* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bez nadpisu
Survey
Document related concepts
Ciprofloxacin wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
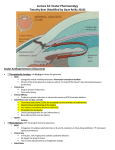
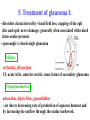
Jiří Slíva, M.D. Administration of the drug to the eye I: Topical application - eye drops eye lotions eye ointments local injection eye drops - instilled into the pocket formed by gently pulling down the lower eyelid and keeping the eye closed for as long as possible after application, preferably 1-2 minutes eye ointment - small amount is applied similarly, melts rapidly, blinking helps to spread it Two different eye-drop preparations - patients should leave an interval of 5 minutes between the two Administration of the drug to the eye II: eye lotions - act mechanically to flush out irritants or foreign bodies as first-aid - systemic effects - absorption from conjunctival vessels absorption from nasal mucosa via tear ducts subconjunctival injections - mydriatics, anti-infective drugs, steroids implants - gradually releasing of a drug over a prolonged period - preparations should be sterile - eye drops for domiciliary use shouldn´t be used more than four weeks after opening 1. Anti-infective eye preparation I: - eye infections of different kind antibacterials antifungals antivirals antibacterials • 1 drop at least every 2 hours then reduce frequency, continue for 48 hours after healing - drops or ointments; event. injections or systemic application chloramphenicol, quinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin), broad bacterial-spectrum antibacterials (gentamicin, neomycin) - Ps. aeruginosa - trachoma - azithromycin, tetracycline - staphylococcal infections -fusidic acid - acanthamoeba keratitis - propamidine isetionate 1. Anti-infective eye preparation II: antifungals - fungal infections of the cornea are rare - agricultural injuries (hot and humid climates) antivirals - herpes simplex - aciclovir, ganciclovir (herpetic keratitis) - cytomegalovirus - fomivirsen, ganciclovir 2. Corticosteroids: - drops, ointments, subconjunctival injections or systemically topical use: - change of symptoms by still unconfirmed diagnosis - steroid glaucoma - steroid cataract - thinning of the cornea and sclera systemic use: - the risk of steroid cataract is very high (75%) when is used more than 15 mg prednisolone in a day for several years - betamethasone, dexamethasone, fluorometholone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, rimexolone 3. Other anti-inflammatory drugs: Antihistamines -antazoline, azelastine, ketotifen, levocabastine Sodium cromoglycate and nedocromil sodium Lodoxamid - stabilisation of mast cells, inhibition of Ca++ influx Emedastine - high afinity to H1-receptors 4. Mydriatics and cycloplegics: - antimuscarinics x sympatomimetics Antimuscarinics atropine, cyclopentolate, homatropine, tropicamide Sympatomimetics phenylephrine 5. Treatment of glaucoma I: - disorders characterised by visual field loss, cupping of the opti disc and optic nerve damage; generally often associated with raised intra-ocular pressure - open-angle x closed-angle glaucoma Miotics carbachol, pilocarpine CI: acute iritis, anterior uveitis, some forms of secondary glaucoma Sympatomimetics adrenaline, dipivefrine, guanethidine - act due to decreasing rate of production of aqueous humour and by increasing the outflow through the ocular meshwork normal vision viewed by a person with glaucoma 5. Treatment of glaucoma II: Beta-blockers - reduce intra-ocular pressure by reducing the rate of production of aqueous humour - oral (side effects) or intra-ocular application - betaxolol, carteolol, levobunolol, metipranolol, timolol Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - acetazolamide, dorzolamide, brinzolamide 5. Treatment of glaucoma III: Osmotic diuretics Short-term acting drugs - intravenous hypertonic mannitol - glycerol by mouth Prostaglandin analogue - latanoprost, travoprost, bimatoprost - increase uveoscleral outflow Laser surgery also called laser trabeculoplasty 6. Local anesthetics: oxybuprocaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, proxymetacaine 7. Miscellaneous ophthalmic preparations: Tear deficiency: • Hypromellose, povidone - in combination with carbomers (cling to the eye surface - reduce frequency of application )or polyvinylalcohol (increase the persistence of the tear film) • Sodium chloride 0.9% Corneal epithelial erosion: Paraffin - temporary visual disturbance, best suited before sleep 8. Ocular diagnostic preparations: • fluorescein, rose bengal - for locating damaged areas of the cornea due to injury or disease (slit lamp) 9. Subfoveal choroidal neovascularisation inhibitors: • verteporfin - for use in the photodynamic treatment of subfoveal choroidal neovascularisation associated with macular degeneration or with pathological myopia. - i.v. infusion, activation by non-thermal red light => cytotoxic derivates

























![Information about Diseases and Health Conditions [Eye clinic] No](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013291748_1-b512ad6291190e6bcbe42b9e07702aa1-150x150.png)