* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANIMALS REVIEW Chapters 33 & 34
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
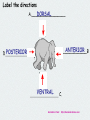
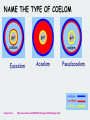
ANIMALS REVIEW Chapters 33 & 34 Image from: http://www.millan.net Label the directions DORSAL A.__________________ POSTERIOR D_______________ ANTERIOR ______________B VENTRAL ___________________ C. Animation from: http://bestanimations.com Animals whose embryos display indeterminate radial cleavage and in which the embryonic blastopore becomes the ANUS deuterostomes Cell with nuclear envelope eukaryote Animals whose embryos display determinate spiral cleavage and in which the embryonic blastopore becomes the MOUTH protostomes Cell without a nuclear envelope prokaryote Name the 3 kinds of nitrogen waste that can be excreted by animals. Ammonia, urea, uric acid Which of these is excreted by birds, reptiles, and insects to conserve water? uric acid If you remove cells from an early deuterostome embryo the _____________ remaining cells can still make the whole organism. Deuterostome Protostome Name the 3 germ layers that form in early triploblastic embryos. endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm Body cavity (space) formed within the mesoderm that surrounds the internal organs ___________________ coelom Animals belong in the Animalia kingdom ____________ and the Eukarya domain __________ Type of coelom in which there is NO space and mesoderm fills the area between ectoderm and endoderm Acoelom ___________________ Type of coelom in which mesoderm is found lining the outside body wall eucoelom and surrounding the gut __________________ Type of coelom in which mesoderm lines the outside body wall but is NOT found around the gut pseudocoelom __________________ Outside body covering in an animal (like skin, scales, feathers, fur) integument Embryonic layer of cells that gives rise to muscles, interior body linings, and most internal organs between the digestive tube and outer covering _____________ mesoderm blastopore In some animals the ____________ in the embryo becomes the anus and in others it becomes the mouth One of three layers of cells in an embryo from which specific organ Germ layer systems develop = _________ The young of animals that show indirect ___________ development start out as an immature larva and undergo metamorphosis to become adults . http://www.enchantedlearning.com NAME THIS TYPE OF CLEAVAGE SPIRAL http://www.zo.utexas.edu/faculty/sjasper/images/so28_04.gif What do we call organisms with this type of cleavage? Protostomes Deuterostomes PROTOSTOMES NAME THE TYPE OF COELOM Eucoelom Images from: Acoelom http://www.lander.edu/RSFOX/310images/310bilatImage.html Pseudocoelom NAME THIS TYPE OF CLEAVAGE http://www.zo.utexas.edu/faculty/sjasper/images/so28_04.gif radial What do we call organisms with this type of cleavage? Protostomes Deuterostomes DEUTEROSTOMES What is the advantage of having a true eucoelom? Outer body wall is independent of gut. Animal can move body muscles without interfering with its digestion Removing cells from an protostome ____________ embryo will result in an organism with parts missing and the organism will die. deterostome protostome Another name for “cold blooded” ectothermic Type of circulatory system seen in vertebrates closed I am a vertebrate deuterostome, with internal fertilization, external development in an amniotic egg, lungs, 3-chambered heart, 2 loop circulatory system. Who am I? Animalia Reptile I am a vertebrate deuterostome, with external fertilization, external development, lungs, 3 chambered heart, who am I? Animalia Amphibian PROTOSTOME? DEUTEROSTOME? DEUTEROSTOMES Indeterminate radial cleavage ______________________ PROTOSTOMES Determinate spiral cleavage _______________________ PROTOSTOMES Blastopore becomes mouth _____________________ DEUTEROSTOMES Blastopore becomes anus ______________________ Can’t make identical twins PROTOSTOMES _______________________ DEUTEROSTOMES Can make identical twins _______________________ PROTOSTOME? DEUTEROSTOME? Includes all vertebrates plus echinoderms DEUTEROSTOMES ____________________ Includes all triploblastic PROTOSTOMES invertebrates except echinoderms ____________________ The process in which the blastopore moves inward in the blastula and the embryonic germ layers form GASTRULATION In most bilaterally symmetrical invertebrates (like mollusks, worms, & arthropods) the blastopore becomes the mouth ________ anus mouth invertebrate An ____________is an animal without a backbone. Type of symmetry seen in jellyfish and adult starfish in which dividing the animal in several directions can produce equal halves. Asymmetry radial bilateral radial Images from: http://www.utm.edu/~rirwin/symmetry2.htm http://www.healthstones.com/ocean_life_store/wild_safari_marine_animals/starfish_purple/starfish_purple.jpg http://www.utm.edu/~rirwin/symmetry2.htm Slicing this mouse down the middle results in halves that are mirror images. This kind of symmetry is bilateral called _____________ Germ layer covering the surface of the embryo that gives rise to the outer covering, brain, and central nervous system ectoderm No matter which way you slice this animal, you never get 2 equal halves. asymmetry. It has ________ Asymmetry bilateral symmetry radial symmetry The young of animals that show _________ direct development start out looking like the adults only smaller. Type of circulatory system in which blood in not enclosed in vessels but circulates freely in the coelom and tissues Open circulation http://www.lander.edu/RSFOX/310images/310bilatImage.html This hollow ball of cells that forms in animal embryos is called a _____________ blastula The depression that forms in the side of the ball when cells move blastopore inward is called the ____________. Image from: http://io.uwinnipeg.ca/~simmons/16cm05/1116/16anim3.htm Rigid covering on the outside of an animals body that acts as a skeleton exoskeleton The blastopore area in an animal embryo becomes part of which body system? digestive Egg laying mammals are called _____________ monotremes 3 Most reptiles have ___chambers in their heart and a ___ 2 loop circulatory system. Name one way DEUTEROSTOMES are different from PROTOSTOMES PROTOSTOMES 1. Blastopore becomes mouth 2. Determinate embryonic cells 3. Spiral cleavage 4. Invertebrates except echinoderms DEUTEROSTOMES 1 Blastopore becomes anus 2.Indeterminate embryonic cells 3.Radial cleavage 4. Vertebrates & echinoderms Why are starfish considered to be BILATERIANS if they have radial symmetry? Their larva have bilateral symmetry and their embryos develop like other deuterostomes Kingdoms (like animals) whose organisms can be traced back to one common ancestor are called monophyletic _____________ Based on molecular similarities, which is the group of triploblastic INVERTEBRATES in which the blastopore becomes the anus? Echinoderms (EX: starfish) Animals with “true tissues” belong in the clade called ____________ EUMETAZOA ANIMALS All METAZOANS are ____________ Name one of the animal groups you learned about that are vertebrates. Mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians Give some common examples of coelomate protostomes Annelids, mollusks, arthropods Type of symmetry seen in humans bilateral All coelomates can be divided into TWO groups based on how their embryos develop. Name these two. Protostomes & deuterostomes Give some characteristics unique to the echinoderms Spiny skin invertebrate deuterostomes water vascular system/tube feet The concentration of sensory and brain structures in the anterior end of an organism is called cephalization __________ Why do zoologists debate the relationship of mollusks and annelids? A ciliated trochophore larva is seen in both marine mollusks and some annelids, but mollusks are not segmented like annelids. Humans show ________ internal fertilization. external internal Which kind of coelom do most animals including humans have? A B C A-true coelom http://www.lander.edu/RSFOX/310images/310bilatImage.html closed circulatory system In a(n) ______ blood circulates throughout the body inside blood vessels An immature form of an organism LARVA is called a ____________ Which of the forms of nitrogen waste excreted by animals is MOST TOXIC and requires the most water to dilute? AMMONIA direct Humans show ________ development. direct indirect Name one of the functions of a coelom Provides space for/cushions internal