* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download animal kingdom - Biology Junction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
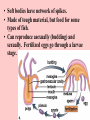
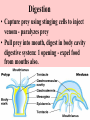
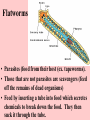
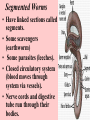
ANIMAL KINGDOM Characteristics of all Animals • They are made of cells, which form tissues, which form organs which form organ systems. • They obtain food by eating other organisms (herbivores, carnivores or omnivores). • Most animals reproduce sexually but some can reproduce asexually. • All animals move in order to satisfy 1 of their basic needs (food, water, shelter, escaping danger) Types of food eaters Carnivore meat eater (either a predator prey relationship or a scavenger) Herbivore plant eater Omnivore - eats plants and meat Division of animals Animals have bilateral symmetry (1 line that can divide the animal into 2 identical parts) or radial symmetry ( many lines that can divide the animal into equal parts). Sub Kingdom: Invertebrates • Phyla Include: • Sponges • Cnidarians • Worms Phylum - Sponge • Simplest form of animal • No tissues or organs • heterotrophic & cells that have specialized jobs • Bodies pierced all over with openings called pores How do Sponges eat & breathe? • Collar cells on the inside of central cavity trap bacteria & protists & digest them. • Sponges get O2 by diffusion. • Soft bodies have network of spikes. • Made of tough material, but food for some types of fish. • Can reproduce asexually (budding) and sexually. Fertilized eggs go through a larvae stage. Phylum - Cnidarians • Carnivores use stinging cells to capture prey & defend selves. • Specialized tissues - no organs. • Radial symmetry Phylum - Cnidarians 2 body types: polyp (like a vase with a mouth opening at the top) and medusa (bowl shaped). Digestion • Capture prey using stinging cells to inject venom - paralyzes prey • Pull prey into mouth, digest in body cavity digestive system: 1 opening - expel food from mouths also. Reproduction • asexually by budding & sexually. • Some have both sexes within 1 individual others in separate individuals. • Examples include jellyfish, sea anemones and coral. Worms - 3 phyla • Flatworms (Platyhelminthes) • Roundworms (Nematoda) • Segmented worms (Annelida) All Worms… • Have tissues, organs and organ systems. • Have bilateral symmetry. • Have a brain. • Reproduce both sexually and asexually. • Can replace parts by a process called regeneration. Flatworms • Parasites (food from their host (ex. tapeworms). • Those that are not parasites are scavengers (feed off the remains of dead organisms) • Feed by inserting a tube into food which secretes chemicals to break down the food. They then suck it through the tube. Roundworms • Live in moist environments. • Some are herbivores, some carnivores, some parasites (worms that dogs and cats get are parasites). • The digestive system is 1 long tube where food goes in 1 end and waste exits at the other end. Segmented Worms • Have linked sections called segments. • Some scavengers (earthworm) • Some parasites (leeches). • Closed circulatory system (blood moves through system via vessels). • Nerve cords and digestive tube run through their bodies.