* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Ears” - Kristen Livingston
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
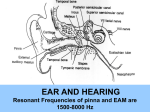
Introduction Images courtesy of Google It affects how we feel and what we know COGNITIVE INFORMATION- info related to mental processes of knowledge, reasoning, memory, judgment, and perception AFFECTIVE INFORMATION- info related to emotion, feeling, and mood. Omnidirectional – it is everywhere Layered and simultaneous Attention demanding Comprehending or assimilating (requires active listening) Paired with visual aids (enhances the sound) Listening to old radio dramas Watching silent films How music makes you feel, even driving in your car How listening ignites memory recollection Colby’s story The human ear is divided into three parts: OUTER EAR – sound waves first reach pinna (visible part of outer ear MIDDLE EAR- sound waves then focus through the ear canal to the ear drum INNER EAR- tympanic membrane is attached to another membrane (oval window) by three small bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) called ossicles. Let’s call the bones hammer, anvil, and stirrup instead. These little guys, the ossicles, act as a lever changing the pressure of sound wave on the eardrum into much greater pressure. The tympanic membrane and awesome action of the ossicles allow the middle ear to protect the inner ear from bad stuff like pressure. Bee Gees Reference; hammer, anvil and stirrup Contains semicircular canals (for balance) and snailshaped structure called the cochlea. Cochlea is filled with fluid (itty bitty, less than a drop) Running through the center of the cochlea is the basilar membrane (hair cells attached to nerve fibers composing the organ of Corti) In other words this is the auditorium of hearing The aforementioned fibers send electrical impulses to the brain. Nerve fibers have cilia attached to them which quiver when sound approaches. Finish “Ears” lecture 1, start “Physics and Psychophysics” lecture 2 Podcast LAB Thursday 1/29 in RM: 112- if you have laptops, bring them! Quiz Review Tuesday 2nd over lecture 1 and lecture 2 BE working on Lab Assignment 1 Here to help!! Don’t over think it! Be creative! How many of you listen to heavy metal? Think about all of the sounds that our poor ears are sensitive to. Most people suffer from hearing loss than from heart disease, cancer, multiple sclerosis, and kidney disease combined. For many people, there is not a need for an increase in the level of sound, but in the clarity. Temporary threshold shift- reversible desensitization in hearing that disappears Auditory fatigue- ears shut down to protect themselves Tinnitus-ringing, whistling, or buzzing in ears from prolonged exposure to loud sounds First, sounds are transmitted to the brain following two paths, one goes to an auditory center for interpretation and the other goes to the brain center where nerves are affected. Decibels are the measurement of sound. Quiet sounds are considered the threshold of hearing and loud sounds are considered the threshold of pain Human ear secretes wax to protect drum. DO NOT CLEAN YOUR EAR WITH A Q-TIP even though I did so last night. It actually pushes wax against the drum Sound Intensity (db) Ticking of a Watch 20 Whisper 30 Normal Speech 50-60 Car Traffic 70 Alarm Clock 80 Lawn Mower 95 Chain Saw 110 Jackhammer 120 Jet Engine 130 http://www.sengpielaudio.com/TableOfSoundPressureLevels.htm http://www.bogen.com/support/pdfs/soundlvl.pdf - Analytical-evaluation of sound, the interpretation of nuances and connotations of the sound quality in addition to the word being spoken Critical Listening-the evaluation of the characteristics of the sound itself MOST IMPORTANTLY, PAY ATTENTION!! “KEEP YOUR EARS OPEN” Individually, select four pictures that represent “times” or “activities” from the four seasons. (jpgs, jpegs, etc.) EX. FALL.jpeg Record 5 foley sounds for each picture (20 secs each) Use a smart phone, audio recorder, OR reserve lab time to record sounds. Save them to AUDIO SPRING 2015 folder in lab, where you will find an individual folder with your name containing “LAB ASSIGNMENT 1) Have each sound labeled Example: FALLsound1, FALLsound2 (wav files) In a Word Document, indicate what you used to create each sound. EX. SoundDescriptions.doc Save this document to your folder as well. Due February 5th at the END of LAB- if you don’t want to come in that day, save it to your folder before Failure to turn in assignment will result in a loss of points (5 points per day). If you have questions, I am here to help! The purpose of this assignment is to familiarize yourself with the equipment and to recognize the obstacles of sound creation for production