* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War (1945
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
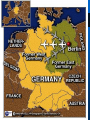
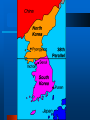
The Cold War The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The United Nations April 25, 1945 • Representatives from 50 countries meet in San Francisco to work on charter for the U.N. October 24, 1945 – U.N. comes into official existence. Official Charter of U.N. is created. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 United Nations Purposes: – Maintain peace – Provide security – Promote justice – Provide general welfare – Establish human rights The Cold War 1946 - 1991 United Nations The General Assembly – The “town meeting” of the world. – All U.N. members are EQUALLY represented – JOB: • To make suggestions on peaceful settlements of disputes • Elect all NON-permanent members of the Security Council and members of other agencies. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The International Court of Justice Modeled after the World Court – Purpose: • To decide legal questions referred to it by disputing nations • It gives advisory opinions when asked to do so, but does not enforce decisions. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Expanding Soviet Influence U.S.S.R. – Considered itself the leader of the Communist Revolution The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Two Worlds United States – Capitalism Soviet Union – Communism The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War Between Soviet Union and United States COLD WAR – A state of tension and military rivalry between nations that stops short of fullscale war. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Soviet Union Believed war against Communism and Capitalism was inevitable Believed the U.S. would lead an attack on Communism The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Soviet Union – No free speech – Crushed opposition – Broadcast anti-American propaganda. – No freedom of the press. – Government controls all industry. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Truman Doctrine Policy of containment – Contain what? • Soviet expansion. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Marshall Plan Secretary of State George C. Marshall The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Marshall Plan Designed to solve Europe’s economic problems – European economies = Poor • Why were they poor? – They had just spent a lot of money fighting World War II. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Marshall Plan Help European: – Factories – Farms – Transportation systems • Get them operating effeciently The Cold War 1946 - 1991 What did it do? Provided – Money – Machinery • To who? – Any nation who would like to participate – INCLUDING the Soviet Union The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Congressional Debate Block communism (contain it) by strengthening Europe’s economies U.S. can’t afford to carry “Europe on its back” The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Congress Approves the Plan The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Berlin Airlift Tension in Germany – Joint occupation of Germany The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Berlin Airlift June 24, 1948 – Soviets block all roads, canals, railways, and means of transportation between their side and the Western side. – Berlin under Soviet control The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Berlin Airlift British and American Planes 2 Million tons of food and supplies – To Berlin – Crisis resolved in 1949 with help of U.N. • Example of U.N. doing what? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 N.A.T.O. North Atlantic Treaty Organization – 9 Western European Nations • U.S. • Canada • Iceland • AN ALLIANCE – Against who? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 N.A.T.O. An attack against one or more of them would be considered an attack against all. – Alliance between: • Western Europe and U.S. Alliance The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Division of Korea 1910-1945 – Korea ruled by Japan – Japanese pushed out of Korea in WWII • General Douglas MacArthur – Named Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers and placed in charge of occupation forces in Japan. – Also in charge of South Korea. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 th 38 Parallel American Occupation – South Korea Soviet Occupation – North Korea The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Individual Governments North Korea – Sets up its own government South Korea – Sets up its own government Both governments claim control of all of Korea – Problem? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Review UN – General Assembly – Security Council – Cold War – Truman Doctrine – Marshall Plan – Berlin Airlift – NATO The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Korean Challenge June 25, 1950 – North Korea launches an invasion of South Korea • South Korea – recognized internationally as legitimate government of the People’s Republic of Korea – United Nations • Take steps to deal with problem The Cold War 1946 - 1991 United Nations Security Council – Votes unanimously for a cease fire between the Koreas. • Why would Soviet Union vote for this? – Or do they? – Soviet Union boycotting U.N. because: • U.N. does not recognize Communist China. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 United Nations Classify North Korea – An aggressor – Meanwhile: • President Truman pledges American Aid to South Korea The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Korean War United States • Truman orders U.S. air and ground forced ordered to Korea. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Problems South Koreans – Outnumbered – Soviet tanks given to North Korean Army – U.S. having trouble defending against tanks – Forced to southeast corner of South Korea The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Korean War General MacArthur – In charge of U.S. forces in Korea – Decides to launch a sea borne attack against the west coast of Korea and move eastward to take Seoul Importance of Seoul? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Seuol Capital of South Korea – Recaptured by MacArthur and the U.S. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 MacArthur Advances General MacArthur – North Korean troops retreat (that can) – Pushes North Koreans backward – Moves all the way to the Yalu River • The Yalu River borders China • China is Communist • What might be a problem for U.S. forces? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Tide Turns Against MacArthur Chinese “Volunteers” – Thousands help North Koreans – U.N. and U.S. troops with lines extended were outnumbered – U.N. and U.S. forces pushed back to 38th Parallel. • So what has been accomplished? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Threat of World War III War with China – Quick decisive action would bring an end to the conflict – according the MacArthur – OR • Start of WWIII – USSR openly would support China and get involved. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Spread of Troops Major war in Asia – Would mean what for the Soviet Union in Europe? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Stalemate in Korea President Truman – Orders MacArthur to establish a strong defense line on 38th Parallel. • Forbade blocking Chinese coast • Bombing China • Or helping Chinese Nationalists invade China • NO WAR with CHINA The Cold War 1946 - 1991 MacArthur vs. Truman MacArthur tries to appeal to Congress – MacArthur is removed – Truman • “I could do nothing else and still be President” • Matthew B. Ridgeway replaces MacArthur. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Point Four Program Extend aid to all less fortunate countries. – Underlying motive? – Think of it as a less intense Marshall Plan for the world. – Scientific Aid – Industrial Aid – Korean War demonstrates the serious threat of the spread of Communism. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Dwight D. Eisenhower Elected President in 1952 Promised to do everything in his power to end the Korean War The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Korea – Peace Talks Panmunjom – July 27, 1952 – Armistice • Recognized division of two countries at 38th Parallel • U.S. promises, in a treaty, to defend South Korea against any attack and to help S. Korea improve its economic conditions. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Korean War End 33,629 American Lives 1.5 Million Communist Casualties An unpopular war – Evidence of this? Increased prestige of U.N. – How? Think in terms of aggression. – Showed that the use of force COULD check Communist aggression. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 U.S. Foreign Policy Change Secretary of State – John Foster Dulles The Cold War 1946 - 1991 John Foster Dulles Brinkmanship – Communists only understood force – In order to maintain peace the United States must be ready for war • To be on the “brink” of war – No longer contain, but push back spread of Communism. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 The Arms Race Hydrogen Bomb – Vastly more powerful than atomic bomb – Soviet Union test first nuclear bomb – 1949 – Stockpiling • How is this dangerous? The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Soviet Union Nikita Khrushchev – Publicly attacked his predecessor • Joseph Stalin • “a cruel tyrant” The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Space Race Soviet Union launches Sputnik – Sputnik – orbited first artificial satellite • Showed that if the U.S.S.R. was capable of launching a satellite into space, the U.S.S.R. could launch a rocket that could deliver a hydrogen bomb to the U.S. • Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM) The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Cuban Missile Crisis Mutually Assured Destruction The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Cuban Missile Crisis Between U.S. and U.S.S.R. – President Kennedy – MAJOR conflict during Cold War The Cold War 1946 - 1991 What was it? October 15, 1962 – U-2 Spy plane photographs reveal: • • • • Construction of missile silos in Cuba Soviet Union behind the construction Cuban 90 miles from Florida What does this mean for U.S.? • Crisis lasts for two weeks The Cold War 1946 - 1991 John F. Kennedy “It shall be the policy of this nation to regard any nuclear missile launched from Cuba against any nation in the Western Hemisphere as an attack on the United States, requiring a full retaliatory response upon the Soviet Union. “ The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Kennedy’s Options an air attack on the missiles a full military invasion the naval blockade of Cuba, which was redefined as a more restrictive The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Cuban Missile Crisis Tension in the U.S. Option chosen: – Naval blockade of Cuba • Soviet Ships headed toward Cuba • Meet the blockage • Soviet Response – Ships turn back – A deal is struck The Cold War 1946 - 1991 Cuban Missile Crises Ends the Soviets dismantle the missiles in Cuba Exchanged for a no invasion agreement A secret removal of the Jupiter and Thor missiles in Turkey. The Cold War 1946 - 1991 U-2 Spy Plane Incident Shot down over Soviet Union Over Soviet Territory – Eisenhower “weather research” – Khrushchev furious Viewed by the Soviets as an act of aggression The Cold War 1946 - 1991