OGT Benchmark: Analyze connections between World War II, the
... • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) The period after World War II is referred o as the “Cold War.” It is called this because the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union • A. had several conflicts that never escalated into a full-scale war • B. used nuclear weapons that lowered the tempera ...
... • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) The period after World War II is referred o as the “Cold War.” It is called this because the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union • A. had several conflicts that never escalated into a full-scale war • B. used nuclear weapons that lowered the tempera ...
OGT Benchmark: Analyze connections between World War II
... • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) The period after World War II is referred o as the “Cold War.” It is called this because the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union • A. had several conflicts that never escalated into a full-scale war • B. used nuclear weapons that lowered the tempera ...
... • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) The period after World War II is referred o as the “Cold War.” It is called this because the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union • A. had several conflicts that never escalated into a full-scale war • B. used nuclear weapons that lowered the tempera ...
chapter 29 affluence and anxiety: from the fair deal to the great society
... Vietnam proved to be a tough test: Since ...
... Vietnam proved to be a tough test: Since ...
chapter 29 affluence and anxiety: from the fair deal to the great society
... 1953, Eisenhower called for disarmament & presented his “Atoms for Peace” plan to the United Nations In 1955, Khrushchev rejected Eisenhower’s “open skies” plan for weapons disarmament ...
... 1953, Eisenhower called for disarmament & presented his “Atoms for Peace” plan to the United Nations In 1955, Khrushchev rejected Eisenhower’s “open skies” plan for weapons disarmament ...
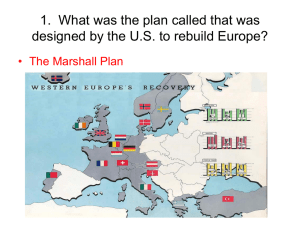
1. What was the plan called that was designed by the U.S. to rebuild
... Why did the U.S. and Soviet Union become enemies after WWII? • Economic and social ...
... Why did the U.S. and Soviet Union become enemies after WWII? • Economic and social ...
File
... • Kent State – student protesters threw rocks & bottles at National Guard, fired into protesters killing 4 ...
... • Kent State – student protesters threw rocks & bottles at National Guard, fired into protesters killing 4 ...
Cold War in the 1960s and 1970s
... The USSR fought in Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989, but was unable to defeat the Afghan resistance The war exhausted Soviet economy & proved as unwinnable as Vietnam was for the United States The war renewed tensions between the USA & USSR ...
... The USSR fought in Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989, but was unable to defeat the Afghan resistance The war exhausted Soviet economy & proved as unwinnable as Vietnam was for the United States The war renewed tensions between the USA & USSR ...
HISTORICAL CRISIS CABINET Time for Opening Speech: 90
... After the fall of France to the axis, the region went under unopposed Japanese occupation, until Ho Chi Minh, a Vietnamese communist revolutionary, revolted against the Japanese in 1941. By 1945, Vietnam declared its independence. However, after the Potsdam Conference of July 1945, the combined chie ...
... After the fall of France to the axis, the region went under unopposed Japanese occupation, until Ho Chi Minh, a Vietnamese communist revolutionary, revolted against the Japanese in 1941. By 1945, Vietnam declared its independence. However, after the Potsdam Conference of July 1945, the combined chie ...
Reader US Foreign Policy part 2
... The US stimulated the creation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), joined by 12 Western powers and later by Greece and Turkey. The Soviet’s response to this was the Warsaw Pact; an organization of Eastern European countries headed (firmly) by the USSR. Korea At the end of WW2 the US ha ...
... The US stimulated the creation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), joined by 12 Western powers and later by Greece and Turkey. The Soviet’s response to this was the Warsaw Pact; an organization of Eastern European countries headed (firmly) by the USSR. Korea At the end of WW2 the US ha ...
pol300_assignment_1
... made with Asian countries, but would no longer take part in their battles, unless it was to intervene when Asia was facing attack from a nation with nuclear powers. Then, the American soldiers who left South East Asia were replaced by South Vietnamese troops. 1973 saw North Vietnam and the United St ...
... made with Asian countries, but would no longer take part in their battles, unless it was to intervene when Asia was facing attack from a nation with nuclear powers. Then, the American soldiers who left South East Asia were replaced by South Vietnamese troops. 1973 saw North Vietnam and the United St ...
File
... • On April 30, 1970, Nixon announced that U.S. troops were sent into Cambodia to attack Communist bases. • Nixon seemed to be expanding the war. ...
