* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 29 affluence and anxiety: from the fair deal to the great society
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
1960 U-2 incident wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
Sino-Vietnamese War wikipedia , lookup
Single Integrated Operational Plan wikipedia , lookup
Mutual assured destruction wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
War in Vietnam (1954–59) wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
North Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
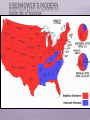
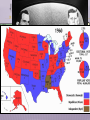
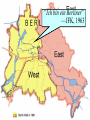
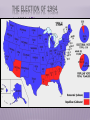
PRESIDENT EISENHOWER’S MODERN REPUBLICANISM EISENHOWER’S MODERN REPUBLICANISM Frustration with the stalemate in Korea & the Red Scare led to a Republican presidential Gov’t Korean War takeover in theCommunism 1952 Corruption WW2 hero Dwight Eisenhower provided an antidote for “K1C2” VP Richard Nixon attacked communism & Once elected, Ike did go to Korea, overturned corruption the U.N. battle plan, &tothreatened China with Eisenhower vowed go to Korea & personally nuclearend warthetowar get an armistice signed in 1953 THE REPUBLICANS IN POWER Regarding McCarthyism, Ike provided McCarthy “just enough rope to hang himself” in 1954 In the televised “Army hearings,” the nation saw McCarthy’s style & fact-less attacks The Senate censured McCarthy & his “communist” attacks quickly died EISENHOWER WAGES THE COLD WAR EISENHOWER & THE COLD WAR Ike was unusually well-prepared to be a Cold War president Ike’s foreign policy goals were to: Take a strong stand against Communism by WW2using military “massive retaliation” with nuclear experience in& covert CIA operations weapons Excellent diplomat Europe & Asia To reduce defense spending & relax Cold War & politician tensions Pragmatic & well organized Chose hard-liner John Foster Dulles to be Sec of State MASSIVE RETALIATION “Massive retaliation” meant targeting civilian targets rather“more than bang military ones Eisenhower wanted for the buck”: Nuclear weapons & long-range delivery missiles cheaper than conventional armed forces Ikewere relied heavily on “brinksmanship” “Massive retaliation” strategy made using in which he used veiled threats of nuclear weapons unlikely nuclear war to accomplish his goals But massive retaliation offered no intermediate course of action if diplomacy failed What are the stakes of war? Massive Retaliation? Mutual Assured Destruction? MASSIVE RETALIATION Chinese did not know if Ike was bluffing so China backed off this territorial expansion …and theInrefusal the USSR to aid aChina added a 1954,of Eisenhower used hard-line ift between Russia to & stop ChinaChinese by the end of the 1950s approach expansion in Asia: Chinese attempts to take over islands near Taiwan led Eisenhower to threaten nuclear war if China did not stop Eisenhower hoped this pressure would drive a wedge between the USSR & communist China MASSIVE RETALIATION In 1956, Egyptian leader Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal: England & France invaded Egypt to take back the canal but the USSR opposed this intervention Eisenhower did not want the USSR to attack so he threatened Russia with nuclear war England, France, & the USSR left Egypt & the U.S. became the leader in Middle East EISENHOWER DOCTRINE Like the Monroe Doctrine in Latin America, The Suez Crisis revealed the vulnerability of the United States emerged as a police power the Middle East to Communism & Ike in a new part of the world responded: In 1957, the Eisenhower Doctrine recommended U.S. armed force to protect the Middle East from Communist aggression In 1957, Ike sent the military to Lebanon to halt Communism & install a pro-Western gov’t COVERT ACTIONS Ike’s administration used covert CIA acts to expand U.S. control: In 1953, the CIA overthrew Mohammed Mossadegh in Iran in favor of a U.S.