* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download W1D4 - The Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
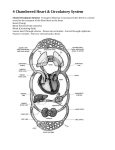
Warm-up Patice takes a bite out of her cheeseburger from McDonalds. Write out all of the digestive system organs the cheeseburger goes through. Mouth Esophagus Stomach Duodenum/ Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum/Anus What does ATP stand for? Adenosine Triphosphate Mr. Mah Living Environment Lecture 4 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AIM: How does the circulatory system help us to main homeostasis? Review: Homeostasis A set of stable conditions that are maintained inside an organism (staying the same). It is necessary for life. An organism that cannot maintain homeostasis may get sick or die Digestive System helps maintain Homeostasis by making sure the body has enough food and nutrients for survival What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body. The Heart pumps blood and substances around the body in tubes called blood vessels. The Heart and blood vessels together make up the Circulatory System. Parts of the Circulatory System Heart Blood Arteries Veins Capillaries The Heart Has 4 chambers; 2 atria (Left Atrium, Right Atrium) and 2 ventricles (Left Ventricle, Right Ventricle). Blood flows through the heart in one direction. Valves control the blood flow. A bunch of nerve cells at the top of the right atrium, called the pacemaker, controls heart rate (how fast the heart beats). Blood Flow Through the Heart Remember, there are 4 chambers of the heart (Left Atrium, Right Atrium, Left Ventricle, Right Ventricle). Blood that comes back from your body first enters the Right Atrium, into the Right Ventricle, where it gets pumped to the Lungs to get oxygen. Blood Flow Through the Heart Follow the Blue Arrows. Blood first enters into the Right Atrium, then goes into the Right Ventricle. It gets pumped to the lungs through the Pulmonary Artery. Respiratory System Interaction Blood from the Right Ventricle travels through the Pulmonary Arteries into the lungs for oxygen Then comes back to the heart into the Left Atrium through the Pulmonary Veins. The blood goes into the Left Ventricle, where it gets pumped to the rest of the body through the Aorta Blood Flow Through the Heart Follow the Red Arrows. Blood first enters into the Left Atrium, then goes into the Left Ventricle. It exits the heart from the Aorta Blood Flow Through the Body Blood Complex mixture of cells, water, and various proteins and sugars. Fifty-five percent is plasma (liquid). Forty-five percent is solid. 4 Main Parts of Blood red blood cell platelets white blood cell plasma What’s In Blood? digested food red blood cells white blood cells oxygen waste (urea) platelets carbon dioxide plasma hormones Arteries Carry blood AWAY from the heart. Large, thick-walled, muscular, and elastic Veins Carry blood back to the heart Blood returns to the heart through the veins. Thin blood vessels with valves which bring the blood back to the heart. Has valves which act to stop the blood from going in the wrong direction. Capillaries CONNECT arteries and veins, it is here that substances are loaded and unloaded into the blood. Dense network of tiny blood vessels that make sure the oxygen and nutrients in our blood reach all the cells in our bodies. The thin capillary walls (ONE CELL THICK!) allow nutrients and gases to diffuse (move) easily between blood cells and surrounding tissue. The CAPILLARY A collection of capillaries is known as a capillary bed. artery vein body cell capillarie s Arteries Capillaries Veins Follow A Red Blood Cell Through the Body Start in the Right Atrium: Right Atrium Right Ventricle Pulmonary Arteries Lungs Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Left Ventricle Aorta Arteries Capillaries Veins Right Atrium Are you alive? Check your PULSE! Place two fingers (index and middle) on your wrist (thumb side) right under your thumb Press firmly against the bone until you feel a pulse Count the number of beats for 30 seconds, then multiply that number by 2