* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
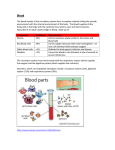
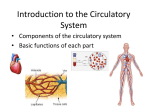
Life Science Unit Overview: Chapter 1 – Structure of Living Things •Lesson 1 – Cells •Lesson 2 – From Cells to Organisms •Lesson 3 – Diversity of Organisms Chapter 2 – Plant Structures and Functions •Lesson 1 – Vascular Plants •Lesson 2 – Plant Transport Systems •Lesson 3 – Photosynthesis and Respiration Chapter 3 – Human Body Systems •Lesson 1 – The Human Body •Lesson 2 – The Digestive System •Lesson 3 The Respiratory System •Lesson 4 – The Circulatory System •Lesson 5 – The Excretory System The Circulatory System Lesson Overview: 1) What do we already know? (The Heart) 2) Vocabulary 3) Drawings 4) Main Ideas 5) Review Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 1 The Circulatory System: What do we already know? BrainPOP Teaser 1) How do the diaphragm and lungs work together? a) The diaphragm helps us inhale and exhale air into and out of the lungs. 2) Where does gas exchange take place? a) In the alveoli Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 2 The Circulatory System: Vocabulary Part I 1) heart: an organ that constantly pumps blood throughout the body. 2) artery: carries blood mixed with oxygen (oxygen rich blood) AWAY from the heart. 3) vein: carries blood mixed with carbon dioxide (oxygen poor blood) BACK to the heart. 4) capillary: smallest blood vessel with very thin walls. Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 3 The Circulatory System: Drawings (pg. 145) Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 4 The Circulatory System: Drawings (pg. 147) You will need to be able to label this on the test. Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 5 The Circulatory System: Drawings (pg. 150) Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 6 The Circulatory System: Main Ideas 1) How are materials transported through your body? (pg. 144-145) a) – First, blood from your heart is pumped into your lungs via arteries. Arteries carry blood rich oxygen and nutrients from your digestive system to your organs, cells and tissues. The blood then returns to the heart via veins carrying carbon dioxide and other waste. Quick Check (pg. 145) -Critical Thinking: Why does your body need a circulatory system? a) It is needed to transport food, oxygen and nutrients to all cells, tissues and organs in the body. It also carries away waste. Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 7 The Circulatory System: Main Ideas 2) What are the parts of the heart? (pg. 146-147) a) aorta, right atrium, left atrium, heart valves, right ventricle and left ventricle. Quick Check (pg. 147) -Critical Thinking: What do you think happens to a person when the heart valves are not working? a) Blood could flow the wrong direction causing serious health concerns. Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 8 The Circulatory System: Main Ideas 3) How do blood and blood vessels work? (pg. 148-149) a) Blood absorbs and transports oxygen, nutrients, waste and carbon dioxide through out the body. Blood vessels are the muscular tubes that blood travel through. Quick Check (pg. 149) -Critical Thinking: Why are there more red blood cells that white blood cells? a) red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients, therefore there needs to be more of them. White blood cells are only a defense system that fights off infections and germs. Human Body Systems: Lesson 4 Page 9 The Circulatory System: Review 1) Summarize the main ideas 1) Click to Watch! 2) Think, Talk, and Write Human Body Systems: Lesson 4