* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fertilization and Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
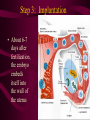
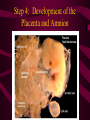
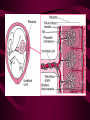
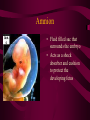
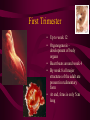
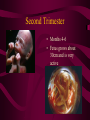
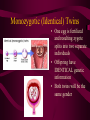
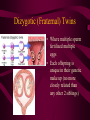
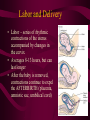
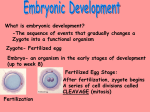
Fertilization and Development Step 1: Fertilization • Process of sperm fusing (joining) with an egg • Produces a zygote (fertilized egg, diploid cell) • In humans, this occurs in the oviduct External fertilization • Gametes fuse outside of the female’s body • Involves hormone/behavior controls • Involves the release of hundreds of gametes at the same time. Internal fertilization • Gametes fuse inside the female’s body • Advantage: no longer need to have part of life cycle attached to water • Requires specialized organs to deliver sperm into the female’s body Step 2: Mitotic Cell Division of the zygote to form embryo • During this time, the embryo is receiving nourishment from a small amount of stored yolk Step 3: Implantation • About 6-7 days after fertilization, the embryo embeds itself into the wall of the uterus Step 4: Development of the Placenta and Amnion Placenta • Organ made up of both mother’s and embryo’s blood vessels • Site of nutrient, oxygen, and waste exchange • Does NOT allow mother and embryo blood to mix rather, the nutrients and wastes DIFFUSE between the blood vessels • Acts a filter for SOME substances (alcohol, caffeine, some viruses CAN pass through) • Umbilical cord – attaches the embryo to the placenta. Is cut away after birth and the scar becomes the naval. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome • Group of disorders caused when a pregnant females consumes alcohol – Includes brain damage, stunted growth, learning disabilities, physical deformities – Most dangerous during first trimester (3 months) because the organs are DEVELOPING the most during this time period – Affects approx. 1 in 750 births (CDC) Amnion • Fluid filled sac that surrounds the embryo • Acts as a shock absorber and cushion to protect the developing fetus Step 5: Cellular Differentiation • As embryo grows, the cells begin to sort themselves into layers which give rise to various organs and organ systems • At specific times, each cell type begins to change in order to carry out its specific function After 8 weeks of development, the embryo is now called a FETUS. First Trimester • Up to week 12 • Organogenesis – development of body organs • Heart beats around week 4 • By week 8 all major structures of the adult are present in rudimentary form • At end, fetus is only 5cm long Second Trimester • Months 4-6 • Fetus grows about 30cm and is very active Third Trimester • Fetal activity decreases as it fills available space • Fetus is ~50 cm long • Lungs complete development Gestation (AKA Pregnancy) • In humans, this typically lasts 40 weeks • Premature birth – babies born prior to completing 37 weeks of development – Increase chance of lung and brain problems – Typically, the earliest survivable birth is 24 weeks Multiple Births • When more than one fetus is carried in the uterus in a single pregnancy period Monozygotic (Identical) Twins • One egg is fertilized and resulting zygote splits into two separate individuals • Offspring have IDENTICAL genetic information • Both twins will be the same gender Dizygotic (Fraternal) Twins • Where multiple sperm fertilized multiple eggs • Each offspring is unique in their genetic make up (no more closely related than any other 2 siblings) Labor and Delivery • Labor – series of rhythmic contractions of the uterus accompanied by changes in the cervix • Averages 8-13 hours, but can last longer • After the baby is removed, contractions continue to expel the AFTERBIRTH (placenta, amniotic sac, umbilical cord) Breech births • Fetus attempts to descent through the birth canal any way but head first – Results in Cesarean section Miscellaneous • Breastfeeding – characteristic that all mammals share – Controlled by hormones – Colostrum – first milk produced, contains ANTIBODIES and WBCs to give newborn limited immunity • Abortion – removal of embryo or fetus, reulting or causing its death • Miscarriage – natural or accidental termination of the pregnancy before 20 weeks (AKA Spontaneous abortion) • Stillbirth – when a fetus is >20 weeks and dies in uterus or during labor