* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Skin - Education Service Center, Region 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
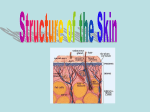
The Integumentary System Skin • The largest organ in your body • Functions • • • • • • • Covers the body and prevents water loss Protects the body from injury and infection Regulates body temperature Eliminates wastes (sweat) Produces vitamin D Gathers information about the environment Stores fat for fuel and insulation Organs of the integumentary system The name is derived from the Latin integumentum, which means “a covering.” skin hair nails Label and color the parts of the integumentary system finger nail Prevents Water Loss Skin prevents water from leaking out of your body. Prevents Infection Skins acts as a barrier to bacteria and viruses. Eliminates Waste Sweating eliminates dissolved waste from your body. Gathers Information Skin contains nerves that can feel pain or pressure. Provide Vitamin D With the help of sunlight, your skin produces vitamin D Vitamin D is essential in calcium absorption from food Maintains Homeostasis Helps to keep the body temperature normal Has blood vessels that tell the body when it is hot or cold Hot – blood vessels get larger and sweating occurs Cold – blood vessels constrict to keep blood in the body’s core Layers of Skin Skin consists of three main layers epidermis dermis subcutaneous layer subcutaneous layer Epidermis Epidermis – the upper layer of skin where nails grow and where melanin in located. Every minute, 30,000 - 40,000 skin cells fall off 95% of your skin cells make new cells 5% make melanin More sun exposure = more melanin (tan) dermis - middle layer of skin that contains nerves, blood vessels, sweat glands, oil glands and hair follicles. subcutaneous layer – acts as a fat storage to provide warmth and to absorb shock. hair Made of a strong, dead protein, called keratin. Grows out of a tiny tube called a follicle. Hair growth is caused by rapid mitosis in the follicle. Hair follicles are everywhere except lips palms soles hair Over 100,000 follicles on the scalp. Each follicle is attached to a gland that secretes sebum (oil). Color is partially determined by melanin. nails Modified hair that grows from your cuticle. Made of keratin. No nerve endings. Protects the end of fingers and toes Takes 6 months to grow from cuticle to tip. nails Fingernails grow faster than toenails. Nails grow faster on your dominant hand. Nails DO NOT grow after death! Body systems that work with the integumentary system; respiratory system to get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. circulatory system to deliver oxygen. excretory system to eliminate waste. The integumentary system is similar to the cell membrane in a cell. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z5VnOS9Ke3g