. the influence of status hierarchies on social interaction Answer: c • Dramaturgical analysis focuses on impression management. 5. Ethnomethodologists stress that everyday interactions could not take place if people were not willing to deviate from shared norms and understandings. a. True b. False Answer: b • Ethnomethodologists do not stress that everyday interactions could not take place if people were not willing to deviate from shared norms and understandings.