* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory, Physical, & Medical Disabilities
Specific language impairment wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
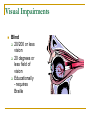
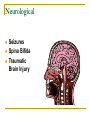
Sensory, Physical, & Medical Disabilities EXC 7770 Dr. Susan Brown Kennesaw State University Limitations adaptive devices attendance fatigue functional limitations medication/treatment effects pain Sensory Impairments Hearing Impairment Visual Impairment Hearing Impairment Prelingual deafness onset before language development Postlingual deafness onset after language development Conductive loss air or bone conduction disruption Sensory loss interference in inner ear or neural pathways Cochlea primary organ of hearing connects inner ear pathways to brain pathways Levels of hearing loss Hard of hearing 35-70 decibel loss Educationally - can learn language through hearing Deaf greater than 70 decibel loss Educationally cannot learn language through hearing Visual Impairment Visual functioning use of residual vision Low vision significant visual impairment but usable vision Partially sighted 20/70 - 20/200 vision Educationally - requires large print Visual Impairments Blind 20/200 or less vision 20 degrees or less field of vision Educationally - requires Braille Developmental maturation Cephalo-caudal (head to tail) Proximal-to-distal (central to peripheral) Gross-to-fine Physiological flexion (general bending at joints) to antigravity control Stability to mobility to skilled movement (Heller, Alberto, Forney & Schwartzman, 1996) Physical Impairments Muscular Muscular dystrophy Muscular sclerosis Skeletal Arthritis Osteogenesis Scoliosis Health Impairments Abuse Aids Allergies Asthma Cancer •Cystic Fibrosis •Diabetes •Hemophilia •Hepatitis •Sickle Cell Anemia Congenital and Acquired Impairments Amputation/missing limbs Eating disorders Heart disorder Respiratory disorders Neurological Seizures Spina Bifida Traumatic Brain Injury