* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download www.thekeep.org
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
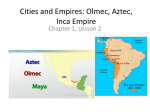
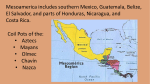
Historical Issues Andean Civilizations Had No Writing Conquistadores Burned and Defaced Much Evidence We learn through physical remains Conquistadors tried to collect some historical knowledge but distorted it Mesoamerica (2000 BC – 1500 AD) Culture Zone in Central-South Mexico and Central America Obsidian is primary weapon / tool material Stone housing City-States Mesoamerican Calendar Sacrifice of blood and humans Archaic Period (8000-2000 BC) Domestication of maize, beans, peppers allows shift to village life Few domestic animals Maize + Beans = more protein than Eurasian grains The Formative Period (2000 BC150 AD): Olmecs The Olmecs San Lorenzo (1200-900 BC) La Venta (900 BC) 110 foot pyramids 1000 inhabitants (Priest Elite) Extensive Jade and Obsidian trade Olmec Inventions Heavily copied by later civilizations Priest-ruled City-States Sacrifice: Bloodletting and Humans Mesoamerican Calendar Writing Idea of Zero The Ballgame Olmec Heads Olmec Heads 17 Survive 20-40 ton weight Carved from single blocks Transported 50 or more miles from mines to cities Unclear purpose; some mutilated Olmec Art Olmec Art / Were-Jaguars Olmec Art mixes humans, jungle animals and half-man / half-Jaguars Degree of mixing varies Were-jaguar babies often are portrayed as held by a stoic, seated adult male. Role of this art uncertain but some is traded to other places Monte Alban Monte Alban Monte Alban Founded around 500 BC where branches of Oxcaca River Meet 5000 people Mesoamerican Calendar is found here too 365 day cycle, 260 day cycle, 52 year 'century' Classical Era (150-900 AD) Maya at their height and Teotihuacan An age of prosperous city-states Warfare is common Pyramid of the Sun--Teotihuacan Teotihuacan (1st Century AD - 8th Century AD) Teotihuacan (1st Century AD - 8th Century AD) Ready Access to Sacred Caves and Obsidian and Farmland 150,000 at height, 9 miles across 2000 Elite homes in center; masses live in apartments further out May have ruled, definitely influenced other cities Large Trade Network Worships a Storm god and goddess and a feathered serpent with blood and humans Decline Shrinks after 500 AD 8th century—destroyed by Fire Yet it remains seen as a golden age The Maya The Maya Most literate; best writing system Greatest City: Tikal 50-70,000 Nobles and retainers rule over numerous commoners Wars are common; losers get sacrificed Maya Religion Nature and Supernatural = the same So Rulers have Secular and Religious power Human sacrifice and blood to appease the gods The Mayan Ballgame Reenacts the conflict between the Hero Twins and the Lords of Xibalba, the Underworld Mayan 'Science' Expert Astronomers and Mathematicians (had idea of zero) The Long Count Calendar—Most Accurate before modern times 11 August 3114 BC is cycle starting point (almost certainly retroactive) Used interactive cycles of days and true length of lunar calendar Base 20 math Giant cycle will end in 2012 AD Tikal, Great City of the Maya Tikal, Great City of the Maya Tikal, Great City of the Maya 3000 buildings, 14 miles Massive Causeways link main buildings Access to flint, swamps, and rivers 39 Kings of the Jaguar Paw Line Ah Cacau (682-723?) Collapse in 8th century AD Collapse 800-900 AD—Total Collapse of original Maya War, Eco-catastrophe, Overcrowding? Maya now move to the Yucatan, building Chichen Itza then Mayapan Weak by time of Spanish (1500s AD) The Post-Classic Period (900 AD1521 AD) The Toltecs: Invade around 900 AD Capital at Tula 60,000 people The Aztecs / Mexica Arrive in Valley of Mexico in 1200s Forced onto islands in Lake Texcoco Build artificial islands of bounded lake muck Build Tenochtitlan on Islands Ally with Texcoco and Tlacopan by 1400s A Tributary Style Empire Aztec Religion Sun god Huitzilopochtli needs human hearts or he will die Warfare must be constant to get sacrifices of live warriors “Flower Wars” used in