organs Can act as a hydrostatic skeleton Can provide space for nutrients/oxygen to circulate Which vertebrates are amniotes? Birds, reptiles, mammals (monotremes) 4 Birds have ___chambers 2 loop in their heart and a ___ circulatory system. Innermost germ layer that lines the digestive tract and gives rise to organs derived from it like liver and lungs endoderm Name the 3 kinds of symmetry you learned about Asymmetry, radial symmetry, & bilateral symmetry Mammals like a kangaroo whose babies spend time in a pouch marsupials are called ____________ 3 Adult amphibians have ___chambers 2 loop in its heart and a ___ circulatory system. Type of reproduction in which one parent copies itself without exchanging genetic material with a partner. asexual Skeleton that is located inside the body. endoskeleton Arthropods have an exoskeleton, ___________ jointed appendages, and open circulation Name the two classes of Vertebrates that are endothermic Birds (Aves) & mammals (Mammalia) Another name for warm blooded endothermic Nephridia, Malpighian tubules, Green glands, and flame cells belong to which body system? excretory Which vertebrate groups are ectothermic? Fish, amphibians, reptiles 2 A fish has ___chambers in its 1 loop circulatory heart and a ___ system. I am a single-celled extremophile, living in high temperature or high salinity environments. Who am I? Archaebacteria I am a heterotroph, with a chitinous cell wall, and multinucleated filamentous hyphae. Who am I? fungi I am a vertebrate deuterostome, with internal fertilization, external development in an amniotic egg, lungs, and a 4-chambered heart, Who am I? Animalia Aves (bird) I am a vertebrate deuterostome, with internal fertilization, external development in an amniotic egg, lungs, fur, milk production, 4-chambered heart, who am I? Animalia Mammalia Monotreme I am a segmented coelomate, with jointed appendages, and a chitinous exoskeleton, Who am I? Animalia Arthropoda I am a coelomate, with spiny skin, invertebrate deuterostome, with radial symmetry as adults, and an endoskeleton, Who am I? Animalia Echinodermata I am/have single-celled, heterotroph, peptidoglycan cell wall, circular DNA but no nuclear envelope, reproduce by binary fission. Who am I? eubacteria 4 Mammals have ___chambers in their heart and a ___ 2 loop circulatory system. I am a multicellular heterotroph, with no cell wall, no symmetry and no distinct tissues, who am I? Animalia Porifera (sponge) I am a soft-bodied coelomate, invertebrate protostome, both terrestrial and aquatic (with gills), many have external shells, who am I? Animalia Mollusca I am bilaterally symmetrical, an invertebrate protostome, with 3 germ tissue layers, an acoelomate, with a <2 opening digestive system. Who am I? Animalia Platyhelminthes (flatworm) I am a segmented coelomate, bilaterally symmetrical, two opening digestive tract, gas exchange through body surface, nephridia for excretion, closed circulation. Who am I? Animalia Annelida (segmented worms) I am a photosynthetic, unicellular, silica cell wall, eukaryotic algae, most common type of phytoplankton and a major oxygen producer, Who am I? Protist (diatom) Which 4 characteristics characterize CHORDATES? Notochord, pharyngeal pouches dorsal nerve cord, post anal tail I am a segmented coelomate, with 2 body segments, 8 legs,and a chitinous exoskeleton, book lungs, and Malpighian tubules. Who am I? Arthropod Arachnid (spider) I am an aquatic, single-celled eukaryote, heterotroph,with pseudopodial movement, Who am I? Protist (amoeba) I am an invertebrate protostome with radial symmetry, both polyp and medusa phases, and stinging nematocysts. Who am I? Animalia Cnidaria (jellyfish) I am an unsegmented pseudocoelomate, invertebrate protostome, bilaterally symmetrical, with 2 opening digestive system, soil and aquatic habitats, some parasitic. Who am I? Animalia Nematoda (round worm) I am a vertebrate deuterstome, with internal fertilization, internal development , fur, mammary glands, and a 4-chambered heart, Who am I? Animalia Mammal I am a coelomate, deuterostome, with bilateral symmetry, and endoskeleton, possess dorsal nerve cord, notochord, post anal tail & pharyngeal slits during development, Who am I? Animalia Chordata I am a