* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cardiovascular System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
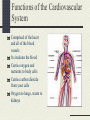
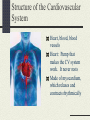
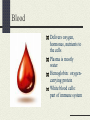
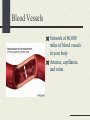
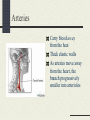
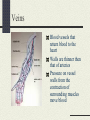
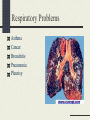
The Cardiovascular System Just Breathe! Functions of the Cardiovascular System Comprised of the heart and all of the blood vessels It circulates the blood Carries oxygen and nutrients to body cells Carries carbon dioxide from your cells Oxygen to lungs, waste to kidneys Structure of the Cardiovascular System Heart, blood, blood vessels Heart: Pump that makes the CV system work. It never rests Made of myocardium, which relaxes and contracts rhythmically How blood moves through the heart http://www.bostonscie ntific.com/templatedat a/imports/HTML/lifeb eatonline/winter2007/l earning.shtml How the heart beats Top of the right atrium is an area of muscle that acts as a natural pacemaker This starts the heart’s electrical system Stimulates the muscles to contract Within the heart, there are four “one-way” values that keep the blood flowing in the right direction Blood Delivers oxygen, hormones, nutrients to the cells Plasma is mostly water Hemoglobin: oxygencarrying protein White blood cells: part of immune system Blood Vessels Network of 60,000 miles of blood vessels in your body Arteries, capillaries, and veins Arteries Carry blood away from the heat Thick elastic walls As arteries move away from the heart, the branch progressively smaller into arterioles Capillaries Small vessels that carry blood between arterioles and venules Responsible for the exchange of gases, nutrients, wastes Play a role in temperature regulation Platelets Cells that prevent body’s loss of blood Release chemicals at an injury site that causes them to clump together Fibrin threats help to form a clot A scab is formed Veins Blood vessels that return blood to the heart Walls are thinner then that of arteries Pressure on vessel walls from the contraction of surrounding muscles move blood Cardiovascular Problems Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular disease Heart Murmur Varicose Veins Anemia Leukemia Hemophilia Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Exchange of gases between body and environment External: exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide that takes place between air and blood Internal: exchange between blood and body cells Structure of Respiratory System Lungs Larynx Trachea Bronchi Diaphragm Respiratory Problems Asthma Cancer Bronchitis Pneumonia Pleurisy