* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spring Primaries & Caucuses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
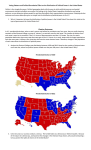
Announcing candidacy & organizing • Candidates officially enter the “race” to the Presidency • Campaign is organized for upcoming events: – Network of workers/volunteers (phone calls, publicity, planners, etc.) – Accounts created for future fundraising abcnews.go.com Pre-primary fundraising, campaigning, and debating • Candidates begin fundraising for the upcoming spring primary/caucus season • Campaigning for the party primary/caucus is in full swing during this time • Debates will be held between the main contenders washingtonpost.com Spring Primaries & Caucuses January-June of Election Year • Primary – an election where party members choose nominee for party • Open – any voter may vote in any party’s primary • Closed – only party members may vote in party primary (PA) • Caucus – meeting of party members to select nominee for party • Provides opportunity for members to debate, bargain, & express preferences • Open only to party members / activists attend Nationaljournal.com Iowa Caucus • First major electoral event in the election process. • Candidates campaign in Iowa months before the caucus – Ads, paid staffers, and publicity is centered around the many precincts in Iowa • The winner of the Iowa caucus has served as an indication of the person who will win their parties nomination New Hampshire Primary • First primary of election year • Focused upon by candidates – Media attention – Early success in contests / must perform well to continue in race nhhistory.org Nominating Convention • Official nomination of party candidate (decided in primaries & caucuses) • Party rally, media event, showcase for fall campaign • Adopt party platform (states party/candidate stance on issues) • Vice Presidential nominee selected & announced • VP chosen by party nominee iop.harvard.edu Fall Campaign After convention to Election Day • Candidates travel from state to state (speaking, rallies fundraising, etc.) • Focus on swing states (states that are contested) • Run TV ads to increase name recognition, spread ideas, “mudsling” • Debates held against opponent (media attention, show “likeability”, appear presidential, etc.) thesoundsofhistory.com General Election • Held on the Tuesday after the first Monday in November – November 2-8 • Eligible citizens of the U.S. cast votes for the candidate of their choice for President. • Popular vote winner in each state helps determine the electors who will cast the official vote in the Electoral College Time.com Electoral College December – After General Election • Distributes votes to states based upon # of senators & representatives • State’s popular vote winner earns all Electoral votes of state • Must earn majority (270) of Electoral votes to win election • Map: 2012 distribution • Used originally to “check” voters (uneducated & uniformed) census.gov Inauguration • Inauguration Day – January 20 – Established by 20th Amend. • “Swearing” in of the President – Presidential term officially begins at noon on January 20th • Supreme Court Chief Justice administers the oath Instanthistory.com “I do solemnly swear (or affirm) that I will faithfully execute the office of President of the United States, and will to the best of my ability, preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution of the United States.” -- Article II Sec. 1 • Inauguration Address