* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AHON Chapter 20 Section 1 Lecture Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
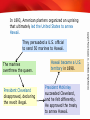
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Expansion in the Pacific TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Describe early attempts by the United States to expand in the Pacific. • List the reasons many Americans came to favor expansion. • Explain how the United States gained the territories of Samoa and Hawaii. • Describe how the United States protected its trading rights in China. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • Matthew C. Perry – Commodore of the navy who led a squadron of U.S. warships to Japan to open trade with the nation • Isolationism – policy of avoiding involvement in other countries’ affairs • Imperialism – building empires by imposing political and economic control over peoples around the world TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Liliuokalani – Queen of Hawaii who advocated for Hawaiian independence • sphere of influence – areas where another nation has economic and political control TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the United States acquire new territory and expand trade in the AsiaPacific region? In the mid-1800s, the United States was ready to take on new challenges. Finding new trading partners Acquiring new land TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. U.S. merchants longed to trade with Japan, which had blocked outside trade for 250 years. In 1853, Matthew C. Perry led U.S. warships into Tokyo Bay. The Japanese were awed by Perry’s ships. In 1854, Japan agreed to trade with the United States. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1867, U.S. Secretary of State William Seward arranged the purchase of Alaska from Russia. • He hoped to open trade in Asia and the Pacific. • Critics thought the land was worthless. They called the deal “Seward’s Folly.” Alaska turned out to be rich in gold and other resources. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Until the late 1800s, American foreign policy differed from that of many European nations. United States The U.S. generally pursued a policy of isolationism. It did not get involved in other nations’ affairs. European Nations Many nations undertook a policy of imperialism. They wanted to expand into new territories. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the late 1800s, however, America was gripped by a new spirit of expansionism. Supporters made several arguments about the benefits of expansionism. Promote economic growth Expansionism Spread American values TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Causes and Effects of U.S. Expansionism Causes • Western frontier closes. • European nations acquire overseas colonies and compete for resources and markets. • U.S. industry needs to acquire raw materials and find new markets in which to sell its products. • Some in the United States want to spread American culture and values. Effects • U.S. Navy grows in size and power. • United States gains control of territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific. • United States issues Open Door Policy (all nations can trade with China). • United States builds Panama Canal. • United States sends troops to Latin American nations to protect its own interests. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. U.S. expansionists expressed interest in many Pacific island chains, including Samoa. Three nations fought for Samoa. U.S. Britain Samoa In 1899, the United States and Germany divided Samoa. Germany The people of Samoa had no say in the matter. American Samoa is now a U.S. territory. German Samoa changed hands. New Zealand administered it until 1962 when it gained its independence, becoming Samoa. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Americans also eyed Hawaii, because its location was ideal for a military outpost between the United States and Asia. 1820 American planters came to Hawaii and set up huge sugar plantations. 1887 Planters forced the Hawaiian king to accept a new constitution. 1891 Liliuokalani became Hawaii’s queen. She advocated for Hawaiian independence. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1893, American planters organized an uprising that ultimately led the United States to annex Hawaii. They persuaded a U.S. official to send 50 marines to Hawaii. The marines overthrew the queen. President Cleveland disapproved, declaring the revolt illegal. Hawaii became a U.S. territory in 1898. President McKinley succeeded Cleveland, and he felt differently. He approved the treaty to annex Hawaii. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Expansion across the Pacific allowed the United States to gain resources, open new markets, and encourage trade. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the late 1800s, China was weakened by war. Other nations took advantage of this weakness. European powers and Japan forced China to grant them land and trading rights. They divided China into spheres of influence. U.S. Secretary of State Hay wanted to keep an “open door” in China. He wanted to preserve trade with China. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. To prevent the other powers from seizing Chinese territory, Hay issued the Open Door Policy. Open Door Policy America intended to preserve open trade with other nations. China should not be broken up into separate pieces. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1900, the United States helped end the Boxer Rebellion in China. • The Boxers opposed foreigners in China. • They staged a violent rebellion in 1900. The United States and other powers sent troops to end the rebellion.