* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human System Powertool with pictures
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
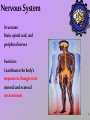
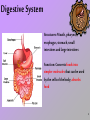
Organ Systems Teamwork 1 11 Systems in the Human Body… Nervous Skeletal Digestive Muscular Integumentary Respiratory Excretory Endocrine Reproductive Lymphatic Circulatory 2 3 Nervous System Structures: Brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves Function: Coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments 4 Digestive System Structures: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines and large intestines Function: Converts foods into simpler molecules that can be used by the cells of the body; absorbs food 5 The digestive system does not work without the help of other organ systems. The digestive system needs the cardiovascular system to deliver the nutrients to other organs in the body such as the muscles and the brain. 6 Circulatory System Structure: Heart, blood vessels, and blood Function: Brings oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells; fights infections; and regulates body temperature 7 Respiratory System Structures: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungs Function: Provides oxygen needed for cellular respiration and removes excess carbon dioxide from the body 8 The circulatory system depends on the pulmonary system (lungs) to deliver oxygen to muscles and other organs. 9 Skeletal System Structures: Bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons Function: Supports the body; protects internal organs; allows movement; stores mineral reserves; and provides a site for blood cell formation 10 Muscular System Structures: Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle Function: Works with skeletal system to produce voluntary movement; helps to circulate blood and move food through the digestive system 11 Muscles and bones work together to produce movement. 12 Excretory System Structures: Skin, lungs, kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Function: Eliminates waste products of metabolism from the body and maintains homeostasis 13 Integumentary System Structure: Skin, sweat and oil glands, hair, and nails Function: Serves as a barrier against infection and injury; helps to regulate body temperature; and provides protection against ultraviolet radiation from the sun 14 Lymphatic System Structures: White blood cells, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and lymph vessels Function: Help protect the body from disease; collects fluid lost from blood vessels and returns the fluid to the circulatory system 15 Getting rid of waste is another necessary function of the body: • Lungs get rid of carbon dioxide. • Lymphatic vessels recycle extra fluids that build-up next to cells and tissues. • Kidneys filter the blood of toxins. • Skin releases excess salts through sweat. 16 Endocrine System Structures: Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries (female), and testes (male) Function: Controls growth, development, metabolism and reproduction 17 Reproductive System Structures: Testes, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, and penis (males); ovaries, Fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina (females) Function: Produces reproductive cells, in females, nurtures and protects developing embryo • Reproduction, growth and development are critical functions of all living things. • The endocrine system provides the chemical messages for growth, development, and proper functioning of the reproductive system. 19 Blood sugar is too high Pancreas releases insulin Sugar level goes to… Sugar level goes to… Homeostasis Homeostasis Pancreas releases glucogen Blood sugar is too low 20 21