* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 1 Respiratory System
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
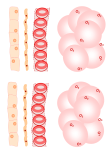
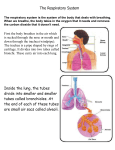
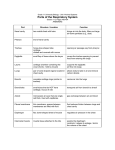
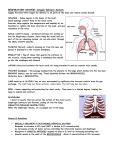
ACTIVITY 1: How do your Ribs move? Inhale at your maximum and measure the circumference of your chest; Exhale at your maximum and measure the circumference of your chest; Write a report on the paper given and get a conclusion. WHY IS OXYGEN SO IMPORTANT? NUTRIENTS + O2 = H2O + CO2 + ENERGY WITHOUT OXYGEN NO LIVING THINGS ARE ABLE TO USE THE NUTRIENTS OBTAINED THROUGH FOOD! What gases compose the air we breathe? Exchanging O2 and CO2 How does O2 get to our cells? O2 and other gases get to our body when we inhale, then red blood cells transport the molecules throughout the body. Why can’t we keep CO2 inside our bodies? CO2 is a toxic gas. ACTIVITY 2: Red Blood Cells and Gas Transportation The Picture shows a Red Blood Cell in two different stages, the “young” and the “mature”; What can you observe and conclude? Use your Science Report to write down your observations and conclusions. Tip: Young cells present all the organelles but when they go mature these organelles are all digested leaving just na empty space inside the cell. HOW DOES AIR MOVE IN AND OUT OF OUR LUNGS? Especialized muscles that help us inhale and exhale: diaphragm, abdominal and pectoral muscles. ACTIVITY 3: The Lung Model Chapter 2, Page 39 INVESTIGATE: LUNGS Develop the model and answer the two questions on the Science Report; Develop the Challenge (list of materials and diagram must be on the report). Cellular Respiration Inside your cells, a process called Cellular Respiration uses O2 in chemical reactions that release energy. NUTRIENTS + O2 = H2O + CO2 + ENERGY (sugars) TOXIC WASTE ! Where does the reaction happen? Mythocondria Structures in the Respiratory System The respiratory system is made up of many structures; These structures function together; They move air in and out your body (keep out harmful material!) Nose Inside your nose, tiny hairs called cilia filter dirt and other particles; Mucus also help trapping particles; Nasal cavity warms and moistures air. Throat and Trachea Right after the nasal cavity air moves down your throat toward a tubelike structure called Trachea; A structure called Epiglottis keeps food from entering your trachea. Esophagus (food) (air) Lungs Lungs Air moves into the lungs through the bronchial tubes (bronchi); Branchial tubes branch throughout the lungs into smaller and smaller tubes; At the ends of the smallest tubes, air enters tiny air sacs called alveoli. ALVEOLI GAS EXCHANGE! Ribs The rib cage encloses a space called the thoracic cavity; This cage is flexible, which makes room for the lungs to expand (O2 intake); Diaphragm The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity; It plays a vital role in the respiratory system! REVIEW... FOR NEXT WEEK... Summarize pages 42 and 43; Answer 2.1 Review (from 1 to 6)