... • On April 30, 1970, Nixon announced that U.S. troops were sent into Cambodia to attack Communist bases. • Nixon seemed to be expanding the war. ...
cold war crisis - my social studies class
... one of the major wars of the US, outranking the Korean War. The nation became deeply divided as the more radical advocates of peace agitated for immediate withdrawal of American forced from South Vietnam. AMERICAN INVOLVEMENT The US became involved in Vietnam after the Japanese during WWII had drive ...
... one of the major wars of the US, outranking the Korean War. The nation became deeply divided as the more radical advocates of peace agitated for immediate withdrawal of American forced from South Vietnam. AMERICAN INVOLVEMENT The US became involved in Vietnam after the Japanese during WWII had drive ...
End of the Cold War
... --Carter asks USSR to withdraw from Afghanistan, they refuse --Carter leads a boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympic games which are held in Moscow, 64 nations in all will boycott --Soviets and their allies will boycott the 1984 Summer Games in ...
... --Carter asks USSR to withdraw from Afghanistan, they refuse --Carter leads a boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympic games which are held in Moscow, 64 nations in all will boycott --Soviets and their allies will boycott the 1984 Summer Games in ...
- Wilson Center Digital Archive
... suffered failure in South Vietnam. For example, the plan for the pacification of Vietnam in 18 months as failed. American imperialism and its servants in South Vietnam have concentrated in a defensive position in those 9 provinces around Saigon. The three points of support of the imperialist forces: ...
... suffered failure in South Vietnam. For example, the plan for the pacification of Vietnam in 18 months as failed. American imperialism and its servants in South Vietnam have concentrated in a defensive position in those 9 provinces around Saigon. The three points of support of the imperialist forces: ...
US Foreign Policy Since World War II
... Differences among the victorious Allied Powers after World War II The Cold War set the framework for 45 years after the end of World War II. It also influenced American ...
... Differences among the victorious Allied Powers after World War II The Cold War set the framework for 45 years after the end of World War II. It also influenced American ...
Chapter 29 Notes
... -Concerned that Vietminh victory would lead to spread of Communism in Asia. -Feared domino theory – that is one country became communist, nearby countries would follow -In July 1954, French and Vietnamese leaders agreed to Geneva Accords. -Temporary division of Vietnam into North Vietnam and South V ...
... -Concerned that Vietminh victory would lead to spread of Communism in Asia. -Feared domino theory – that is one country became communist, nearby countries would follow -In July 1954, French and Vietnamese leaders agreed to Geneva Accords. -Temporary division of Vietnam into North Vietnam and South V ...
Chapter 22 Section 1
... patrol boat fired a torpedo at an American destroyer, the USS Maddox, which was patrolling in the Gulf of Tonkin off the North Vietnamese coast. The torpedo missed its target, but the Maddox returned fire and inflicted heavy damage on the patrol boat. Two days later, the Maddox and another destroyer ...
... patrol boat fired a torpedo at an American destroyer, the USS Maddox, which was patrolling in the Gulf of Tonkin off the North Vietnamese coast. The torpedo missed its target, but the Maddox returned fire and inflicted heavy damage on the patrol boat. Two days later, the Maddox and another destroyer ...
Kennedy and the Space Program - Waverly
... domino theory, warning that if America did not support France in stopping the Communists in Indochina, all of the Eastern, India and Southeastern Asia would fall to the "Communist ...
... domino theory, warning that if America did not support France in stopping the Communists in Indochina, all of the Eastern, India and Southeastern Asia would fall to the "Communist ...
Cold War and Vietnam PRE FINAL testx
... ______ 15. As a result of the attack in the previous question the United States responded with the ____________________ which allowed the President to protect America against further attacks and possibly began a war with Vietnam. A. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution ...
... ______ 15. As a result of the attack in the previous question the United States responded with the ____________________ which allowed the President to protect America against further attacks and possibly began a war with Vietnam. A. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution ...
In 1920, after being rejected by the United States in
... Ho Chi Minh: Communist or Nationalist? In 1920, Ho Chi Minh went to Versailles to meet US President Woodrow Wilson. Ho Chi Minh had heard about Wilson’s Fourteen Points and how the US was in favor of countries gaining their independence. However, he was never allowed to speak to Wilson and his ideas ...
... Ho Chi Minh: Communist or Nationalist? In 1920, Ho Chi Minh went to Versailles to meet US President Woodrow Wilson. Ho Chi Minh had heard about Wilson’s Fourteen Points and how the US was in favor of countries gaining their independence. However, he was never allowed to speak to Wilson and his ideas ...
