* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an Animals PPT notes
Territory (animal) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Animal testing wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Remote control animal wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
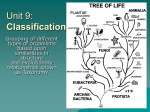
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – What is an Animal? Animals & Their Environment 2016 So, what is an animal? Take a few minutes and at your table discuss characteristics that help to define what an animal is. Share Now… let’s see how close we came... An animal is… What is an Animal? To recap the video Animals are Heterotrophs They need to eat other organisms (plants or animals) Plants are autotrophs – they get their energy from the sun and make their own food Animals are capable of movement DNA and Genetics DNA demonstrates that animals share similar characteristics Animals are grouped into families Plants are also grouped into families, but different DNA Animals are multicellular SO are many other organisms, but this is a definite characteristic of animals Cells can specialize in animals, unlike cells in plants. Cells create organs, eyes, skin, bones, etc. From the video we know that… Animals are Heterotrophs (must eat other organisms) Animals can move Animal DNA is able to demonstrate shared characteristics to group into families Animals are multicellular Animal cells can specialize (bones, tissue, organs) So, is there more? Metabolic Dormancy All living things enter into some state of dormancy Three types of dormancy Hibernation “winter sleep” Low body temperature Slow breathing Low heart rate Low metabolism Aestivation Similar to Hibernation Found in areas of HIGH temperatures Lower metabolic rate Inactivity – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Torpor A state of reduced activity Winter – Hibernation Summer(heat) – Aestivation Decreased physiological activity in response to limited food Can be days, weeks, or months Reproduction Most animals reproduce through sexual reproduction (male and female A few exceptions – Asexual reproduction – Offspring develop as a growth on the parent – Examples are Jellyfish and corals Haploid and Diploid (cell types) Diploid – Have 2 complete sets of chromosomes – Reproduce through Mitosis (exact replicas) – Examples: skin, blood, muscle cells Haploid – Have only 1 complete set of chromosomes (half) – Reproduce through Meosis – Cells for sexual reproduction – “Gametes” or sperm and ova – Predator, Prey Or Scavenger? Predator Hunts other animals as primary food source Top level is the one at the top of the food chain Some predators can be prey – Prey Any animal that is eaten by another animal Some prey animals are also considered predators Some are simply prey animals Scavengers Animals that eat Carrion (dead animals) Some predators will scavenge when prey is not available Food Source Carnivore – eats meat Herbivore – eats plants Omnivore – eats plants and meat Binomial Classification System As early as 350 B.C. man has been classifying animals and plants Aristotle developed the first classification “ladder of nature” Latin is the typical language used to classify living organisms Common names can be confusing New species are being found even today – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Name of a species from the classification systems groups them into similar characteristics Classification System Domain Based on RNA Three domains: – Archaea (Single cell organisisms – Prokaryotes) Have no cell nucleus – Bacteria – Eukarya (Eukaryotes) Cells have a nucleus – animals fall into this category Kingdoms (six of them) Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria) Eubacteria (true bacteria) Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia (ANIMALS) Phylum (organisms that have something in common) Animal Phylum – Chordate – have a backbone (Fish, Reptiles, Birds, Amphibians, and Mammals) – Arthropod – exoskeleton (Insects, Arachnids, and Crustaceans) – Mollusk - soft body with hard shell (Snails, Slugs, Octopus, Squid, Clams, Oysters, and Mussels) – Annelid – segmented worms (worms and leeches) – Rotifer – microscopic with wheel-shaped mouths – Nematodes – non-segmented worms (roundworms) – Tardigrade – tiny slow-moving animals with 4 body segments & 8 legs (water bears) – Cnidarian – soft-bodied, jelly-like, with tentacles (Hydra, Jellyfish, Anemones, and Coral – Echinoderm – spiny with arms reaching out from center (starfish and sea urchins) – Platyhelminthes – soft, flat-bodied worms (planarians and tapeworms) – Class smaller groups The Chordate phylum splits into – Mammalia (mammals) – Actinopterygii (bony fish) – Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous Fish) – Aves (Birds) – Amphibia (Amphibians) – Reptilia (Reptiles) Order Even smaller groups! – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Mammalia splits into several including: – Carnivora – Primate – Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates – hoofed animals) – Rodentia – Family Different groups that have similar features Carnivora splits into smaller groups such as: – Felidae (Cats) – Canidae (Dogs) – Ursidae (Bears) – Mustelidae (Weasels) Genus First part of a “scientific name” Smaller group with very similar features and closely related Felidae splits into: – Felis (small Cats and domestic Cats) – Panthera (Tigers, Leopards, Jaguars and Lions) – Puma (Panthers and Cougars) Species Second part of a scientific name Use both Genus and Species when Identifying animals This is a unique group – all have the same characteristics So… what’s in a name? Tiger Kingdom: Animalia (Animal)Phylum: Chordata (Vertebrate) Class: Mammalia (Mammal) Order: Carnivora (Carnivore) Family: Felidae (Cat) Genus: Panthera Species: Panthera tigris (Tiger) Activity Pick 4 animals and complete the worksheet to “classify” them