vertebrate deuterstome, with internal fertilization, internal development but must be completed externally in pouch, lungs, and a 4-chambered heart, who am I? Animalia Mammal Marsupial I am an aquatic, single-celled eukaryote, that contains numerous chloroplasts, flagellated, reproduce by mitosis, who am I? Protist (euglena) Why is segmentation important? Efficient way to add length; Permits specialization in body regions; Allows parts to move independently Why are amniotic eggs significant? Amniotic eggs have specialized membranes to protect the embryo and prevent dehyration. Allowed descendants of amphibians to move out onto land and not have to return to water to lay eggs. What are the two forms of shape seen in Cnidarians? Polyp and medusa Which membrane stores nitrogen waste and is involved in gas exchange in an amniotic egg? allantois Which membrane surrounds the other three membranes in an amniotic egg and forms the baby’s portion of the placenta? chorion How are cnidarian medusa and polyp forms different? Polyps are sessile; medusa are free swimming What is the significance of a true coelom? Body wall and gut are separated so can move independently What are some unique characteristics common to the cnidarians? Diploblastic radial symmetry gastrovascular cavity Tissues/specialized cells (nematocysts) Give an example of a cnidarian Jellyfish, coral, anemones Tell some characteristics of arthropods Segmentation exoskeleton of chitin Jointed appendages Open circulatory system many undergo metamorphosis Tell some characteristics of reptiles Dry,scaly skin ectothermic internal fertilization amniotic eggs Most 3 chamber heart/2 loop circulatory system Excrete uric acid Type of reproduction in which the egg is covered with a shell, but is kept inside the mother’s body until it hatches or right before it hatches, and the egg provides nourishment to the embryo, ovoviviparity Which kinds of animals display this kind of reproduction? Some reptiles (snakes) Tell some characteristics of birds feathers/wings Lightweight hollow bones internal fertilization 4 chamber heart/2 loop circulatory system lay amniotic eggs Endothermic excrete uric acid Efficient lungs with air sacs Type of reproduction in which the egg is covered with a shell, is laid outside the mother’s body, and the egg provides nourishment to the embryo oviparity Which kinds of animals display this kind of reproduction? Reptiles, birds, monotreme mammals The membrane that surrounds the developing embryo in an amniotic egg amnion The membrane that functions in gas exchange and stores nitrogen waste in an amniotic egg allantois Outer membrane that surrounds all the other membranes in an amniotic egg chorion Tell some characteristics of mammals Endothermic 4 chamber heart/2 loop circulatory system Fur Make milk for young Most viviparous (live young) Tell some characteristics of bony fish Ectothermic 2 chamber heart/1 loop circulatory system Swim bladder/lungs Endoskeleton of bone or cartilage Scales/fins Name the three kinds of reproduction seen in mammals Monotremes (egg layers) Marsupials (pouch) Placental (eutheria)-true placenta inside mom Give some characteristics of annelids Segmentation Invertebrate protostomes Eucoelomate 2 opening digestive system Closed circulatory system Most hermaphrodites (both ovary/testes) Which of the cnidarian body forms is characteristic of sea anemones? polyp Type of reproduction in which the egg is not covered with a shell, but is kept inside the mother’s body, and embryo is supplied nourishment from the mother via a placenta viviparity Which kinds of animals display this kind of reproduction? Mammals (placental & marsupial) Which membrane surrounds the developing embryo and the fluid in which it floats in an amniotic egg? amnion Which membrane surrounds the fat rich food supply in an amniotic egg? Yolk sac Type of reproduction in which young develop from unfertilized eggs parthenogenesis Why are arthropods regarded as the most successful animal phylum? Greatest diversity of species, distribution, and total numbers of all animal groups Which kingdom is polyphyletic and contains the widest array of organisms? protista Which of the cnidarian body forms is characteristic of a jellyfish? medusa THE END