Ch 3941 Stormy Sixties Questions and
... discrimination in most private facilities open to the public, including theaters, hospitals, and restaurants. It strengthened the federal government’s power to end segregation in schools and other public places. It created the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) to eliminate discriminatio ...
... discrimination in most private facilities open to the public, including theaters, hospitals, and restaurants. It strengthened the federal government’s power to end segregation in schools and other public places. It created the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) to eliminate discriminatio ...
The Cold war
... invade Cuba. Castro struck a deal with the Soviet Union and its leader Nikita Khrushchev. Khrushchev had taken over as First Secretary of the USSR’s Communist Party after Stalin died in 1953. Although the Soviet government was no longer a dictatorship under Khrushchev, the new leader was still a tou ...
... invade Cuba. Castro struck a deal with the Soviet Union and its leader Nikita Khrushchev. Khrushchev had taken over as First Secretary of the USSR’s Communist Party after Stalin died in 1953. Although the Soviet government was no longer a dictatorship under Khrushchev, the new leader was still a tou ...
The Cold War
... • Gen. Douglas MacArthur then attempted (without Pres. Truman’s consent) to drive the communists completely out of Korea into China. ...
... • Gen. Douglas MacArthur then attempted (without Pres. Truman’s consent) to drive the communists completely out of Korea into China. ...
10.9 Lecture – Wars in Korea and Vietnam
... trade 2. 1987 adopted a democratic constitution and free elections. d. With the threat of North Korea and their nuclear weapons, the countries have stayed divided. ...
... trade 2. 1987 adopted a democratic constitution and free elections. d. With the threat of North Korea and their nuclear weapons, the countries have stayed divided. ...
North Vietnam
The Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; Vietnamese: Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), commonly known in English as North Vietnam, was a Marxist–Leninist government founded in 1945, laying claim to all of Vietnam yet comprising most of North Vietnam from September 1945 to December 1946, controlling pockets of territory throughout the country until 1954, and governing territory north of the 17th parallel until 1976, when the government led by the Communist Party reunified with the Southern Provisional Government governed from Hanoi.As an era of post-dynastic Vietnamese history, the republic was preceded by the Nguyễn dynasty and followed by the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The state was proclaimed by Ho Chi Minh in Hanoi in 1945 after assuming power following the abdication of Emperor Bảo Đại a few days earlier, Later that year, the French reoccupied Hanoi and the First Indochina War followed. Bảo Đại became head of the Saigon government in 1949, which was then renamed the State of Vietnam. The DRV was re-established formally in the eyes of the West following the 1954 Geneva Conference at the end of the First Indochina War, when the country was partitioned at the 17th parallel. The DRV became the government of the North while the State of Vietnam retained control in the South.The communist Viet Minh (""League for the Independence of Vietnam"") shared power with non-communists and together controlled areas of North Vietnam between December 18, 1946 and July 20, 1954. However the communists gradually eliminated all the non-communists until, in February 1951, they announced the formation of the Lao Động Party (en: ""Labor"" Party) and openly avowed communism for North Vietnam. The communists (Lao Động Party) controlled the northern half of what is now the Socialist Republic of Vietnam between July 20, 1954 and July 2, 1976.The Geneva Accords promised elections in 1956 to determine a national government for a united Vietnam. The French accepted the proposal of Viet Minh delegate Phạm Văn Đồng, who proposed that Vietnam eventually be united by elections under the supervision of ""local commissions"". The United States countered with what became known as the ""American Plan,"" with the support of the State of Vietnam (which later became South Vietnam) and the United Kingdom. It provided for unification elections under the supervision of the United Nations, but was rejected by the Soviet delegation. During the Vietnam War (1955–75), North Vietnam and the Viet Cong supported by its communist allies, including the Soviet Union and China, fought against the military of the Republic of Vietnam government, the U.S. and the Free World Military Forces, including Australia, South Korea, Thailand and various smaller players. North Vietnam also fought alongside indigenous communist rebels in Cambodia and Laos against their respective US-backed governments. China and the Soviet Union feuded with each other over their influence in North Vietnam, as both wanted to make the country their satellite state. The war ended when the North Vietnamese forces violated the peace treaty and defeated the South Vietnamese army, which dwindled after American combat troops withdrew from the South about two years early. The two halves of Vietnam were reunited into one country, the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, in 1976.