peacetime Children sacrificed to Tlaloc to get rain Huitzilopochtli Tenochtitlan Linked to mainland by causeways Ritual center and Imperial Palace at center Divided into Wards (capulli) Grid System Aqueducts bring fresh water Aztec Society Classes Nobles / Priests Merchants (pochteca) and Artisans Commoners Dress Codes for each class Commoners are part of capulli; each has tribute obligations and local temple Aztec Trade Guild System Cacao Beans for small purchases Fixed lengths of Cotton Cloth(quachtli) for large Examples: Small Rabbit: 30 beans Tamale: 1 bean 1 quachtli = 65 to 300 beans by quality 20 quachtli = 1 year commoner income Sell your daughter = 500 to 700 beans Aztec Warfare All young men learn to fight Some will become professional warriors Battle involves mass combat with little strategy; largely one on one fights to capture people Clubs and swords of wood with obsidian set in it and cotton armor Aztec Women More rights than medieval / early-modern European women Hold property Inherit property Trade in marketplace Craftwork Low-level priests But couldn't be warriors PUMP OUT THOSE BABIES Death in Childbirth or battle = high position in afterlife! Aztec Technology High Tech Aqueducts and superb sanitation Skilled Irrigation Expert Stone, gold and silver work Low Tech Little use of Iron or Bronze, No Wheel Obsidian Weapons Poor to no ships Andean South America: Preceramic and Initial Period: 3000-800 BC Oldest Ritual Center: 2800 BC Mix of Seafood, Squash, Beans, Chili Peppers Cotton Clothing 2500 BC: The Llama is domesticated 2000 BC – Pottery is invented, Agriculture Rises Chavin de Huantar and the Early Horizon (800 BC-200 AD) Chavin de Huantar and the Early Horizon (800 BC-200 AD) Chavin de Huantar—900 BC, Peru Highlands Trade and Agriculture Declines between 500 and 300 B.C Skilled metal workers and textile makers Religion involved hallucinogens and shamanism The Early Intermediate Period (200 BC-600 AD) The Nazca (100 BC – 700 AD) A Coastal People Used underground irrigation to turn desert to farms Nazca art—animals and plants, severed human heads Skilled with making llama cloth from wool Most famous for their geoglyphs = “Nazca Lines” Nazca Lines Moche Culture (200-700 AD) Moche Valley in Highlands Sun and Moon Pyramids Sun Pyramid = largest adobe structure in the Andes 1200 feet long, 500 feet wide, 60 feet high, made of over 143 million adobe bricks Irrigation style farmers Art shows many facets of life Mass produced but highly diverse pottery with art showing normal life The Middle Horizon Through the Late Intermediate Period (600 AD1475 AD) Tiwanaku (Bolivia) and Huari (Peru) Expansionist Cultures in highlands Tiwanaku—12,000 feet above sea level 20-40,000 by Lake Titicaca Raised Field Agriculture Huari 20-30,000 Terraced hills and mountainsides Chimu Empire Coastal Empire Chan Chan (Capital) 30-40,000 people Big Nobles, Small Nobles, Artisans Worshipped the Moon Chimu make monochromatic pottery and work with precious metals Pottery shaped like a creature or human Shiny black finish Chimu Pottery Inca Empire The Inca Empire (13th-16th Century AD) 2600 miles of coastline Ruled by a Divine King Incan Civilization revolved around maintaining elaborate irrigation—strong rule needed Potatoes, Gains, Fish, Vegetables, Nuts, Maize, Camelid and Cuyes meat Primitive Socialism, managed by King and his minions Incas II Labor Taxation System Mita System of Labor Tax Men owed military service State Employees: – Virgins of the Sun—cloth and ceremonial beer makers Men managing Imperial herds and warehouses Dress conveys rank and ethnicity Inca Technology Stoneworkers and builders of incredible skill Reshape mountains to their needs Expert with pottery and textiles Art and medicine But only a knot code for writing Little bronze and no iron and no wheels Very crude weaponry North America Forest Tribes Mound Builders Foot Nomads Pacific Northwest Tribes Urbanized Farmers Plains Tribes Mobile Temporary Farm Villages Seagoing Fishers; Totem Pole and Potlach Customs Arid Southwest Elevated Towns; irrigation agriculture