-friendly shah In 1954, the CIA overthrew a leftist regime in Guatemala These interventions led to anti-American In 1959, the CIA took a hard-line against new hostilitiesCuban in the Middle & after Latin dictator FidelEast Castro hisAmerica coup THE EFFECTS OF SPUTNIK The “space race” intensified the Cold War between USA & USSR In 1957, the launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik led to fears that the USSR was leading the race to create intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) Khrushchev used Sputnik to put the U.S. on The U.S. sped “We up it plans buildyou. ICBMs & IRBM the defensive: will to bury Your submarineswill live under Communism.” grandchildren THE EFFECTS OF SPUTNIK Sputnik led to fears that America was growing soft & was losing its competitive edge & work ethic The U.S. gov’t responded with: National Space Administration The Aeronautics advanced &placement (AP) in 1958 program is a byproduct of the NDEA! National Defense Education Act was created to promote math, science, & technology education SPUTNIKSeven—Mercury IN 1957 Alan Shepard was the The Original Astronauts st 1 American in space WAGING PEACE Ike tried to end the nuclear arms race as both sides tested hydrogen bombs & ICBMs In 1953, Eisenhower called for disarmament & presented his “Atoms for Peace” plan to the United Nations In 1955, Khrushchev rejected Eisenhower’s “open skies” plan for weapons disarmament MILITARY-INDUSTRIAL COMPLEX This military-industrial complex is part of the reason for the Soviet demise in the late 1980s In his farewell address in 1960, Eisenhower & end of the Cold War in 1991 warned against the Military-Industrial Complex: The massive military spending that dominate domestic & foreign politics CONCLUSIONS By 1960, the American people were more optimistic than in 1950 Americans were no longer afraid of a return of another Great Depression Anxiety over the Cold War continued but was not as severe KENNEDY’S COLD WAR LBJ as well it FRONTIER was not the 1st time TV JFK’SBut, NEW influenced The election of 1960 politics… between Richard Nixon st to use TV & John F. Kennedy was the 1 Eisenhower used McCarthy was destroyed by debates: TV in the Army-Senate TV to campaign hearings in 1952 & 1956 Nixon was much better known but the TV debates helped swing undecided voters towards JFK 1960 marked the beginning of television dominance in politics Image & appearance became essential traits for candidates JFK’S NEW FRONTIER Kennedy’ administration reflected youth, energy, & sharp break from Eisenhower JFK promised a New Frontier: The JFK era began Domestic reforms in education, health care, & “Camelot” civil rights comparisons with JFKcommitted to defeating the A foreign policy as a modern-day Soviet Union & winning the Cold War Lancelot KENNEDY INTENSIFIES THE COLD WAR KENNEDY INTENSIFIES THE COLD WAR Addressing U.S. foreign policy & containing Communism was JFK’s top priority as president: JFK believed Ike compromised with the USSR when the Cold War could have been won JFK aimed to close the “missile gap” & increase U.S. defenses Looked to solve issues in Berlin, Vietnam, & Cuba FLEXIBLE RESPONSE JFK shifted from Ike’s “mutually assured destruction” to a “flexible response” capable of responding to a variety of future problems: Increased nuclear arsenal to 1,000 ICBMs & 32 Polaris subs to create a “first-strike” capability JFK was convinced that the USSR had more Increased the army & air force missiles, but covert reallyoperations the U.S. &had the lead with Expanded created the Green To combat Communism & warheads to help 600Berets B-52s, 2 Polaris subs, 2,000 underdeveloped countries, JFK created the Peace Corps & the Alliance for Progress THE SPACE The RACE Apollo Program JFK hoped to avoid another Sputnik & hoped to beat the Soviets to the moon: JFK greatly expanded NASA & announced that the U.S. would get to the moon by 1970 The U.S. landed a man on the moon in 1969 CRISIS OVER BERLIN JFK’s 1st confrontation with the Soviet Union came in Berlin: Khrushchev was upset with the exodus of skilled workers from East Germany to West Berlin The USSR threatened to remove all U.S. influence from West Berlin, but settled on building the Berlin Wall in 1961 “Ich bin ein Berliner” —JFK, 1963 CONTAINMENT IN VIETNAM Vietnam proved to be a tough test: Since 1954, Communist leader Ho Chi Minh gained popularity in North Vietnam; By 1961, he gained a foothold in the South The U.S. gave aid to unpopular South leader Ngo Dihn Diem When Diem lost control of the South, JFK gave the OK for a coup against Diem in 1963 VIETNAM Viet Minh are Vietnamese communists in North Vietnam Viet Cong are Vietnamese communists in South Vietnam CONTAINING CASTRO: BAY OF PIGS Fidel Castro took over Cuba