* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood - Everglades High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
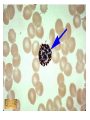
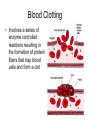
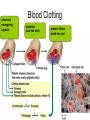
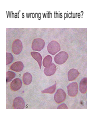
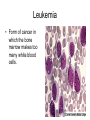
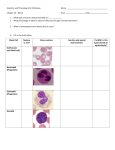
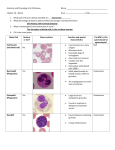
Circulatory System Blood Blood • In general, the blood is a fluid tissue helping to maintain homeostasis for all cells in the body. • Transport of needed substances to body cells. (oxygen, amino acids, glucose, fatty acids, glycerol, salts, etc.) • Transport of wastes from cells. (urea, water, carbon dioxide in the form of the bicarbonate ion) • Helps to maintain a constant body temperature • Aids the body in fighting disease Composition of blood • Blood transports materials through out the body inside blood vessels. • Blood is a tissue of fluid & cells – plasma • liquid part of blood • dissolved salts, sugars, proteins, and more – cells • red blood cells (RBC) – transport O2 in hemoglobin • white blood cells (WBC) – defense & immunity • platelets – blood clotting Plasma • Straw colored, nonliving part of blood. • 90% Water • Helps to regulate body temperature • Contains Electrolytes • Plasma transports blood cells, products of digestion and hormones throughout the body. How much blood is in the human body? • About 5 liters About 7 % of your body mass About 4.5- 5.6 Liters in an adult human Men = 5.6 Liters Women = 4.5 Liters Pregnant woman = 5.0 Liters The Functions of Blood - Delivers: Picks Up: Nutrients - waste kidneys Oxygen, Water, - carbon dioxide lungs minerals Hormones and enzymes - heat skin Pollutants Erythrocytes Red Blood cells: • Shaped like round plates indented in the center. • Have no nucleus when mature • Most numerous • Smaller than white blood cells • Produced in the red marrow of long bones • Destroyed in the liver and spleen • Contains the iron protein compound HEMOGLOBIN whose chief function is to combine with oxygen and carry it to cells Why is blood red? • Blood is red because it contains hemoglobin and iron rich pigment. What does hemoglobin do • Hemoglobin picks up the oxygen molecules and drops off CO2 • 250,000 hemoglobins in 1 red blood cell Carbon Monoxide • Binds to RBC better than oxygen. • Not good • Kills us silently • Cant smell it or taste it. Anemia • Occurs when the blood does not have enough hemoglobin. • Treated by taking in more iron • Because iron makes up hemoglobin Leukocytes White blood cells • Fight infections by forming antibodies or engulfing bacteria • Large in size, several different types • Have a nucleus • Phagocyte • About 8,000 per drop of blood • Most are formed in the bone marrow or in the lymph tissue Phagocytes • Engulf bacteria and viruses by phagocytosis • Able to leave the bloodstream and move between the cells of the body by squeezing through the capillary walls Lymphocytes • Produce antibodies which clump bacterial poisons or bacteria (antigens) – Antigens: foreign substances in the body Platelets • • • • Smallest part of blood No nucleus Live 2-4 days Involved in clotting of blood • Creates fibrin – Enzyme that helps clot blood Blood Clotting • Involves a series of enzyme controlled reactions resulting in the formation of protein fibers that trap blood cells and form a clot chemical emergency signals Blood Clotting platelets seal the hole protein fibers build the clot What’s wrong with this picture? Sickle Cell Anemia • Genetic disease • Red blood cells become sickle shape • Cant carry as much oxygen Malaria • Disease that attacks the RBC. • Causes high fever • If you have sickle cell shaped RBC can not get the disease. Leukemia • Form of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells.