* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Breeding and Plant Biotechnology
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
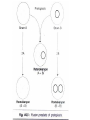
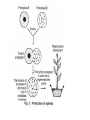
Plant Tissue Culture Techniques Huseyin Tombuloglu, Phd. GBE 304 Spring 2015 Definition the culture of plant seeds, organs, tissues, cells, or protoplasts on nutrient media under sterile conditions. Tissue culture relies on three fundamental abilities of plant there are: Totipotency Dedifferentiation Competency Three Fundamental Abilities of Plants Totipotency the potential or inherent capacity of a plant cell to develop into an entire plant if suitably stimulated. It implies that all the information necessary for growth and reproduction of the organism is contained in the cell Dedifferentiation Capacity of mature cells to return to meristematic condition and development of a new growing point, follow by redifferentiation which is the ability to reorganise into new organ Competency the endogenous potential of a given cells or tissue to develop in a particular way HISTORY Haberlandt early 1900’S • proposed concept of totipotency • cells cultured under right conditions • Callus cultured from tree cambium Gautheret, Nobecourt, Whire In the 1930s. • cells kept alive but did not develop 6 INORGANIC & ORGANIC SUPLLEMENTS COUMPOUNDS Mg/Ml NH4NO3 1,650.00 KNO3 1,900.00 CaCl2 (anhyd) 332.20 MgSO4 (anhyd) 180.70 KH2PO4 170.00 Na2EDTA 37.25 FeSO4.7H2O H3BO3 27.80 6.20 MnSO4.H2O 16.90 ZnSO4.H2O 5.37 KI 0.83 Na2Mo4.2H2O 0.25 Sucrose 30,000.00 i-Inositol 100.00 Thiamine.HCl 0.40 7 Antibiotics : Streptomycin, kanamycin Activated charcoal Other organic supplements : Protein, coconut milk,yeast,malt extract, orange juice, and tomato juice Growth regulators : Auxins, cytokinins Water : Demineralized or distilled water Solidifying agents : Agar, gelatin. pH adjusters : 5 - 6 it is considered to be optimum. 8 Basis for Plant Tissue Culture Two Hormones Affect Plant Differentiation: Auxin: Stimulates Root Development Cytokinin: Stimulates Shoot Development Generally, the ratio of these two hormones can determine plant development: Auxin ↓Cytokinin = Root Development Cytokinin ↓Auxin = Shoot Development Auxin = Cytokinin = Callus Development EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS VESSELS & GLASS WARE : • All the glassware should be of Pyrex. • Large test tubes,flasks,graduated pipettes etc.. are used. EQUIPMENT : • • • • • • • • Scissors,scapels,foreceps are used for explants preparation. A spirit burner for flame sterilization. Hot air oven. A PH meter. A BOD incubator. Laminar air flow chamber. A balance to weigh nutrients. Data collection and recording room. 10 Knife Laminar air flow chamber 11 ESTABLISHMENT OF PLANT TISSUE CULTURE In vitro culturing of plant tissue culture involves the following steps. Collecting & sterilization of glassware tools/vessels. Preparation of explant. Surface sterilization of Explant. Production of callus from explant. Proliferation of culture. Sub culturing of callus. Suspension culture 12 EXPLANT PREPARATION EXPLANT : It is defined as a portion of plant body, which has been taken from the plant to establish a culture • Explant may be taken from any part of the plant like root,stem,leaf,or meristematic tissue like cambium, floral parts like anthers, stamens etc.. •Age of the explant. • Homozygous plants are preferred. 13 flower leaf 14 SURFACE STERILISATION OF EXPLANT For surface sterilization chromic acid, Hgcl(0.11%),calcium hypochlorite, sodium hypochlorite(1-2%),alcohal(70%) are used. Process depends on the type of explant. SEED : absolute ethyl alcohol calcium hypochlorite bromine water sterile water FRUIT : ethyl alcohol sodium hypochlorite sterile water STEM : running water sodium hypochlorite sterile water LEAF : surface clean Hgcl2 sterile water dried explant PRODUCTION OF CALLUS FROM EXPLANT • • • • Sterilized explant is transferred aseptically onto defined medium. Transfer to incubator. Temperature (25 ± 2 ͦ) and light is necessary for callus production. Callus produced with in 3-8 days. 16 PROLIFERATION OF CULTURE • if callus is well developed, it should cut into small pieces & transferred to another fresh medium containing hormones, which supports growth. •The medium used for production of more amount of callus is called proliferation medium. 