* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxygen - Noadswood Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
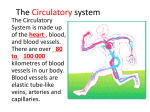
How does oxygen get around your body? L/O ;- To know the pathway of oxygen through the circulatory system Is blood ever blue? Human blood is never blue but some animals e.g. the horseshoe crab have copper in their blood instead of iron which makes it blue instead of iron What is the job of the circulatory system? What organs do you think are in the circulatory system? The circulatory system consists of the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries Circulatory System Oxygen • Oxygen is initially absorbed into the blood within the lungs (via diffusion) • It will now travel through a variety of systems in order to get to the cell, where it is needed for… RESPIRATION! Traveling • Blood travels through three types of vessel - arteries, veins and capillaries with have specific properties: – Arteries are thick-walled muscular tubes which carry blood away from the heart - fast flowing! – Veins are thin walled tubes which carry blood back to the heart – they have a large diameter and valves as the blood flows slower – Capillaries are extremely narrow tubes which carry blood through our tissues: their walls are just one cell thick - so thin that oxygen, food and waste products can easily pass through them Blood • Blood is a liquid tissue whose function is to fight disease and to transport materials around the body • • • • Blood plasma (liquid) containing glucose, amino acids, nutrients, hormones, as well as waste materials like urea Red blood cells contain haemoglobin, a protein which picks up oxygen molecules in the lungs White blood cells fight disease by making antibodies and fighting germs Platelets are cell fragments. Together with fibrinogen they form clots to repair cuts or tears in nearby tissue Heart • What do you know about our heart? How does it work? How is it specialised? • The heart pumps blood around the body – in humans this is a four chambered pump • The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen • The left side of the heart pumps the oxygenated blood from the lungs around the rest of the body (which is why it is more muscular) Heart • The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen • The left side of the heart pumps the oxygenated blood from the lungs around the rest of the body (which is why it is more muscular) Cells • Oxygen and glucose leak out of the capillaries and the cells close by absorb the required oxygen and glucose • The waste products (including carbon dioxide) pass out of the cells and into this fluid, that is then reabsorbed by the blood • Capillaries do not join up to every cell - instead fluid is passed out of them, with cells close by absorbing what they need Summary • Oxygen enters the body in the lungs, via breathing • It is absorbed into the blood, where it passes through the heart and then throughout the body (via the circulatory system) • It travels through arteries, veins and capillaries • Cells and blood exchange materials in the fluid, which is released adjacent to the capillaries • The cells then use this oxygen for respiration Worksheet • Match the circulatory key words with their function • Complete the circulatory system worksheet Arteries Heart Veins Capillaries One cell thick