* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Red Blood Cells - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
ABO blood group system wikipedia , lookup
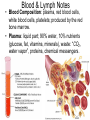
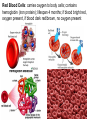
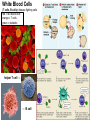
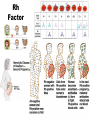
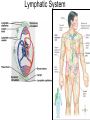
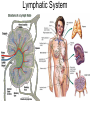
OBJ: Given notes, activity sheet SWBAT explain blood composition, blood types and the function of the Lymphatic System with 70% accuracy. BRING IN TEXTBOOK DN: HW check- A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Booklet; Watch Video: Blood, Blood Types ACT: Introduction to Blood and Lymph (Notes) Text, Read p. 91-97, Work on Blood & Lymph Booklet Watch Video: Lymphatic System HW: Complete Blood & Lymph Booklet; Work on CRE Review Sheets; CRE EXAM, March 9; INERH EXAM, March 20. Blood & Lymph Notes • Blood Composition: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets; produced by the red bone marrow. • Plasma: liquid part; 90% water, 10% nutrients (glucose, fat, vitamins, minerals), waste: “CO2, water vapor”, proteins, chemical messengers. Red Blood Cells: carries oxygen to body cells; contains hemoglobin (iron protein); lifespan 4 months; if blood bright red, oxygen present, if blood dark red/brown, no oxygen present Blood & Lymph Notes • White Blood Cells: disease fighting cells; lifespan months-years; specialized cells • Example: – Cells: alarm system (T-cells & B-cells) – Cells produce chemicals (antibodies) to fight invasion – Cells that attack the invaders Immune System (WBC’s) Platelets: clot blood; produces fibrin protein White Blood Cells (T cells, B cells): disease fighting cells red = red blood cells orange = T cells green = platelets helper T cell → ← B cell Blood & Lymph Notes Blood Types: A, B, AB, O; three allele types: A, B, O Universal Receiver: AB Universal Donor: O Transfusion: transfer of blood from one organism to another organism; if blood clumps, clogs capillaries, results in death Blood & Lymph Notes • Blood Type: surface molecules found on red blood cells • Rh Factor: also surface molecules found on red blood cells – If Rh +, have Rh factor – If RH -, don’t have RH factor – If Rh- but have received RH+ blood, leads to clumping of blood and death Rh Factor Blood & Lymph Notes • Lymphatic (Filtering) System: cleans and returns fluid to Circulatory System • Lymph: contains water, glucose, white blood cells • Lymph Nodes: traps invaders microorganisms (bacteria); node – “filter” Lymphatic System Lymphatic System