* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction (1865-1876) - US History-
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
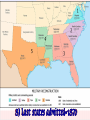
President Lincoln’s Plan 10% Plan * When 10% of the voting population in the 1860 election had taken an oath of loyalty and established a government, it would be recognized. * Believed punishment would only delay healing the Union * Pardon to all but the highest ranking military and civilian Confederate officers. Radicals’ Plan Considered Lincoln’s plan too mild Wade-Davis Bill Senator Thaddeus Stevens Required 50% of the number of 1860 voters to take an “iron clad” oath of allegiance (swearing they had never voluntarily aided the rebellion ). Required a state constitutional convention before the election of state officials (only white males who did not fight could participate) Charles Sumner Former confederates were barred from office New state constitutions had to ban slavery President Johnson’s Plan (10%+) Offered amnesty upon simple oath to all except Confederate civil and military officers and those with property over $20,000 (they could apply directly to Johnson) Allowed only loyal, pardoned whites to vote for delegates He opposed African Americans having equal rights or the vote Growing Northern Alarm! Many Southern state constitutions fell short of minimum requirements. Johnson granted 13,500 special pardons. Revival of southern defiance. BLACK CODES 2) Freedmen’s Bureau (1865) Helped blacks adjust to freedom Distributed food and clothing Provided medical services Set up schools 3) How did states get back to the Union? Had to denounce secession and end slavery Ratify the 13th Amendment 4) Why did many Republicans not want Southern reps in Congress? Many Republicans opposed readmitting the South on such easy terms 5) Black Codes Laws aimed at controlling freed men and women Permitted plantation owners to exploit black workers and allowed officials to arrest and fine jobless blacks Banned blacks from owning/renting farms 5) How were Black Codes Challenged? Freedmen's Bureau Courts Civil Rights Bill of 1866 Made blacks full citizens and gave the fed gov the right to intervene in state affairs to protect blacks Congress Breaks with the President February, 1866 President vetoed the Freedmen’s Bureau bill. March, 1866 Johnson vetoed the 1866 Civil Rights Act. Congress passed both bills over Johnson’s vetoes 1st in U. S. history!! 6) Radical Reconstruction A time when Republicans in congress took control and Pres Johnson could do little to stop them because Congress could easily override him 7) Reconstruction Acts of 1867 Military Reconstruction Act * Restart Reconstruction in the 10 Southern states that refused to ratify the 14th Amendment *1) Divide the 10 “unreconstructed states” into 5 military districts, each under control of a military commander *2) Guaranteed black males the right to vote *3) Prevented former Confed leaders from holding office *4) Had to ratify the 14th Amendment 8) Last states admitted=1870 9) Tenure of Office Act Tenure of Office Act * The President could not remove any officials [esp. Cabinet members] without the Senate’s consent, if the position originally required Senate approval. Designed to protect radical members of Lincoln’s government A question of the constitutionality of this law Edwin Stanton 10) President Johnson’s Impeachment Johnson removed Sec of War Stanton in February, 1868 Johnson replaced generals in the field who were more sympathetic to Radical Reconstruction. The HOR impeached him on February 24 before even drawing up the charges by a vote of 126 – 47! 11) The Senate Trial 11 week trial. Defenders claimed he was exercising his right to challenge laws he felt were unconstitutional Accusers argued that congress should retain the supreme power to make laws Johnson acquitted 35 to 19 (one short of required 2/3s vote). 12) President Ulysses S. Grant Election in 1868 13) Scalawags and Carpetbaggers Scalawags—Name given by former Confederates to Southern whites who supported Republican Reconstruction Carpetbaggers—Name given to northern whites who moved south after the War and supported the Republicans 14) Loss of Support for Reconstruction During Grant’s tenure, many northerners were losing interest in Reconstruction “South should solve their own problems” Old Radical leaders retired or died Racial prejudice in the North 15) Amnesty Act of 1872 Liberal Republicans called for expanded amnesty towards white southerners It pardoned most former confederates and nearly all white southerners could vote and hold office again Democrats started to regain power 16) Voting Restrictions Poll tax Literacy Test (had to read/explain parts of the state or U.S. Const) Grandfather Clause: You could vote if your grandfather was able to vote (helped illiterate whites) 17) Jim Crow Laws Required African Americans and whites to be separated in almost every public place 18) Plessy vs. Ferguson Court ruled that segregation was legal as long as African Americans had access to public facilities or accommodations equal to those of whites Overturned in 1954— Brown vs. Board of Education 19) Impact of Reconstruction Helped South recover and begin rebuilding Blacks gained greater equality and joined whites in new governments, but it did not make good on the promise of true freedom—with troop withdraws, they lost most of their gains Civil War Amendments 13th: Banned Slavery Civil War Amendments 14th: All persons born or naturalized in the U.S. are citizens 2) It guaranteed that people of all races born in the U.S. are citizens—required every state to grant all citizens equal protection under the law 3) Privileges and Immunities: Right to property, govt protection, BOR 4) Due Process: Idea that gov must follow procedures established by law and guaranteed by the Constitution Civil War Amendments 15th: Grants African American males the right to vote