* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download circulatory and respiratory systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
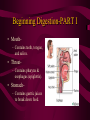
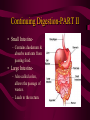
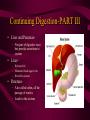
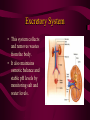
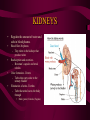
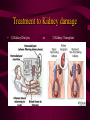
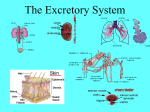
DIGESTIVE AND EXCRETORY SYSTEMS Science, Technology, & Society MR. CANOVA Period 11 THE NEED FOR FOOD • Food • Energy • Vitamins, Minerals, and Water Food • The amount of energy you need depends on many factors such as age, sex, rate of growth, and physical activity. • Nutrient- a substance required by the body for: – Energy – Growth – Repair – Maintenance • Digestion- The process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use. (ATP) • calorie- the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius • Calorie (food)= 1000 calories SOURCES OF ENERGY • CARBOHYDRATES: – • PROTEINS: – • Organic compounds with Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen the provide nutrients. • Breads, Pasta, Grains, Cereals, Potatoes, Fruit Organic compounds with one or more chains of amino acids • Fish, Eggs, Poultry, Beef, Pork, Nuts, Legumes, Milk, Cheese, Tofu FATS: – Organic compounds (lipids) that are insoluble in water. Act as padding and insulation • Milk, Cheese, Meats, Butter,Olives, Avocados, Fried Foods, Oils, Chips Building Materials • Substances that don’t provide energy, but regulate the amount released within the body. • VITAMINS – • MINERALS – • ORGANIC NATURALLY OCCURING INORGANIC WATER – NATURALLY OCCURING • • 2/3 OF BODY’S WEIGHT IS WATER OBESITY- BEING MORE THAN 20 PERCENT HEAVIER THAN YOUR IDEAL BODY WEIGHT – BMI INDEX DIGESTIVE SYSTEM • Food • Energy • Vitamins, Minerals, and Water • The taking in of food, breaking it down into molecules small enough for the body to absorb, and getting rid of undigested molecules and waste – IMPORTANT FACTS: • STARTS AT THE MOUTH, ENDS AT THE ANUS • FOOD TRAVELS MORE THAN 26 FEET • HAS OVER 10 STRUCTURES INVOLVED IN THE PROCESS Beginning Digestion-PART I • Mouth– Contains teeth, tongue, and saliva. • Throat– Contains pharynx & esophagus (epiglottis). • Stomach– Contains gastric juices to break down food. Continuing Digestion-PART II • Small Intestine– Contains duodenum & absorbs nutrients from passing food. • Large Intestine– Also called colon, allows the passage of wastes. – Leads to the rectum. Continuing Digestion-PART III • Liver and Pancreas– Not part of digestive tract but provide secretions to system • Liver– Releases bile – Maintains blood sugar levels – Detoxifies poisons • Pancreas– Also called colon, all the passage of wastes. – Leads to the rectum. Excretory System • This system collects and removes wastes from the body. • It also maintains osmotic balance and stable pH levels by monitoring salt and water levels. EXCRETION • The process that rids the body of toxic chemicals, excess water, salts, and CO2 • Major Organs – Lungs (CO2) – Kidneys (Nitrogen waste (urea)) – Skin (Water, Salts) KIDNEYS • Regulate the amount of water and salts in blood plasma. • Blood filter-Nephrons – Tiny tubes in the kidneys that produce urine Reabsorption and secretion– Bowman’s capsule and renal tubules Urine formation- Ureters – Tubes that carry urine to the urinary bladder Elimination of urine- Urethra – Tube that urine leaves the body through • • • • Male (penis) Female (Vagina) Damage to the KIDNEYS • • • • Diseases Accidents Infection, Diabetes, high blood pressure, body’s own immune system Household chemicals – Paint, Varnishes, Furniture oils, glues, aerosol sprays, air fresheners, lead • When any of the above occur: – Toxic wastes such as urea, accumulate in the plasma and bloodplasma ion levels increase to dangerous amounts. Treatment to Kidney damage • 1) Kidney Dialysis or 2) Kidney Transplant