17 15 DAYS 30 DAYS CALLUS GROWTH 50 DAYS 80 DAYS 18 SUBCULTURING OF CALLUS •After sufficient growth of callus it should be periodically transferred to fresh medium to maintain viability of cells. •This subculture will be done at the interval of 4-6 weeks. •After a maximum growth transfer into a pottling soil under required condition. SUSPENSION CULTURE •It contains a uniform suspension of separate cells in a liquid medium callus liquid medium agitated continuously finally cells separated sub-culture the cells •This can be achieved by rotary shaker attached within the incubator at a rate of 50-150 rpm. 20 Protoplasts Landmark: 1960: E. C. Cocking (Univ Nottingham) isolated protoplasts by treating explants with concentrated cellulase isolated from a fungus. [Commercial cellulase and macerozyme were not available till 1968]. Tobacco protoplasts Protoplast fusion 1. Somatic hybrids 2. Cybrids A cytoplasmic hybrid (or cybrid a portmanteau of the two words Inter-specific fusions Datura innoxia X D. stramonium = D. straubii Tomato X Potato = Tomoffel 4n Synkaryon 2n x 2n (O. Schieder) (G. Melchers) Somatic hybrids 2n Heterokaryon Fusion of haploid protoplasts (derived from anther cultures) n + n= 2n Cybrid Technology Mixing two cytoplasm without hybrid formation. TomTato plant tomoffel Haploid Culture Haploid plant (n) = recessive mutations displayed n+n= double haploid Occur spontaneously in inter-specific cross or induced by irradiating pollen prior to pollination. Extremely poor efficiency. Later: Microspore cultures. Protoplast fusion: gametic hybridization Haploid cells nXn Protoplast (n) 2n (synkaryon) Anther culture techniques/ fusion has been extensively used in rice breeding program Applications of tissue culture to plant breeding 1. Haploid production (rice, wheat and barley) 2. Triploid production (fruits and poplar) 3. Embryo Rescue/ Wide hybridization (numerous examples) 4. Somatic hybridization (scientific examples, few commercial products) 5. Somaclonal Variations ( Tomato with altered color, taste and texture by Fresh World Farms; Imidazolinone resistant maize, American Cyanimid; Bermuda grass (Brazos R-3) with increased resistance to fall armyworm etc.) 1. Production of disease free plants. 2. Clonal propagation 3. Secondary metabolite production (eg. Taxol production from cell cultures derived from the bark cuttings of pacific yew tree) 4. Germplasm conservation (cryopreservation) TYPES OF CULTURE Callus culture Suspension culture Root tip culture Leaf or leaf primordial culture Shoot tip culture Complete flower culture Anther & pollen culture Ovule & embryo culture Protoplast culture 31 Callus culture Ovule culture Protoplast culture Suspension culture Root tip culture Leaf primordial culture Pollen culture Shoot tip culture Flower culture 32 ADVANTAGES : Availability of raw materials. Fluctuation in supplies & quantity. Easy purification of the compound. 33 Modifications of chemical structure. Disease free & desired propagule. Crop improvement. Bio-synthetic pathway. 34 Seedless watermelon triploid that produces excellent fruit with a dark green skin, consistent round shape, sweet taste (with an average Brix sugar content level of 11 degrees), deep red color, density and texture. In addition, it has intermediate resistance* to both Anthracnose and Fusarium wilt race 1. The available genetic resources for citrus fruit are predominantly diploid. Nonetheless, polyploidy can give citrus fruit interesting characteristics. Thus, the genetic breeding programmes aim to create triploid varieties, which are sterile and produce seedless fruit.