* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The War to End All Wars
Australian contribution to the Allied Intervention in Russia 1918–1919 wikipedia , lookup
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
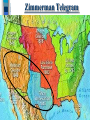
FQ: How did World War I affect the entire world? DO NOW Review Homework List 3 key points from the notes Agenda 5min- Do NOW 15 min- Mini Lesson: Notes- The War Ends 30 min- Movie Clip- Film Dependent Questions 10 min- Share out- How did the technological advance during WWI impact/change society Setting the Stage As war on both European fronts promised to be a grim, drawn-out affair, all the Great powers looked for new allies to tip the balance. A Global Conflict Japan entered the war on the Allies sides. The Ottoman Turks and later Bulgaria allied themselves with Germany and the Central Powers. Italy joined the Allies in April of 1915. The only major neutral power left was the United States. The Great War was a “world war” The United States Enter the War Reasons U.S. joined the War 1. Economic & historic ties to the Allies (England & France) 2. Unrestricted Submarine Warfare- In 1917, the focus of the war shifted to the high seas. That year, the Germans intensified the submarine warfare. In January 1917, the Germans announced their submarines would sink without warning any ship in the waters around Britain. This policy was called unrestricted submarine warfare. U.S. Losses German Submarines Germany usedtoU-boats to create a naval from 1916-1918 blockade of England The United States Enter the War 3. Sinking of the Lusitania- On May 7, 1915, a German submarine, or U-boat, sunk the British passenger ship Lusitania. The attack left 1,198 people dead, including 128 U.S. citizens. The American public was outraged. The United States Enter the War 4. Zimmermann Note- The British intercepted a telegram from German foreign minster, Arthur Zimmermann, to the German ambassador in Mexico. The message said that Germany would help Mexico “reconquer” the land it had lost to the United States if Mexico would ally itself with Germany. Zimmerman Telegram The United States Enter the War The Zimmermann Note proved to be the last straw. On April 2, 1917, President Wilson asked Congress to declare war. The United States entered the war on the side of the Allies. On April 2, 1917 the US entered WWI Total War The war had claimed the lives of millions and had changed countless lives forever. The Great War, as WW1 came to be called, affected everyone. Total War World War I soon became a total war. This meant that countries devoted all their resources to the war effort. Economy-The wartime government took control of the economy. Governments told factories what to produce and how much. Rationing-So many goods were in short supply that government turned to rationing. Under this system, people could buy only small amounts of those items that were also needed for the war effort. Total War Propaganda- Governments also used propaganda- one-sided information designed to persuade- to keep up moral and support for the war. In nations throughout Europe, striking, colorful posters urged support for the war by painting the enemy as monsters and allies as heroes. Recruitment Posters Anti-German Propaganda Total War Women’s Roles- total war meant that governments turned to help from women as never before. Thousands of women replaced men in factories, offices, and shops. Curtis-Martin German Women U.Factory Factory S. homefront Aircraft Workers Plant Factories on the French Women Workers The Allies Win The War With the United States finally in the war, the balance of power was about to tip in the Allies favor. Russia Withdraws-By March 1917, civil unrest in Russia-due in part to war-related shortages of food and fuel-had brought the Czar Nicholas’s government to the brink of collapse. In November 1917, Communist leader Vladimir Lenin seized power. One of his first acts was to offer Germany a truce. In March 1918, Germany and Russia signed a treaty, which ended the war between them. The Allies Win The War Failed Final Push- Russia’s withdrawal from the war at last allowed Germany to send nearly all its forces to the Western Front. In 1918, the Allies and Germans clashed at the Second Battle of Marne. With the arrival of 2 million more American troops, the Allied forces began to advance steadily toward Germany. The Central Powers began to crumble. In Germany, soldiers mutinied, and the public turned on the Kaiser. Allies Win- In a railway car near Paris, the two sides signed an armistice, or an agreement to stop fighting. On November 11, World War I came to and end. The Allies Win The War After 4 years of slaughter and destruction, the time had come to forge a peace settlement. Leaders of the victorious nations gathered outside Paris to work out the terms of peace. Share out Name a technology and explain its impact on society (Analysis) Know for Thematic Essay exam!