* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 Ss of the Civil War
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
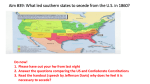
•Think about a recent conflict or argument you have been in •Why did it happen? •Did anything happen to make it worse? SS8H6 The student will analyze the impact of the Civil War and Reconstruction on Georgia. a. Explain the importance of key issues and events that led to the Civil War; include slavery, states’ rights, nullification, Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850 and the Georgia Platform, Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott case, election of 1860, the debate over secession in Georgia, and the role of Alexander Stephens. What were the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? •The South needed slavery to help keep its economy strong •Westward expansion resulted in new territories and states. Each had to decide if they would allow slavery. •Slave and free states argued because of representation in Congress. •Remember the Three-Fifths Compromise? •Missouri Compromise, 1820 •Missouri = slave state •Maine = free state •All new states north of 36/30 line are free; all new states south of that line allow slavery •Hoping to maintain the peace •Compromise of 1850 •California = free state •Western territories can decide by popular sovereignty •Meaning they would vote •Established the Fugitive Slave Law but most Northerners ignored it. •Caused division in the South •Alexander Stephens •A Georgia Congressman •Helped secure support in the South for the Compromise of 1850, along with Robert Toombs GOLD STAR QUESTION! •Alexander Stephens •He was a sickly man, but was called the “strongest man in the South.” •He voted against secession at the state convention (cooperationalist) even though he supported states’ rights. •Once Georgia made the decision to secede, he quickly became a key figure in the new government as Vice President of the Confederacy •Georgia Platform •Written at a special convention held to vote on the Compromise of 1850 and secession. •Stated: •Georgia will accept the Compromise of 1850 •Georgia would not hesitate to resist Congress if they try to outlaw slavery in the new territories. •Kansas-Nebraska Act •Originally, Kansas and Nebraska were free territories •Kansas-Nebraska Act said these territories could vote on slavery (popular sovereignty) •Basically repealed the Missouri Compromise •Led to a civil war in Kansas; fighting became so violent the area became known as “Bleeding Kansas” •The Dred Scott Case •He was a slave who sued for his freedom when his master died. •The Court ruled he had no rights because he was considered property •Basically meant that slaveholders could keep their slaves in any state •How would this make the Northern states feel? What about the Southern states? DEFINITION: people in any given area think their ideas and interests are correct and more important than those of people in any other region •Examples: •South wanted states’ rights but the North wanted the federal government to have more power •Slave or free? •How does sectionalism affect me? •Short for LIFESTYLE •North: •Large cities, opera and theater, dinner parties, industry •South: •Few large cities, hunting, religion, farming •Short for Class Structure •The position that one group has in relation to other groups •South: •Structure based on land and slavery •Very hard to move to another group •North: •Structure based on wealth •Easier to move to another group DEFINITION: the ability to pay all debts •Congress passed laws instituting tariffs on all imported goods from Great Britain. The south bought many goods from Great Britain, so this hurt them •Congress was trying to make the Southern states buy from Northern factories •Great Britain retaliated with tariffs on goods imported from the south. •South Carolina threatened to secede because of these high tariffs! •Nullification •Nullify means cancel •10th Amendment: powers not delegated to national government are reserved for the states •Southerners thought this meant they could nullify federal laws they thought were unconstitutional. (Doctrine of Nullification) •South Carolina invoked this doctrine in 1832 when they threatened to secede over tariffs. •Panic of 1857: Depression! •Many Northern factories went bankrupt and could not pay back the money they borrowed to open their factories •To help the North, Congress raised tariffs on imports. This made the Southern states angry. •Because of all of the tension between north and south, many Southerners felt the only option was to break away from the Union •Politics also played a big role: •1854: Free Soilers (anti-slavery Democrats) and Whigs came together to form the Republicans •Election of 1860: Republicans nominated Abraham Lincoln •Southerners did not trust Lincoln. They thought he wanted to end slavery, not just limit it. •Result? •December 1860: South Carolina secedes! •The southern states set up a new government and called themselves the Confederate States of America •Georgia’s Decision to Secede •A heated debate began after Lincoln’s election •Two groups: •Radical secessionists: wanted to leave the Union right away •Cooperationists: wanted the southern states to organize and plan before secession •Gov. Joseph Brown called a legislative session. They voted to have a convention, where Georgians elected to leave the Union. Georgia officially seceded on January 19, 1861. •Use the 6 S’s chart and fill in the big ideas for each “s” 1. Slavery 2. Sectionalism 3. Style 4. Structure 5. Solvency 6. Secession