* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 15 Pseudocoelomate Animals
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
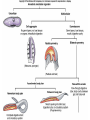
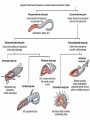
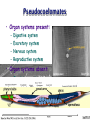
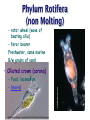
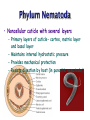
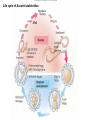
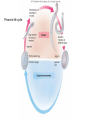
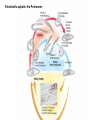
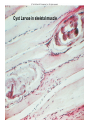
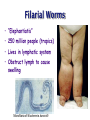
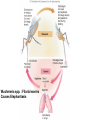
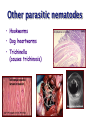
Ch 11 Pseudocoelomates “soo-doe-see-low-mates” Acrobeles complexus Pseudocoelomates (Aschelminthes) • 7 phyla: Do not molt – Rotifera – Acanthocephala Molt – Nematoda – Nematomorpha – Kinoryncha – Loricifera – Priapulida Phylogeny Two Hypothesis 1. Phyla related based on anatomy, pseudocoelom, cuticle, muscular pharynx, and adhesive glands. 2. Phyla not related, thus are polyphyletic absence in single unique feature independent evolution a. similarities result of convergent evolution in similar environments. Pseudocoelomates • A heterogeneous group: – Size: microscopic several meters – some are exclusively marine; some (e.g., nematodes) live in a variety of habitats, esp. soil; and some are exclusively parasitic Plant ectoparasite A. lumbricoides Pseudocoelomates • Common characteristics: 1. First animal to posses a distinct body cavity, but they lack the peritoneal lining and membranes (mesenteries) 2. Pseudocoelom- fluid filled, gelatinous substance, serves for circulation, aids in digestion, acts as hydroskeleton. Common characteristics: 1) Pseudocoelom • body cavity (pseudocoelom/ pseudocoel) • a space b/w gut and mesodermal components of body wall • Body cavity is not lined with a mesodermal sheet – Does not cover inner surface of body wall Common characteristics: 1) Pseudocoelom • Pseudocoelom is spacious, fluid-filled and Contains visceral organs • • No muscular tissue associated with gut tract No membranes suspend organs in body cavity Common characteristics: 2) Eutely • Eutely (thrift) a condition in which the number of cells is constant (i.e. C. elegans = 959 adult) Common characteristics: 3) complete digestive tract (mouth and anus) • Found in most other higher animals http://www.wormatlas.org/handbook/alimentary/alimentary2.htm Common characteristics: 1. Bilateral symmetry 2. Unsegmented, tribploblastic, and cylindrical in cross section 3. Protonephridia 4. Some cephalization is evident (primitive brain, mouth, sense organs) 5. Dioecious 6. Complete digestive tract (mouth and anus) 7. All have cuticle Evolutionary advantages of pseudocoel: – Greater freedom of movement – Space for development and differentiation of organ systems (ie. digestive, excretory) • differentiation: process by which cells become different, specialized – Simple means of circulation/distribution of materials throughout body – Storage place for waste products to be discharged to outside – Hydrostatic skeleton • Fluid enclosed by muscular wall support Pseudocoelomates • Organ systems present: – – – – Digestive system Excretory system Nervous system Reproductive system • Organ systems absent: – Circulatory system – Respiratory system Phylum Rotifera Phylum Rotifera (non Molting) – rota= wheel (wave of beating cilia) – fera= bearer Freshwater, some marine B/w grains of sand • Ciliated crown (corona) – Food, locomotion – (movie) http://www.microscopyu.com/galleries/dxm1200/images/collothecalarge.jpg Phylum Rotifera • Mostly microscopic • 1800 species • Many resistant to desiccation • dioecious http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/phasegallery/images/rotifer.jpg Phylum Rotifera • Brain • Muscular pharynx- mastax • Protonephridia with flame cells • Pedal glands Internal Anatomy of a Typical Rotifer Phylum Nematoda The roundworms Phylum Nematoda (Molt) • 16,000 species – 500,000 possible • Cylindrical body (vermiform) • Excretory system -renette • Mostly dioecious • Only longitudinal muscles – Undulate/thrash around (don’t crawl) movie Phylum Nematoda • Noncellular cuticle with several layers – Primary layers of cuticle- cortex, matrix layer and basal layer – Maintains internal hydrostatic pressure – Provides mechanical protection – Resists digestion by host (in parasitic nematodes) Phylum Nematoda (cont’d) • Found everywhere – Oceans (free living and parasitic) – Polar ice – Hot springs – Soil Some play an important role in nutrient recycling 5 billion per acre Phylum Nematoda (cont’d) • Eat just about every type of organic material – Rotting substance – Living tissue • Parasites of nearly all plant and animal species! Do these questions now… • What type of germ layer lines the pseudocoelom in nematode embryos? • What organ systems are present/absent in pseudocoelomates • What are the advantages of having a pseudocoelom vs. no coelom? Ascaris lumbricoides • Human parasite – Up to 30cm long • 1.2 billion people – Many in southeast US • Females lay 200,000 eggs a day • Unsanitary habits contaminate ground – Ingest eggs – Hatch bury into veins lungs pharynx – Swallowed intestine Life cycle of Ascaris lumbicoides Figure 11.10 Migrate to Molt Pinworms • Most common parasite in US • 30% children; 16% adults • Large intestine • Lay eggs (first-stage larva) in perianal area at night • Itch and Spread – Fecal oral route – Larval molt four times in Small Intestines and migrate to large Intestines Pinworm life cycle Figure 11.11 Trinchinella spiralis: the Porkworm Figure 11.13 (a) Figure 11.13 (b) Cyst Larvae in skeletal muscle Filarial Worms • “Elephantiatis” • 250 million people (tropics) • Lives in lymphatic system • Obstruct lymph to cause swelling Microfilaria of Wuchereria bancrofti Figure 11.15 Wuchereria spp. : Filarial worms Causes Elephantiasis Other parasitic nematodes • Hookworms • Dog heartworms • Trichinella (causes trichinosis) • biomedical research – C. elegans C. elegans • Free living nematode • 959 cells – Development of every cell is known (movie) • Genome sequenced – NCBI • C. elegans – Nobel Prize (2002) Brenner, Sulston and Horvitz – “Genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death” Sydney Brenner - C. elegans since 1963 http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2002/press.html