in 1959 & developed ties with Russia The Eisenhower administration (directed by the CIA) had been training Cuban exiles for an invasion & overthrow of Castro JFK blamed the Republicans for In 1961, JFK gave the OK for the CIA to initiate allowing a “communist satellite” the Bay of Pigs invasion to arise on “our very doorstep” The invasion called for U.S. air support but JFK canceled the air strike; without air support, Castro squashed the invasion Kennedy took full responsibility for the failure of Bay of Pigs, but did not apologize for coup CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS 24 medium-range & 18 short range ICBMs To protect Cuba from another U.S. invasion, the USSR began a secret build-up of nuclear missiles On Oct 14, 1962 a U-2 spy plane discovered Cuban missile camps How would the U.S. respond? Immediate air strike? Full-scale Cuba invasion? Kennedy chose to “quarantine” to keep new missiles out & an invasion of Diplomacy: trade nukes in Naval blockade to if the USSR did not remove its nukes CubaCuba for nukes in Turkey? keep warheads out? Kennedy announced a quarantine (blockade) to The Cuban Missile Crisis keep more missiles out & demanded that the Soviets remove the missiles already in Cuba of CUBAN And…U.S. MISSILEremoval CRISIS nuclear weapons in Turkey The standoff ended when Russia removed its Cuban missiles & the USA vowed to never invade Cuba The impact of the crisis: Seen as a political victory for JFK Installed a “hot line” to improve US-Soviet communications This near-nuclear war convinced both sides to move from confrontation to negotiation "LET US CONTINUE" On Nov 22, 1963 in Dallas, JFK was assassinated & VP Lyndon Johnson became president: LBJ helped push through the greatest array of was a master politician with a reputation for liberal LBJ legislation in U.S. history (“Great getting results Society”), surpassing FDR’s New Deal LBJ promised to continue Kennedy's liberal agenda LBJ ultimately exceeded JFK’s record on providing economic & racial equality Americans were stunned this rapid succession of events THE ELECTION OF 1964 In 1964, LBJ ran against: Conservative Republican Barry Goldwater rejected LBJ’s liberal welfare programs & called for a stronger foreign policy stance Segregationist George Wallace LBJ won in a landslide & the Democrats took control of Congress for 1st time in 25 years JOHNSON ESCALATES THE VIETNAM WAR LBJ ESCALATES THE VIETNAM WAR “ILBJ amcontinued not goingJFK’s to lose Vietnam. am strong foreignIpolicy not going to be the president who saw positions too: Southeast Asia go the way China He supported CIA-sponsored coups went.” in Brazil, Panama, & the Dominican Republic —LBJ LBJ continued Eisenhower & JFK policies towards Vietnam But in doing so, LBJ found himself under attack from Congress, the media, & universities LBJ ESCALATES THE VIETNAM WAR During the Gulf of Tonkin affair in Aug 1964, the military bombed North Vietnam in retaliation for an attack on the USS Maddox The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution gave LBJ the authority to: Defend Vietnam at any cost Unlimited military intervention to be used at LBJ’s discretion ESCALATION LBJ’s advisors wanted 100,000 troops in 1965 & a plan for 100,000 more in 1966; Estimations 1965 marked the beginning of full-scale U.S. were 500 U.S. deaths per month involvement in Vietnam LBJ was informed that “without U.S. action, defeat is inevitable” LBJ authorized bombing raids into North Vietnam & requested 50,000 U.S. soldiers sent to Asia LBJ never explained to the American people how thetook gov’tmiddle plannedroad to win war inU.S. LBJ of the limited Vietnam intervention: not a withdrawal & not a full-scale invasion of North Vietnam STALEMATE By 1968, 500,000 U.S. troops stationed to keep Vietnam from falling to Communism U.S. bombings & “search & destroy” attacks were ineffective Soviet & Chinese weaponry freely flowed into North Vietnam Reckless bombings killed thousands of innocent civilians The bloody stalemate & media depiction of the war led to protests CONCLUSIONS The early 1960s under JFK represented consume spending, a strong stance on the Cold War, & more social reforms at home The transition to LBJ in 1963 brought success at home (civil rights & the Great Society) But, heightened involvement in Vietnam signaled the onset of the counter-culture movement by 1968